Abstract
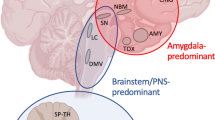
The ultimate origin of Lewy body disorders, including Parkinson’s disease (PD) and Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), is still incompletely understood. Although a large number of pathogenic mechanisms have been implicated, accumulating evidence support that aggregation and neuron-to-neuron propagation of alpha-synuclein may be the core feature of these disorders. The synuclein, origin, and connectome (SOC) disease model of Lewy body disorders was recently introduced. This model is based on the hypothesis that in the majority of patients, the first alpha-synuclein pathology arises in single location and spreads from there. The most common origin sites are the enteric nervous system and the olfactory system. The SOC model predicts that gut-first pathology leads to a clinical body-first subtype characterized by prodromal autonomic symptoms and REM sleep behavior disorder. In contrast, olfactory-first pathology leads to a brain-first subtype with fewer non-motor symptoms before diagnosis. The SOC model further predicts that body-first patients are older, more commonly develop symmetric dopaminergic degeneration, and are at increased risk of dementia—compared to brain-first patients. In this review, the SOC model is explained and compared to alternative models of the pathogenesis of Lewy body disorders, including the Braak staging system, and the Unified Staging System for Lewy Body Disorders. Postmortem evidence from brain banks and clinical imaging data of dopaminergic and cardiac sympathetic loss is reviewed. It is concluded that these datasets seem to be more compatible with the SOC model than with those alternative disease models of Lewy body disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not available.
References
Adler CH, Beach TG (2016) Neuropathological basis of nonmotor manifestations of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 31(8):1114–1119. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26605
Altunisik E, Baykan AH (2019) Comparison of the olfactory bulb volume and the olfactory tract length between patients diagnosed with essential tremor and healthy controls: findings in favor of neurodegeneration. Cureus 11(10):e5846. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.5846
Annerino DM, Arshad S, Taylor GM, Adler CH, Beach TG, Greene JG (2012) Parkinson’s disease is not associated with gastrointestinal myenteric ganglion neuron loss. Acta Neuropathol 124(5):665–680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-012-1040-2
Arotcarena ML, Dovero S, Prigent A, Bourdenx M, Camus S, Porras G, Thiolat ML, Tasselli M, Aubert P, Kruse N, Mollenhauer B, Trigo Damas I, Estrada C, Garcia-Carrillo N, Vaikath NN, El-Agnaf OMA, Herrero MT, Vila M, Obeso JA, Derkinderen P, Dehay B, Bezard E (2020) Bidirectional gut-to-brain and brain-to-gut propagation of synucleinopathy in non-human primates. Brain 143(5):1462–1475. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awaa096
Bauckneht M, Chincarini A, De Carli F, Terzaghi M, Morbelli S, Nobili F, Arnaldi D (2018) Presynaptic dopaminergic neuroimaging in REM sleep behavior disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev 41:266–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2018.04.001
Beach TG, Adler CH, Lue L, Sue LI, Bachalakuri J, Henry-Watson J, Sasse J, Boyer S, Shirohi S, Brooks R, Eschbacher J, White CL 3rd, Akiyama H, Caviness J, Shill HA, Connor DJ, Sabbagh MN, Walker DG, Arizona Parkinson’s Disease C (2009) Unified staging system for Lewy body disorders: correlation with nigrostriatal degeneration, cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol 117(6):613–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0538-8
Beach TG, Adler CH, Sue LI, Vedders L, Lue L, White Iii CL, Akiyama H, Caviness JN, Shill HA, Sabbagh MN, Walker DG (2010) Multi-organ distribution of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein histopathology in subjects with Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuropathol 119(6):689–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0664-3
Beach TG, Adler CH, Sue LI, Shill HA, Driver-Dunckley E, Mehta SH, Intorcia AJ, Glass MJ, Walker JE, Arce R, Nelson CM, Serrano GE (2021) Vagus Nerve and stomach synucleinopathy in Parkinson’s disease, incidental Lewy body disease, and normal elderly subjects: evidence against the “body-first” hypothesis. J Parkinsons Dis 11(4):1833–1843. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-212733
Bethlem J, Den Hartog Jager WA (1960) The incidence and characteristics of Lewy bodies in idiopathic paralysis agitans (Parkinson’s disease). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 23:74–80. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.23.1.74
Blesa J, Foffani G, Dehay B, Bezard E, Obeso JA (2022) Motor and non-motor circuit disturbances in early Parkinson disease: which happens first? Nat Rev Neurosci 23(2):115–128. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-021-00542-9
Boeve BF, Silber MH, Ferman TJ, Kokmen E, Smith GE, Ivnik RJ, Parisi JE, Olson EJ, Petersen RC (1998) REM sleep behavior disorder and degenerative dementia: an association likely reflecting Lewy body disease. Neurology 51(2):363–370. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.51.2.363
Borghammer P (2021) The alpha-synuclein origin and connectome model (SOC Model) of Parkinson’s disease: explaining motor asymmetry, non-motor phenotypes, and cognitive decline. J Parkinsons Dis 11(2):455–474. https://doi.org/10.3233/jpd-202481
Borghammer P, Van Den Berge N (2019) Brain-first versus gut-first Parkinson’s disease: a hypothesis. J Parkinsons Dis 9(s2):S281–S295. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-191721
Borghammer P, Horsager J, Andersen K, Van Den Berge N, Raunio A, Murayama S, Parkkinen L, Myllykangas L (2021) Neuropathological evidence of body-first vs. brain-first Lewy body disease. Neurobiol Dis 161:105557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105557
Borghammer P, Just MK, Horsager J, Skjaerbaek C, Raunio A, Kok EH, Savola S, Murayama S, Saito Y, Myllykangas L, Van Den Berge N (2022) A postmortem study suggests a revision of the dual-hit hypothesis of Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 8(1):166. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41531-022-00436-2
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003a) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24(2):197–211
Braak H, Rub U, Gai WP, Del Tredici K (2003b) Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: possible routes by which vulnerable neuronal types may be subject to neuroinvasion by an unknown pathogen. J Neural Transm (vienna) 110(5):517–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-002-0808-2
Cao R, Chen X, Xie C, Hu P, Wang K (2020) Serial dopamine transporter imaging of nigrostriatal function in Parkinson’s disease with probable REM sleep behavior disorder. Front Neurosci 14:349. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00349
Cheng HC, Ulane CM, Burke RE (2010) Clinical progression in Parkinson disease and the neurobiology of axons. Ann Neurol 67(6):715–725. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21995
Collij LE, Heeman F, Salvado G, Ingala S, Altomare D, de Wilde A, Konijnenberg E, van Buchem M, Yaqub M, Markiewicz P, Golla SSV, Wottschel V, Wink AM, Visser PJ, Teunissen CE, Lammertsma AA, Scheltens P, van der Flier WM, Boellaard R, van Berckel BNM, Molinuevo JL, Gispert JD, Schmidt ME, Barkhof F, Lopes Alves I, Alfa Study ftAsDNI, Consortium A (2020) Multitracer model for staging cortical amyloid deposition using PET imaging. Neurology 95(11):e1538–e1553. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000010256
De Pablo-Fernandez E, Lees AJ, Holton JL, Warner TT (2019) Prognosis and neuropathologic correlation of clinical subtypes of Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.4377
Del Tredici K, Rub U, De Vos RA, Bohl JR, Braak H (2002) Where does parkinson disease pathology begin in the brain? J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61(5):413–426. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/61.5.413
Djaldetti R, Ziv I, Melamed E (2006) The mystery of motor asymmetry in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 5(9):796–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70549-X
Ehrminger M, Latimier A, Pyatigorskaya N, Garcia-Lorenzo D, Leu-Semenescu S, Vidailhet M, Lehericy S, Arnulf I (2016) The coeruleus/subcoeruleus complex in idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder. Brain 139(Pt 4):1180–1188. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aww006
Engelender S, Isacson O (2017) The threshold theory for Parkinson’s disease. Trends Neurosci 40(1):4–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2016.10.008
Fanucci A, Cerro P, Fanucci E (1988) Normal small-bowel measurements by enteroclysis. Scand J Gastroenterol 23(5):574–576. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365528809093914
Fedorova TD, Knudsen K, Andersen KB, Horsager J, Skjaerbaek C, Beier CP, Sommerauer M, Svendsen KB, Otto M, Borghammer P (2022) Imaging progressive peripheral and central dysfunction in isolated REM sleep behaviour disorder after 3 years of follow-up. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 101:99–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2022.07.005
Fereshtehnejad SM, Romenets SR, Anang JB, Latreille V, Gagnon JF, Postuma RB (2015) New clinical subtypes of parkinson disease and their longitudinal progression: a prospective cohort comparison with other phenotypes. JAMA Neurol 72(8):863–873. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.0703
Franzmeier N, Neitzel J, Rubinski A, Smith R, Strandberg O, Ossenkoppele R, Hansson O, Ewers M, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging I (2020) Functional brain architecture is associated with the rate of tau accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Commun 11(1):347. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14159-1
Fumimura Y, Ikemura M, Saito Y, Sengoku R, Kanemaru K, Sawabe M, Arai T, Ito G, Iwatsubo T, Fukayama M, Mizusawa H, Murayama S (2007) Analysis of the adrenal gland is useful for evaluating pathology of the peripheral autonomic nervous system in lewy body disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66(5):354–362. https://doi.org/10.1097/nen.0b013e3180517454
Gabilondo I, Llorens V, Rodriguez T, Fernandez M, Concha TP, Acera M, Tijero B, Murueta-Goyena A, Del Pino R, Cortes J, Gomez-Esteban JC (2019) Myocardial MIBG scintigraphy in genetic Parkinson’s disease as a model for Lewy body disorders. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 46(2):376–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-018-4183-0
Gelpi E, Navarro-Otano J, Tolosa E, Gaig C, Compta Y, Rey MJ, Marti MJ, Hernandez I, Valldeoriola F, Rene R, Ribalta T (2014) Multiple organ involvement by alpha-synuclein pathology in Lewy body disorders. Mov Disord 29(8):1010–1018. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25776
Goedert M, Masuda-Suzukake M, Falcon B (2017) Like prions: the propagation of aggregated tau and alpha-synuclein in neurodegeneration. Brain 140(Pt 2):266–278. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aww230
Goldstein DS, Sewell L, Sharabi Y (2011) Autonomic dysfunction in PD: a window to early detection? J Neurol Sci 310(1–2):118–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2011.04.011
Gonzalez-Rodriguez P, Zampese E, Surmeier DJ (2020) Selective neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Brain Res 252:61–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pbr.2020.02.005
Halliday G, Lees A, Stern M (2011) Milestones in Parkinson’s disease–clinical and pathologic features. Mov Disord 26(6):1015–1021. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23669
Hawkes CH, Del Tredici K, Braak H (2007) Parkinson’s disease: a dual-hit hypothesis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 33(6):599–614. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2990.2007.00874.x
Helander HF, Fandriks L (2014) Surface area of the digestive tract - revisited. Scand J Gastroenterol 49(6):681–689. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365521.2014.898326
Hobson DE (2012) Asymmetry in parkinsonism, spreading pathogens and the nose. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.06.011
Hoffmann C, Ziegler U, Buschmann A, Weber A, Kupfer L, Oelschlegel A, Hammerschmidt B, Groschup MH (2007) Prions spread via the autonomic nervous system from the gut to the central nervous system in cattle incubating bovine spongiform encephalopathy. J Gen Virol 88(Pt 3):1048–1055. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.82186-0
Hogl B, Stefani A, Videnovic A (2018) Idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder and neurodegeneration - an update. Nat Rev Neurol 14(1):40–55. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2017.157
Hoglinger GU, Alvarez-Fischer D, Arias-Carrion O, Djufri M, Windolph A, Keber U, Borta A, Ries V, Schwarting RK, Scheller D, Oertel WH (2015) A new dopaminergic nigro-olfactory projection. Acta Neuropathol 130(3):333–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1451-y
Holst MC, Kelly JB, Powley TL (1997) Vagal preganglionic projections to the enteric nervous system characterized with Phaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin. J Comp Neurol 381(1):81–100
Horsager J, Andersen KB, Knudsen K, Skjaerbaek C, Fedorova TD, Okkels N, Schaeffer E, Bonkat SK, Geday J, Otto M, Sommerauer M, Danielsen EH, Bech E, Kraft J, Munk OL, Hansen SD, Pavese N, Goder R, Brooks DJ, Berg D, Borghammer P (2020) Brain-first versus body-first Parkinson’s disease: a multimodal imaging case-control study. Brain 143(10):3077–3088. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awaa238
Horsager J, Knudsen K, Sommerauer M (2022) Clinical and imaging evidence of brain-first and body-first Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 164:105626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105626
Ismail R, Parbo P, Madsen LS, Hansen AK, Hansen KV, Schaldemose JL, Kjeldsen PL, Stokholm MG, Gottrup H, Eskildsen SF, Brooks DJ (2020) The relationships between neuroinflammation, beta-amyloid and tau deposition in Alzheimer’s disease: a longitudinal PET study. J Neuroinflammation 17(1):151. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01820-6
Jagust WJ, Landau SM, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging I (2021) Temporal dynamics of beta-amyloid accumulation in aging and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 96(9):e1347–e1357. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000011524
Jansen WJ, Ossenkoppele R, Knol DL, Tijms BM, Scheltens P, Verhey FR, Visser PJ, Amyloid Biomarker Study G, Aalten P, Aarsland D, Alcolea D, Alexander M, Almdahl IS, Arnold SE, Baldeiras I, Barthel H, van Berckel BN, Bibeau K, Blennow K, Brooks DJ, van Buchem MA, Camus V, Cavedo E, Chen K, Chetelat G, Cohen AD, Drzezga A, Engelborghs S, Fagan AM, Fladby T, Fleisher AS, van der Flier WM, Ford L, Forster S, Fortea J, Foskett N, Frederiksen KS, Freund-Levi Y, Frisoni GB, Froelich L, Gabryelewicz T, Gill KD, Gkatzima O, Gomez-Tortosa E, Gordon MF, Grimmer T, Hampel H, Hausner L, Hellwig S, Herukka SK, Hildebrandt H, Ishihara L, Ivanoiu A, Jagust WJ, Johannsen P, Kandimalla R, Kapaki E, Klimkowicz-Mrowiec A, Klunk WE, Kohler S, Koglin N, Kornhuber J, Kramberger MG, Van Laere K, Landau SM, Lee DY, de Leon M, Lisetti V, Lleo A, Madsen K, Maier W, Marcusson J, Mattsson N, de Mendonca A, Meulenbroek O, Meyer PT, Mintun MA, Mok V, Molinuevo JL, Mollergard HM, Morris JC, Mroczko B, Van der Mussele S, Na DL, Newberg A, Nordberg A, Nordlund A, Novak GP, Paraskevas GP, Parnetti L, Perera G, Peters O, Popp J, Prabhakar S, Rabinovici GD, Ramakers IH, Rami L, Resende de Oliveira C, Rinne JO, Rodrigue KM, Rodriguez-Rodriguez E, Roe CM, Rot U, Rowe CC, Ruther E, Sabri O, Sanchez-Juan P, Santana I, Sarazin M, Schroder J, Schutte C, Seo SW, Soetewey F, Soininen H, Spiru L, Struyfs H, Teunissen CE, Tsolaki M, Vandenberghe R, Verbeek MM, Villemagne VL, Vos SJ, van Waalwijk van Doorn LJ, Waldemar G, Wallin A, Wallin AK, Wiltfang J, Wolk DA, Zboch M, Zetterberg H (2015) Prevalence of cerebral amyloid pathology in persons without dementia: a meta-analysis. JAMA 313(19):1924–1938. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.4668
Jelistratova I, Teipel SJ, Grothe MJ (2020) Longitudinal validity of PET-based staging of regional amyloid deposition. Hum Brain Mapp 41(15):4219–4231. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.25121
Jellinger KA (2019) Is Braak staging valid for all types of Parkinson’s disease? J Neural Transm (vienna) 126(4):423–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-018-1898-9
Jellinger KA (2022) Are there morphological differences between Parkinson’s disease-dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies? Parkinsonism Relat Disord 100:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2022.05.024
Johnson ME, Stecher B, Labrie V, Brundin L, Brundin P (2019) Triggers, facilitators, and aggravators: redefining Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Trends Neurosci 42(1):4–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2018.09.007
Kalaitzakis ME, Graeber MB, Gentleman SM, Pearce RK (2008) The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus is not an obligatory trigger site of Parkinson’s disease: a critical analysis of alpha-synuclein staging. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 34(3):284–295. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2990.2007.00923.x
Kashihara K, Imamura T, Shinya T (2010) Cardiac 123I-MIBG uptake is reduced more markedly in patients with REM sleep behavior disorder than in those with early stage Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 16(4):252–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2009.12.010
Khashab MA, Pickhardt PJ, Kim DH, Rex DK (2009) Colorectal anatomy in adults at computed tomography colonography: normal distribution and the effect of age, sex, and body mass index. Endoscopy 41(8):674–678. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1214899
Kim JS, Park HE, Park IS, Oh YS, Ryu DW, Song IU, Jung YA, Yoo IR, Choi HS, Lee PH, Lee KS (2017) Normal “heart” in Parkinson’s disease: is this a distinct clinical phenotype? Eur J Neurol 24(2):349–356. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13206
Knudsen K, Fedorova TD, Hansen AK, Sommerauer M, Otto M, Svendsen KB, Nahimi A, Stokholm MG, Pavese N, Beier CP, Brooks DJ, Borghammer P (2018) In-vivo staging of pathology in REM sleep behaviour disorder: a multimodality imaging case-control study. Lancet Neurol 17(7):618–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30162-5
Knudsen K, Fedorova TD, Horsager J, Andersen KB, Skjaerbaek C, Berg D, Schaeffer E, Brooks DJ, Pavese N, Van Den Berge N, Borghammer P (2021) Asymmetric dopaminergic dysfunction in brain-first versus body-first Parkinson’s disease subtypes. J Parkinsons Dis 11(4):1677–1687. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-212761
Kok EH, Savola S, Raunio A, Oinas M, Tuimala J, Polvikoski T, Kero M, Kaivola K, Tienari PJ, Paetau A, Myllykangas L (2021) Alpha-synuclein pathology of olfactory bulb/peduncles in the Vantaa85+ cohort exhibit two divergent patterns: a population based study. Acta Neuropathol 142(4):777–780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-021-02364-6
Kong WL, Huang Y, Qian E, Morris MJ (2020) Constipation and sleep behaviour disorder associate with processing speed and attention in males with Parkinson’s disease over five years follow-up. Sci Rep 10(1):19014. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-75800-4
Lee NJ, Park IS, Koh I, Jung TW, Rhyu IJ (2009) No volume difference of medulla oblongata between young and old Korean people. Brain Res 1276:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.04.027
Leta V, Urso D, Batzu L, Weintraub D, Titova N, Aarsland D, Martinez-Martin P, Borghammer P, van Wamelen DJ, Yousaf T, Rizos A, Rodriguez-Blazquez C, Chung-Faye G, Chaudhuri KR (2021) Constipation is associated with development of cognitive impairment in de novo Parkinson’s disease: a longitudinal analysis of two international cohorts. J Parkinsons Dis 11(3):1209–1219. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-212570
Martin WRW, Younce JR, Campbell MC, Racette BA, Norris SA, Ushe M, Criswell S, Davis AA, Alfradique-Dunham I, Maiti B, Cairns NJ, Perrin RJ, Kotzbauer PT, Perlmutter JS (2023) Neocortical Lewy body pathology parallels Parkinson’s dementia, but not always. Ann Neurol 93(1):184–195. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26542
McBride PA, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Donaldson M, Bruce M, Diringer H, Kretzschmar HA, Beekes M (2001) Early spread of scrapie from the gastrointestinal tract to the central nervous system involves autonomic fibers of the splanchnic and vagus nerves. J Virol 75(19):9320–9327. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.75.19.9320-9327.2001
McKeith IG, Boeve BF, Dickson DW, Halliday G, Taylor JP, Weintraub D, Aarsland D, Galvin J, Attems J, Ballard CG, Bayston A, Beach TG, Blanc F, Bohnen N, Bonanni L, Bras J, Brundin P, Burn D, Chen-Plotkin A, Duda JE, El-Agnaf O, Feldman H, Ferman TJ, Ffytche D, Fujishiro H, Galasko D, Goldman JG, Gomperts SN, Graff-Radford NR, Honig LS, Iranzo A, Kantarci K, Kaufer D, Kukull W, Lee VMY, Leverenz JB, Lewis S, Lippa C, Lunde A, Masellis M, Masliah E, McLean P, Mollenhauer B, Montine TJ, Moreno E, Mori E, Murray M, O’Brien JT, Orimo S, Postuma RB, Ramaswamy S, Ross OA, Salmon DP, Singleton A, Taylor A, Thomas A, Tiraboschi P, Toledo JB, Trojanowski JQ, Tsuang D, Walker Z, Yamada M, Kosaka K (2017) Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: fourth consensus report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 89(1):88–100. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000004058
Merola A, Romagnolo A, Dwivedi AK, Padovani A, Berg D, Garcia-Ruiz PJ, Fabbri M, Artusi CA, Zibetti M, Lopiano L, Pilotto A, Bonacina S, Morgante F, Zeuner K, Griewing C, Schaeffer E, Rodriguez-Porcel F, Kauffman M, Turcano P, de Oliveira LM, Palermo G, Shanks E, Del Sorbo F, Bonvegna S, Savica R, Munhoz RP, Ceravolo R, Cilia R, Espay AJ (2020) Benign versus malignant Parkinson disease: the unexpected silver lining of motor complications. J Neurol 267(10):2949–2960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-09954-6
Miyamoto T, Miyamoto M, Inoue Y, Usui Y, Suzuki K, Hirata K (2006) Reduced cardiac 123I-MIBG scintigraphy in idiopathic REM sleep behavior disorder. Neurology 67(12):2236–2238. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000249313.25627.2e
Mollenhauer B, Trautmann E, Sixel-Doring F, Wicke T, Ebentheuer J, Schaumburg M, Lang E, Focke NK, Kumar KR, Lohmann K, Klein C, Schlossmacher MG, Kohnen R, Friede T, Trenkwalder C, DeNoPa Study G (2013) Nonmotor and diagnostic findings in subjects with de novo Parkinson disease of the DeNoPa cohort. Neurology 81(14):1226–1234. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182a6cbd5
Nag S, Yu L, VanderHorst VG, Schneider JA, Bennett DA, Buchman AS, Wilson RS (2019) Neocortical Lewy bodies are associated with impaired odor identification in community-dwelling elders without clinical PD. J Neurol 266(12):3108–3118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09540-5
Nagayama H, Hamamoto M, Ueda M, Nagashima J, Katayama Y (2005) Reliability of MIBG myocardial scintigraphy in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76(2):249–251. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2004.037028
Nishikawa N, Murata M, Hatano T, Mukai Y, Saitoh Y, Sakamoto T, Hanakawa T, Kamei Y, Tachimori H, Hatano K, Matsuda H, Taruno Y, Sawamoto N, Kajiyama Y, Ikenaka K, Kawabata K, Nakamura T, Iwaki H, Kadotani H, Sumi Y, Inoue Y, Hayashi T, Ikeuchi T, Shimo Y, Mochizuki H, Watanabe H, Hattori N, Takahashi Y, Takahashi R, Japan Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative study g (2022) Idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder in Japan: an observational study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 103:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2022.08.011
Noorian AR, Rha J, Annerino DM, Bernhard D, Taylor GM, Greene JG (2012) Alpha-synuclein transgenic mice display age-related slowing of gastrointestinal motility associated with transgene expression in the vagal system. Neurobiol Dis 48(1):9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2012.06.005
Oka H, Umehara T, Nakahara A, Matsuno H (2020) Comparisons of cardiovascular dysautonomia and cognitive impairment between de novo Parkinson’s disease and de novo dementia with Lewy bodies. BMC Neurol 20(1):350. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-020-01928-5
Orimo S, Uchihara T, Nakamura A, Mori F, Kakita A, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (2008) Axonal alpha-synuclein aggregates herald centripetal degeneration of cardiac sympathetic nerve in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131(Pt 3):642–650. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awm302
Orimo S, Yogo M, Nakamura T, Suzuki M, Watanabe H (2016) Brain imaging in aging special issue of ageing research reviews I-meta-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) cardiac scintigraphy in alpha-synucleinopathies. Ageing Res Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.01.001
Pao WC, Boeve BF, Ferman TJ, Lin SC, Smith GE, Knopman DS, Graff-Radford NR, Petersen RC, Parisi JE, Dickson DW, Silber MH (2013) Polysomnographic findings in dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurologist 19(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/NRL.0b013e31827c6bdd
Parkkinen L, Pirttila T, Alafuzoff I (2008) Applicability of current staging/categorization of alpha-synuclein pathology and their clinical relevance. Acta Neuropathol 115(4):399–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-008-0346-6
Petrou M, Dwamena BA, Foerster BR, MacEachern MP, Bohnen NI, Muller ML, Albin RL, Frey KA (2015) Amyloid deposition in Parkinson’s disease and cognitive impairment: a systematic review. Mov Disord 30(7):928–935. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26191
Pilotto A, Romagnolo A, Tuazon JA, Vizcarra JA, Marsili L, Zibetti M, Rosso M, Rodriguez-Porcel F, Borroni B, Rizzetti MC, Rossi C, Vizcarra-Escobar D, Molano JR, Lopiano L, Ceravolo R, Masellis M, Espay AJ, Padovani A, Merola A (2019) Orthostatic hypotension and REM sleep behaviour disorder: impact on clinical outcomes in alpha-synucleinopathies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 90(11):1257–1263. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2019-320846
Postuma RB, Iranzo A, Hu M, Hogl B, Boeve BF, Manni R, Oertel WH, Arnulf I, Ferini-Strambi L, Puligheddu M, Antelmi E, Cochen De Cock V, Arnaldi D, Mollenhauer B, Videnovic A, Sonka K, Jung KY, Kunz D, Dauvilliers Y, Provini F, Lewis SJ, Buskova J, Pavlova M, Heidbreder A, Montplaisir JY, Santamaria J, Barber TR, Stefani A, St Louis EK, Terzaghi M, Janzen A, Leu-Semenescu S, Plazzi G, Nobili F, Sixel-Doering F, Dusek P, Bes F, Cortelli P, Ehgoetz Martens K, Gagnon JF, Gaig C, Zucconi M, Trenkwalder C, Gan-Or Z, Lo C, Rolinski M, Mahlknecht P, Holzknecht E, Boeve AR, Teigen LN, Toscano G, Mayer G, Morbelli S, Dawson B, Pelletier A (2019) Risk and predictors of dementia and parkinsonism in idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder: a multicentre study. Brain 142(3):744–759. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awz030
Poulin JF, Caronia G, Hofer C, Cui Q, Helm B, Ramakrishnan C, Chan CS, Dombeck DA, Deisseroth K, Awatramani R (2018) Mapping projections of molecularly defined dopamine neuron subtypes using intersectional genetic approaches. Nat Neurosci 21(9):1260–1271. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0203-4
Raunio A, Kaivola K, Tuimala J, Kero M, Oinas M, Polvikoski T, Paetau A, Tienari PJ, Myllykangas L (2019) Lewy-related pathology exhibits two anatomically and genetically distinct progression patterns: a population-based study of Finns aged 85. Acta Neuropathol 138(5):771–782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-019-02071-3
Riederer P, Jellinger KA, Kolber P, Hipp G, Sian-Hulsmann J, Kruger R (2018) Lateralisation in Parkinson disease. Cell Tissue Res 373(1):297–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-018-2832-z
Sakakibara R, Tateno F, Aiba Y, Ogata T, Kishi M, Terada H, Inaoka T, Nakatsuka T, Matsuoka K (2019) MIBG myocardial scintigraphy identifies premotor PD/DLB during a negative DAT scan period: second report. Mov Disord Clin Pract 6(1):46–50. https://doi.org/10.1002/mdc3.12697
Seidel K, Mahlke J, Siswanto S, Kruger R, Heinsen H, Auburger G, Bouzrou M, Grinberg LT, Wicht H, Korf HW, den Dunnen W, Rub U (2015) The brainstem pathologies of Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain Pathol 25(2):121–135. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12168
Sommerauer M, Fedorova TD, Hansen AK, Knudsen K, Otto M, Jeppesen J, Frederiksen Y, Blicher JU, Geday J, Nahimi A, Damholdt MF, Brooks DJ, Borghammer P (2018) Evaluation of the noradrenergic system in Parkinson’s disease: an 11C-MeNER PET and neuromelanin MRI study. Brain 141(2):496–504. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awx348
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388(6645):839–840. https://doi.org/10.1038/42166
Surmeier DJ, Obeso JA, Halliday GM (2017) Parkinson’s disease is not simply a prion disorder. J Neurosci 37(41):9799–9807. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1787-16.2017
Tanaka R, Yamashiro K, Ogawa T, Oyama G, Nishioka K, Umemura A, Shimo Y, Hattori N (2020) The absence of orthostatic heart rate increase is associated with cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 15(10):e0240491. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240491
Tanei ZI, Saito Y, Ito S, Matsubara T, Motoda A, Yamazaki M, Sakashita Y, Kawakami I, Ikemura M, Tanaka S, Sengoku R, Arai T, Murayama S (2021) Lewy pathology of the esophagus correlates with the progression of Lewy body disease: a Japanese cohort study of autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol 141(1):25–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-020-02233-8
Tremblay C, Serrano GE, Intorcia AJ, Sue LI, Wilson JR, Adler CH, Shill HA, Driver-Dunckley E, Mehta SH, Beach TG (2022) Effect of olfactory bulb pathology on olfactory function in normal aging. Brain Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.13075
Tsujikawa K, Hasegawa Y, Yokoi S, Yasui K, Nanbu I, Yanagi T, Takahashi A (2015) Chronological changes of 123I-MIBG myocardial scintigraphy and clinical features of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 86(9):945–951. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2015-310327
Uchihara T, Giasson BI (2016) Propagation of alpha-synuclein pathology: hypotheses, discoveries, and yet unresolved questions from experimental and human brain studies. Acta Neuropathol 131(1):49–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1485-1
Ulusoy A, Rusconi R, Perez-Revuelta BI, Musgrove RE, Helwig M, Winzen-Reichert B, Di Monte DA (2013) Caudo-rostral brain spreading of alpha-synuclein through vagal connections. EMBO Mol Med 5(7):1051–1059. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201302475
Ulusoy A, Phillips RJ, Helwig M, Klinkenberg M, Powley TL, Di Monte DA (2017) Brain-to-stomach transfer of alpha-synuclein via vagal preganglionic projections. Acta Neuropathol 133(3):381–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-016-1661-y
van de Beek M, van Steenoven I, van der Zande JJ, Barkhof F, Teunissen CE, van der Flier WM, Lemstra AW (2020) Prodromal dementia with Lewy bodies: clinical characterization and predictors of progression. Mov Disord 35(5):859–867. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27997
Van Den Berge N, Ferreira N, Gram H, Mikkelsen TW, Alstrup AKO, Casadei N, Tsung-Pin P, Riess O, Nyengaard JR, Tamguney G, Jensen PH, Borghammer P (2019) Evidence for bidirectional and trans-synaptic parasympathetic and sympathetic propagation of alpha-synuclein in rats. Acta Neuropathol 138(4):535–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-019-02040-w
van Keulen LJ, Vromans ME, Dolstra CH, Bossers A, van Zijderveld FG (2008) Pathogenesis of bovine spongiform encephalopathy in sheep. Arch Virol 153(3):445–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-007-0007-4
Vogt A, Schmid S, Heinimann K, Frick H, Herrmann C, Cerny T, Omlin A (2017) Multiple primary tumours: challenges and approaches, a review. ESMO Open 2(2):e000172. https://doi.org/10.1136/esmoopen-2017-000172
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Takeda S, Ohama E, Ikuta F (1988) Parkinson’s disease: the presence of Lewy bodies in Auerbach’s and Meissner’s plexuses. Acta Neuropathol 76(3):217–221
Walker Z, Costa DC, Walker RW, Lee L, Livingston G, Jaros E, Perry R, McKeith I, Katona CL (2004) Striatal dopamine transporter in dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson disease: a comparison. Neurology 62(9):1568–1572. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000123248.39847.1d
Wohlwill F (1928) Zur pathologischen anatomie des peripherischen sympathicus. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd 107:124–150
Zhang J, Xu CY, Liu J (2017) Meta-analysis on the prevalence of REM sleep behavior disorder symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. BMC Neurol 17(1):23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-017-0795-4
Acknowledgements
The author (PB) holds research grants from The Lundbeck Foundation, Michael J Fox Foundation, and Danish Parkinson’s disease foundation. These grants are only indirectly related to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Borghammer, P. The brain-first vs. body-first model of Parkinson’s disease with comparison to alternative models. J Neural Transm 130, 737–753 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-023-02633-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-023-02633-6