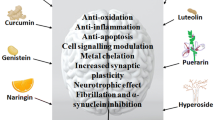
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by typical motor symptoms, loss of dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra, and accumulation of Lewy body composed of mutated α-synuclein. However, now it is considered as a generalized disease with multiple pathological features. Present available treatments can ameliorate symptoms at least for a while, but only a few therapies could delay progressive neurodegeneration of dopamine neurons. Lewy body accumulates in peripheral tissues many years before motor dysfunction becomes manifest, suggesting that disease-modifying therapy should start earlier during the premotor stage. Long-termed regulation of lifestyle, diet and supplement of nutraceuticals may be possible ways for the disease-modification. Diet can reduce the incidence of Parkinson’s disease and phytochemicals, major bioactive ingredients of herbs and plant food, modulate multiple pathogenic factors and exert neuroprotective effects in preclinical studies. This review presents mechanisms underlying neuroprotection of phytochemicals against neuronal cell death and α-synuclein toxicity in Parkinson’s disease. Phytochemicals are antioxidants, maintain mitochondrial function and homeostasis, prevent intrinsic apoptosis and neuroinflammation, activate cellular signal pathways to induce anti-apoptotic and pro-survival genes, such as Bcl-2 protein family and neurotrophic factors, and promote cleavage of damaged mitochondria and α-synuclein aggregates. Phytochemicals prevent α-synuclein oligomerization and aggregation, and dissolve preformed α-synuclein aggregates. Novel neuroprotective agents are expected to develop based on the scaffold of phytochemicals permeable across the blood–brain–barrier, to increase the bioavailability, ameliorate brain dysfunction and prevent neurodegeneration.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARE:
-
Antioxidant responsive element
- ALP:
-
Autophagy-lysosome pathway
- αSyn:
-
α-Synuclein
- GCase:
-
Glucocerebrosidase
- HMGB1:
-
High-mobility group box 1
- MMP:
-
Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization
- mPTP:
-
Mitochondrial permeability transition pore
- RPCT:
-
Randomized, placebo-controlled trial
- TSPO:
-
The outer membrane translocator protein 18 kDa
- UPDRS:
-
Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale
- UPS:
-
Ubiquitin–proteasome system
References
Ahmed T, Raza SH, Maryam A et al (2016) Ginsenoside Rb1 as neuroprotective agents: a review. Brain Res Bull 125:30–43
Ahsan N, Mishra S, Jain MK, Surolia A, Gupta S (2015) Curcumin pyrazole and its derivative (N-(3-nitrophenylpyrazole) curcumin inhibit aggregation, disrupt fibrils and modulate toxicity of wild type and mutant α-synuclein. Sci Rep 5:9862
Arbo BD, Andre-Miral C, Nasre-Nasser RG et al (2020) Resveratrol derivatives as potential treatments for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 12:103
Ardah MT, Paleologou KE, Lv G et al (2015) Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits fibrillation and toxicity of alpha-synuclein and disaggregates preformed fibrils. Neurobiol Dis 74:89–101
Ascherio A, Zhang SM, Hernan MA et al (2001) Prospective study of caffeine consumption and risk of Parkinson’s disease in men and women. Ann Neurol 50(1):56–63
Barichella M, Cereda E, Cassani E et al (2017) Dietary habits and neurological features of Parkinson’s disease patients: implications for practice. Clin Nutr 36(4):1054–1061
Barker RA, Björklund A, Gash DM et al (2020) GDNF and Parkinson’s disease: where next? A summary from a recent workshop. J Parkinsons Dis 10(3):875–891
Bastianetto S, Menard C, Qurion R (2015) Neuroprotective action of resveratrol. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852(6):1195–1201
Bieschke J, Russ J, Friedrich RP, Ehrnhoefer DE, Wobst H, Neugebauer K, Wanker EE (2010) EGCG remodels mature α-synuclein and amyloid-β fibrils and reduces cellular toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(17):7710–7715
Billingsley K, Barbosa IA, Bandres-Ciga S et al (2019) Mitochondria function associated genes contribute to Parkinson’s disease risk and later age at onset. NPJ Parkinson Dis 5:8
Braak H, Tredici KD, Rüb U, de Vos RAI, Jansen Steur ENH, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24(2):197–211
Burbulla LT, Song P, Mazzulli JR et al (2017) Dopamine oxidation mediates mitochondrial and lysosomal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Science 357(6357):1255–1261
Caruana M, Högen T, Levin J, Hillmer A, Giese A, Vassallo N (2011) Inhibition and disaggregation of α-synuclein oligomers by natural polyphenol compounds. FEBS Lett 585(8):1113–1120
Chen C, Vincent AE, Blain AP, Smith AL, Turnbull DM, Reeve AK (2020) Investigation of mitochondrial biogenesis defects in single substantia nigra neurons using post-mortem human tissues. Neurobiol Dis 134:104631
Cryan JF, O’Riordan KJ, Cowan CSM et al (2019) The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol Rev 99(4):1877–2013
Cuervo AM, Stefanis L, Fredenburg R, Lansbury PT, Sulzer D (2004) Impaired degradation of mutant α-synuclein by chaperone-mediated autophagy. Science 305(5688):1292–1295
Das S, Mitrovsky G, Vasanthi H, Das DK (2014) Antiaging properties of a grape-derived antioxidant are regulated by mitochondrial balance of fission and fission leading to mitophagy triggered by a signaling network of Sirt1-Sirt3-Foxo3-Pink1-Parkin. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014:345105
De Marchi U, Biasutto L, Garbisa S, Toninello A, Zorratti M (2009) Quercetin can act either as an inhibitor or an inducer of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore: a demonstration of the ambivalent redox character of polyphenols. Biochim Biophys Acta 1787(12):1425–1432
Devi L, Raghavendran V, Prabhu BM, Avadhani NG, Anandatheerthavarada HK (2008) Mitochondrial import and accumulation of α-synuclein impair complex I in human dopaminergic neuronal cultures and Parkinson disease brain. J Biol Chem 283(14):9089–9100
Dos Santos TW, Pereira QC, Teixeira L, Gambero A, Villena JA, Ribeiro ML (2018) Effects of polyphenols on thermogenesis and mitochondrial biogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 19(9):2757
Ehrnhoefer DE, Bieschke J, Boeddrich A et al (2008) EGCG redirects amyloidogenic polypeptides into unstructured, off-pathway oligomers. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15(6):558–566
Espay AJ, Brundin P, Lang AE (2017) Precision medicine for disease modifying in Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol 13(2):119–126
Fanaei H, Khayat S, Kasaeian A, Javadimehr M (2016) Effect of curcumin on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in women with premenstrual syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neuropeptides 56:25–31
Fereshtehnejad SM, Yao C, Pelletier A, Montplaisir JY, Gagnon JF, Postuma RB (2019) Evolution of prodromal Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies: a prospective study. Brain 142(7):2051–2067
Ferretta A, Gaballo A, Tanzarella P et al (2014) Effect of resveratrol on mitochondrial function: implications in parkin-associated familiar Parkinson’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842(7):902–915
Figueira I, Garcia G, Pimao RC et al (2017) Polyphenols journey through blood-brain barrier towards neuronal protection. Sci Rep 7(1):11456
Filomeni G, Graziani I, De Zio D, Dini L, Centonze D, Rotilio G, Ciriolo MR (2012) Neuroprotection of kaempferol by autophagy in models of rotenone-mediated acute toxicity: possible implications for Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 33(4):767–785
Furukawa Y, Vigouroux S, Wong H et al (2002) Brain proteasomal function in sporadic Parkinson’s disease and related disorders. Ann Neurol 51(6):779–782
Gao X, Cassidy A, Schwarzschild MA, Rimm EB, Ascherio A (2012) Habitual intake of dietary flavonoids and risk of Parkinson disease. Neurology 78(15):1138–1145
Gavrilova SI, Preuss UW, Wong JW, Hoerr R, Kaschel R, Bachinskaya N, GIMCIPlus Study Group (2014) Efficacy and safety of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 in mild cognitive impairment with neuropsychiatric symptoms: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multi-center trial. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 29(10):1087–1095
Gogada R, Prabhu V, Amadori M, Scott R, Hashmi S, Chandra D (2011) Resveratrol induced p53-independent, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP)-mediated Bax protein oligomerization on mitochondria to initiate cytochrome c release and caspase activation. J Biol Chem 286(33):28749–28760
Goto S, Kogure K, Abe K, Kimura Y, Kitahama K, Yamashita E, Terada H (2001) Efficient radical trapping at the surface and inside the phospholipid membrane is response for highly potent antiperoxidative activity of the carotenoid astaxanthin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1512(2):251–258
Gundimeda U, McNeill TH, Fan TK, Deng R, Rayudu D, Chen Z, Cadenas E, Gopalakrishna R (2014) Green tea catechins potentiate the neurogenic action of brain-derived neurotrophic factor: role of 67-kDa laminin receptor and hydrogen peroxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 445(1):218–224
Guo YJ, Dong SY, Cui XX et al (2016) Resveratrol alleviates MPTP-induced motor impairments and pathological changes by autophagic degradation of α-synuclein via SIRT1-deacetylated LC3. Mol Nutr Food Res 60(10):2161–2175
Han YS, Bastianetto S, Dumont Y, Quirion R (2006) Specific plasma membrane binding sites for polyphenols, including resveratrol, in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 318(1):228–245
He J, Xiang Z, Zhu X et al (2016) Neuroprotective effects of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone on midbrain dopaminergic neurons in MPP+-treated monkey. Sci Rep 6:34339
Henchcliffe C, Beal MF (2008) Mitochondrial biology and oxidative stress in Parkinson disease pathogenesis. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 4(11):600–609
Henriquez G, Comez A, Guerrero E, Narayan M (2020) Potent role of natural polyphenols against protein aggregation toxicity: in vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies. ACS Chem Neurosci 11(19):2915–2934
Higashida K, Kim SH, Jung SR, Asaka M, Holloszy JO, Han DH (2013) Effects of resveratrol and Sirt1 on PGC-1α activity and mitochondrial biogenesis: a reevaluation. PLoS Biol 11(7):e1001603
Ho L, Zhao D, Ono K et al (2019) Heterogeneity in gut microbiota drive polyphenol metabolism that influences α-synuclein misfolding and toxicity. J Nutr Biochem 64:170–181
Holczer M, Besze B, Zambo V, Csala M, Banhegyi G, Kapuy O (2018) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) promotes autophagy-dependent survival via influencing the balance of mTOR-AMPA pathways upon endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:6721530
Huang X, Li N, Pu Y, Zhang T, Wang B (2019) Neuroprotective effects of ginseng phytochemicals: recent perspectives. Molecules 24(16):2939
Huhn S, Beyer F, Zhang R et al (2018) Effects of resveratrol on memory performance, hippocampus connectivity and microstructure in older adults—a randomized controlled trial. Neuroimage 174:177–190
Hwang SL, Yen GC (2011) Effects of hesperetin against oxidative stress via ER- and TrkA-mediated actions in PC12 cells. J Agric Food Chem 59(10):5779–5785
Jha NN, Ghosh D, Das S et al (2016) Effect of curcumin analogs on α-synuclein aggregation and cytotoxicity. Sci Rep 6:28511
Jin CF, Shen SR, Zhao BL (2001) Different effects of five catechins on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. J Agric Food Chem 49(12):6033–6038
Jinsmaa J, Isonaka R, Sharabi Y, Goldstein DS (2020) 3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl-acetaldehyde is more efficient than dopamine in oligomerizing and quinonizing α-synuclein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 372(2):157–165
Kaur N, Chugh H, Sakharkar MK, Dhawan U, Chidambaram SB, Chandra R (2020) Neuroinflammation mechanisms and phytotherapeutic intervention: a systemic review. ACS Chem Neurosci 11(22):3707–3731
Kumar S, Kumar R, Kumari M, Kumari R, Saha S, Bhavesh NS, Maiti TK (2021) Ellagic acid inhibits α-synuclein aggregation at multiple stages and reduces its cytotoxicity. ACS Chem Neurosci 12(11):1919–1930
Kurauchi Y, Hisatsune A, Isohama Y, Mishima S, Katsuki H (2012) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester protects nigral dopaminergic neurons via dual mechanisms involving haem oxygenase-1 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Br J Pharmacol 166(3):1151–1169
Lee H, James WS, Cowley SA (2017) LRRK2 in peripheral and central nervous system innate immunity: its link to Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Soc Trans 45(1):131–139
Lewadowska U, Szewczyk K, Hrabec E, Janecka A, Gorlach S (2013) Overview of metabolism and bioavailability enhancement of polyphenols. J Agric Food Chem 61(50):12183–12199
Li XH, Dai CF, Chen L, Zhou WT, Han HL, Domg ZF (2016) 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone ameliorates motor deficits via suppressing α-synuclein expression and oxidative stress in the MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurosci Ther 22(7):617–624
Li J, Chen L, Li G et al (2020) Sub-acute treatment of curcumin derivative J147 ameliorates depression-like behavior through 5-HT1A-mediated cAMP signaling. Front Neurosci 14:701
Lim H, Min DS, Park H, Kim HP (2018) Flavonoids interfere with NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 355:93–102
Lin CY, Tsai CW (2019) PINK1/parkin-mediated mitophagy is related to neuroprotection by carnosic acid in SH-SH5Y cells. Food Chem Toxicol 125:430–437
Liu S, Sawada T, Lee S et al (2012) Parkinson’s disease-associated kinase PINK1 regulates Miro protein level and axonal transport of mitochondria. PLoS Genet 8(3):e1002537
Liu X, Obianyo O, Chan CB et al (2014) Biochemical and biophysical investing of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor mimetic 7,8-dihydroxyflavone in the binding and activation of the TrkB receptor. J Biol Chem 289(40):27571–27584
Lopresti A, Maes M, Maker G, Hood SD, Drummond PD (2014) Curcumin for the treatment of major depression: a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study. J Affect Disord 167:368–375
Lorenzen N, Nielsen SB, Yoshimura Y et al (2014) How epigallocatechin gallate can inhibit α-synuclein oligomer toxicity in vitro. J Bol Chem 289(31):21299–21310
Ludtmann MHR, Angelova PR, Horrocks MH et al (2018) α-Synuclein oligomers interact with ATP synthase and open the permeability transition pore in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Commun 9(1):2294
Lv R, Du L, Liu X, Zhou F, Zhang Z, Zhang L (2019) Rosmarinic acid attenuates inflammatory responses through inhibiting HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signal pathway in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Life Sci 223:158–165
Maclennan KM, Darlington CL, Smith PF (2002) The CNS effects of Ginkgo biloba extracts and gingolide B. Prog Neurobiol 67(3):235–257
Manzoni C, Lewis PA (2013) Dysfunction of the autophagy/lysosomal degradation pathway is a shared feature of the genetic synucleinopathies. FASEB J 27(9):3424–3429
Mohammad-Beigi H, Aliakbari F, Sahin C et al (2019) Oleuropein derivatives from olive fruit extracts reduce α-synuclein fibrillation and oligomer toxicity. J Biol Chem 294(11):4215–4232
Mohankumar T, Chandramohan V, Lalithamba HS et al (2020) Design and molecular dynamic investigations of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone derivatives as potential neuroprotective agents against alpha-synuclein. Sci Rep 10(1):599
Murota K, Nakamura Y, Uehara M (2018) Flavonoid metabolism: the interaction of metabolites and gut microbiota. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 82(4):600–610
Naoi M, Inaba-Hasegawa K, Shamoto-Nagai M, Maruyama W (2017) Neurotrophic function of phytochemicals for neuroprotection in aging and neurodegenerative disorders: modulation of intracellular signaling and gene expression. J Neural Transm 24(12):1515–1527
Naoi M, Wu Y, Shamoto-Nagai M, Maruyama W (2019) Mitochondria in neuroprotection by phytochemicals: bioactive polyphenols modulate mitochondrial apoptosis system, function and structure. Int J Mol Sci 20(10):2451
Naoi M, Maruyama W, Shamoto-Nagai M (2020) Rasagiline and selegiline modulate mitochondrial homeostasis, intervene apoptosis system and mitigate α-synuclein cytotoxicity in disease-modifying therapy for Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 127(2):131–147
Nebrisi EE, Javed H, Ojha SK, Oz M, Shehab S (2020) Neuroprotective effects of curcumin on the nigrostriatal pathway in a 6-hydroxydopamine-induced rat model of Parkinson’s disease by α-7-nicotinic receptors. Int J Mol Sci 21(19):7329
Neshatdoust S, Saunders C, Castle SM et al (2016) High-flavonoid intake induces cognitive improvements linked to changes in serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor: two randomized controlled trials. Nutr Healthy Aging 4(1):81–93
Nieman DC, Williams AS, Shanely RA, Jin F, McAnulty SR, Triplett NT, Austin MD, Henson DA (2010) Quercetin’s influence on exercise performance and muscle mitochondrial biogenesis. Med Sci Sports Exerc 42(2):338–345
Olanow CW, Rascol O, Hauser R et al (2009) A double-blind, delayed-start trial of rasagiline in Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 361(13):1268–1278
Olanow CW, Kieburtz K, Katz R (2017) Clinical approaches to the development of a neuroprotective therapy for PD. Exp Neurol 298(Pt B):246–251
Pan T, Kondo S, Le W, Jankovic J (2008) The role of autophagy-lysosome pathway in neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131(Pt 8):1969–1978
Parain K, Murer MG, Yan Q, Faucheux B, Agid Y, Hirsch E, Raisman-Vozari R (1999) Reduced expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein in Parkinson’s disease substantia nigra. NeuroReport 10(3):557–561
Parkinson Study Group QE3 investigators (2014) A randomized clinical trial of high-dose coenzyme Q10 in early Parkinson disease: no evidence of benefit. JAMA Neurol 71(5):543–552
Poole AC, Thomas RE, Andrews LA, McBride HM, Whitworth AJ, Pallanck LJ (2008) The PINK1/Parkin pathway regulates mitochondrial morphology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(5):1638–1643
Rainey-Smith SR, Brown B, Sohrabi HR, Shah T, Goozee KG, Cupta VB, Martins RN (2016) Curcumin and cognition: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of community-dwelling older adults. Br J Nutr 115(12):2106–2113
Reyes-Izquierdo T, Nemzer B, Shu C, Argumedo R, Keller R, Piertrzkowski Z (2013) Modulatory effect of coffee fruit extract on plasma levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in healthy subjects. Br J Nutr 110(3):420–425
Rostovtseva T, Gurnev PA, Protchenko O, Hoogerheide DP, Yap TL, Philpott CC, Lee JC, Bezrukov SM (2015) α-Synuclein shows high affinity interaction with voltage-dependent anion channel, suggesting mechanisms of mitochondrial regulation and toxicity in Parkinson disease. J Biol Chem 290(30):18467–18477
Sadowska-Krepa E, Klapcinska B, Pokora I, Domaszewski P, Kempa K, Podgorski T (2017) Effects of six-week Ginkgo biloba supplementation on aerobic performance, blood pro-antioxidant balance, and serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor in physically active men. Nutrients 9(8):803
Sampson TR, Debelius JW, Thron T et al (2016) Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell 167(6):1469–1480
Santos D, Esteves AR, Silva D, Januario C, Cardoso SM (2015) The impact of mitochondrial fusion and fission modulation in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 52(1):573–586
Sarubbo F, Esteban S, Miralles A, Moranta D (2018) Effects of resveratrol and other polyphenols on Sirt1: relevance to brain function during aging. Curr Neuropharmacol 16(2):126–136
Scrivo A, Bourdenx M, Pampliega O, Cuervo AM (2018) Selective autophagy as a potential therapeutic target for neurodegenerative disorders. Lancet Neurol 17(9):802–825
Sekikawa T, Kizawa Y, Li Y, Takara T (2020) Cognitive function improvement with astaxanthin and tocotrienol intake: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Biochem Nutr 67(3):307–316
Shishtar E, Rogers GT, Blumberg JB, Au R, DeCarli C, Jacques P (2020) Flavonoid intake and MRI markers of brain health in the Framingham offspring cohort. J Nutr 150(6):1545–1553
Singh P, Bhat R (2019) Binding of noradrenaline to native and intermediate states during the fibrillation of α-synuclein leads to the formation of stable and structured cytotoxic species. ACS Chem Neurosci 10(6):2741–2755
Sun X, Xiong Z, Zhang Y et al (2012) Harpagoside attenuates MPTP/MPP+ induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration and movement disorder via elevating glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurochem 120(6):1072–1083
Sun W, Wang X, Hou C et al (2017) Oleuropein improves mitochondrial function to attenuate oxidative stress by activating the Nrf2 pathway in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Neuropharmacology 113(Pt A):556–566
Tatsuta T, Langer T (2008) Quality control of mitochondria: protection against neurodegeneration and ageing. EMBO J 27(2):306–314
Taub PR, Ramairez-Sanchez I, Patel M et al (2016) Beneficial effects of dark chocolate on exercise capacity in sedentary subjects: underlying mechanisms. A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled trial. Food Funct 7(9):3686–3693
Tewari D, Ahmed T, Chirasani VR, Singh PK, Maji SK, Senapati S, Bera AK (2015) Modulation of the mitochondrial voltage dependent anion channel (VDAC) by curcumin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1848(Pt A):151–158
Tian M, Xie Y, Meng Y et al (2019) Resveratrol protects cardiomyocytes against anoxia/reoxygenation via dephosphorylation of VDAC1 by Akt-GSK3 β pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 843:80–87
Trinh D, Israwi AR, Arathoon LR, Gleave JA, Nash JE (2021) The multi-faceted role of mitochondria in the pathology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 156(6):715–752
Valenti D, De Rasmo D, Signorile A et al (2013) Epigalocatchin-3-gallate prevents oxidative phosphorylation deficit and promotes mitochondrial biogenesis in human cells from subjects with Down’s syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832(4):542–552
Vauzour D, Vafeiadou K, Rice-Evans C, Williams RJ, Spencer JPE (2007) Activation of pro-survival Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways underlie the anti-apoptotic effects of flavanones in cortical neurons. J Neurochem 103(4):1355–1367
Vogiatzi T, Xilouri M, Vekrellis K, Stefanis L (2008) Wild type α-synuclein is degraded by chaperone-mediated autophagy and macroautophagy in neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 284(35):23542–23556
Wang ZY, Liu JY, Yang CB, Malampati S, Huang YY, Li MX, Li M, Song JX (2017) Neuroprotective natural products for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease by targeting the autophagy-lysosome pathway: a systematic review. Phytother Res 31(8):1119–1127
Whone A, Luz M, Boca M et al (2019) Randomized trial of intermittent intraputamenal glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 142(3):512–525
Wightman E, Haskell CF, Forster JS, Veasey RC, Kennedy DO (2012) Epigallocatechin gallate, cerebral blood flow parameters, cognitive performance and mood in healthy humans: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover investigation. Hum Psychopharmacol 27(2):177–186
Witte AV, Kerti L, Margulies DS, Flöel A (2014) Effects of resveratrol on memory performance, hippocampal functional connectivity, and glucose metabolism in healthy older adults. J Neurosci 34(23):7862–7870
Wu Y, Shamoto-Nagai M, Maruyama W, Osawa T, Naoi M (2017) Phytochemicals prevent mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and protect SH-SY5Y cells against apoptosis induced by PK11195, a ligand for outer membrane translocator protein. J Neural Transm 124(1):89–98
Xu SL, Bi CWC, Choi RCY, Zhu KY, Miernisha A, Dong TTX, Tsim KWK (2013) Flavonoids induce the synthesis and secretion of neurotrophic factors in cultured rat astrocytes: a signaling response mediated by estrogen receptor. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:127075
Yamazaki TR, Ono K, Ho L, Pasinetti GM (2020) Gut microbiome-modified polyphenolic compounds inhibit α-synuclein seeding and spreading in α-synucleinopathy. Front Neurosci 14:398
Yang F, Wolk A, Hakansson N, Pedersen NL, Wirdefeld K (2017a) Dietary antioxidants and risk of Parkinson’s disease in two population-based cohorts. Mov Disord 32(11):1631–1636
Yang JE, Rhoo KY, Lee S, Lee JT, Park JH, Bhak G, Paik SR (2017b) EGCG-mediated protection of the membrane disruption and cytotoxicity caused by the ‘active oligomer’ of α-synuclein. Sci Rep 7(1):17945
Yang Y, Han C, Guo L, Guan Q (2018) High expression of the HMGB1-TLR4 axis and its downstream signaling factors in patients with Parkinson’s disease and the relationship of pathological staging. Brain Behav 8(4):e00948
Yao Y, Tang Y, Wei G (2020) Epigallocatechin gallate destabilizes α-synuclein fibril by disrupting the E46–E80 salt-bridge and inter-protofibril interface. ACS Chem Neurosci 11(24):4351–4361
Yoritake A, Kawajiri S, Yamamoto Y et al (2015) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot trial of reduced coenzyme Q10 for Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 21(8):911–916
Youdim KA, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph JA (2004) Flavonoids and the brain: Interactions at the blood–brain-barrier and their physiological effects on the central nervous system. Free Radic Biol Med 37(11):1683–1693
Zanforlin E, Zagotto G, Ribaudo G (2017) The medical chemistry of natural and semisythetic compounds against Parkinson’ and Huntington’s diseases. ACS Chem Neurosci 8(11):2356–2368
Zhang X, Wu M, Lu F, Luo N, He ZP, Yang H (2014) Involvement of α7nAcR signaling cascade in epigallocatechin gallate suppression of β-amyloid-induced apoptotic cortical neuronal insults. Mol Neurobiol 49(1):66–77
Zilocchi M, Finzi G, Lualdi M, Sessa F, Fasano M, Alberio T (2018) Mitochondrial alterations in Parkinson’s disease human samples and cellular models. Neurochem Int 118:61–72
Funding
The authors’ research of food-derived bioactive compounds is supported by the Grants-in-Aids for Scientific Research, No. 18Kk07430 (WM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from that disclosed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naoi, M., Maruyama, W. & Shamoto-Nagai, M. Disease-modifying treatment of Parkinson’s disease by phytochemicals: targeting multiple pathogenic factors. J Neural Transm 129, 737–753 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-021-02427-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-021-02427-8