Abstract
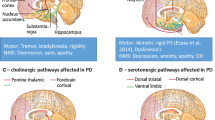
Parkinson disease (PD) is no longer considered a complex motor disorder characterized by parkinsonism but rather a systemic disease with variegated non-motor deficits and neurological symptoms, including impaired olfaction, sleep disorders, gastrointestinal and urinary abnormalities and cardiovascular dysfunction, in addition to other symptoms and signs such as pain, depression and mood disorders. Many of these alterations appear before or in parallel with motor deficits and then worsen with disease progression. Although there is a close relation between motor symptoms and the presence of Lewy bodies (LBs) and neurites filled with abnormal α-synuclein, other neurological alterations are independent of LBs, thereby indicating that different mechanisms probably converge in the degenerative process. This review presents cardinal observations at very early stages of PD and provides personal experience based on the study of a consecutive series of brains with PD-related pathology and without parkinsonism, mainly cases categorized as stages 2–3 of Braak. Alterations in the substantia nigra, striatum and frontal cortex in pPD are here revised in detail. Early modifications in the substantia nigra at pre-motor stages of PD (preclinical PD: pPD) include abnormal small aggregates of α-synuclein which is phosphorylated, nitrated and oxidized, and which exhibits abnormal solubility and truncation. This occurs in association with a plethora of altered molecular events including increased oxidative stress, altered oxidative stress responses, altered balance of L-ferritin and H-ferritin, reduced expression of neuronal globin α and β chains in neurons with α-synuclein deposits, increased expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress markers, increased p62 and ubiquitin immunoreactivity in relation to α-synuclein deposits, and altered distribution of LC3 and other autophagosome/lysosome markers. In spite of the relatively small decrease in the number of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, which does not reach thresholds causative of parkinsonism, levels of tyrosine hydroxylase and cannabinoid 1 receptor are reduced, whereas levels of adenosine receptor 2A are increased in the caudate in pPD. Moreover, biochemical alterations are also present in the cerebral cortex (at least in the frontal cortex) in pPD including increased oxidative stress and oxidative damage to proteins α-synuclein, β-synuclein, superoxide dismutase 2, aldolase A, enolase 1, and glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase, among others, indicating post-translational modifications of PD-related proteins, and suggesting altered function of pathways involved in glycolysis and energy metabolism in the cerebral cortex in pPD. Current evidence suggests convergence of several altered metabolic pathways leading to chronic neuronal dysfunction, mainly manifested as sub-optimal energy metabolism, altered synaptic function, oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress damage and corresponding altered responses, among others. By understanding that these alterations occur at very early stages of PD and that neuronal fatigue and exhaustion may precede, for years, cell death and neuronal loss, we may direct therapeutic strategies towards the prevention and delay of disease progression starting at pre-parkinsonian stages of PD.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Erviti L, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Cooper JM, Caballero C, Ferrer I, Obeso JA, Schapira AHV (2010) Chaperone-mediated autophagy markers are abnormal in Parkinson’s disease brain. Arch Neurol [Epub ahead of print]
Andersen JK (2004) Iron dysregulation and Parkinson’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 6:S47–S52
Anderson JP, Walker DE, Goldstein JM, Laat R, Banducci K, Caccavello RJ, Barbour R, Huang J, Kling K, Lee M, Diep L, Keim PS, Shen X, Chartaway T, Schlossmacher MG, Seubert P, Schenk D, Sinha S, Gai WP, Chilcote TJ (2006) Phosphorylation of Ser 129 is the dominant pathological modification of synuclein in familial and sporadic Lewy body disease. J Biol Chem 281:29739–29759
Anglade P, Vyas S, Javoy-Agid F, Herrero MT, Michel PP, Marquez J, Mouatt-Prigent A, Ruberg M, Hirsch EC, Agid Y (1997) Apoptosis and autophagy in nigral neurons of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Histol Histopathol 12:25–31
Baba M, Nakajo S, Tu PH, Tomita T, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Iwatsubo T (1998) Aggregation of α-synuclein in Lewy bodies of sporadic Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Am J Pathol 152:879–884
Barnham KJ, Bush AI (2008) Metals in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 12:222–228
Beach TG, Adler CH, Lue L, Sue LI, Bachalakuri J, Henry-Watson J, Sasse J, Boyer S, Shirohi S, Brooks R, Eschbacher J, White CL 3rd, Akiyama H, Caviness J, Shill HA, Connor DJ, Sabbagh MN, Walker DG, Arizona Parkinson’s Disease Consortium (2009) Unified staging system for Lewy body disorders: correlation with nigrostriatal degeneration, cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol 117:613–634
Biagioli M, Pinto M, Cesselli D, Zaninello M, Lazarevic D, Roncaglia P, Simone R, Vlachouli C, Plessy C, Bertin N, Beltrami A, Kobayashi K, Gallo V, Santoro C, Ferrer I, Rivella S, Beltrami CA, Carninci P, Raviola E, Gustincich S (2009) Unexpected expression of alpha- and beta-globin in mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons and glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:15454–15459
Bloch A, Probst A, Bissing H, Adams H, Tolnay M (2006) Alpha-synuclein pathology of the spinal and peripheral autonomic nervous system in neurologically unimpaired elderly subjects. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 32:284–295
Braak H, del Tredici K (2008) Cortico-basal ganglia-cortical circuitry in Parkinson’s disease reconsidered. Exp Neurol 212:226–229
Braak H, Sandmann-Keil D, Gai W, Braak E (1999) Extensive axonal Lewy neurites in Parkinson’s disease: a novel pathological feature revealed by alpha-synuclein immunocytochemistry. Neurosci Lett 265:67–69
Braak H, del Tredici K, Bratzke H, Hamm-Clement J, Sandemann-Keil D, Rub U (2002) Staging of the intracerebral inclusion body pathology associated with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (preclinical and clinical stages). J Neurol 249(suppl 3):1–5
Braak H, del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RAI, Jansen Steur ENH, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211
Braak H, Ghebremedhin E, Rüb U, Bratzke H, del Tredici K (2004) Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res 318:121–134
Braak H, Rüb U, Jansen Steur EN, del Tredici K, de Vos RA (2005) Cognitive status correlates with neuropathologic state in Parkinson disease. Neurology 64:1404–1410
Braak H, Muller CM, Rüb U, Ackermann H, Bratzke H, de Vos RA, del Tredici K (2006) Pathology associated with sporadic Parkinson’s disease: where does it end? J Neural Transm Suppl 70:89–97
Buira SP, Dentesano G, Albasanz JL, Moreno J, Juvés S, Martín M, Ferrer I, Barrachina M (2010) Increased striatal ying yang-1 levels in Parkinson ‘s disease: a potential negative regulator of adenosine A2a receptor expression levels. J Neurochem 112:1273–1285
Chaudhuri KR, Yates L, Martínez-Martín P (2005) The non-motor symptom complex of Parkinson’s disease: a comprehensive assessment is essential. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 5:275–283
Chiba-Falek O, Lopez GJ, Nussbaum RL (2006) Levels of alpha-synuclein mRNA in sporadic Parkinson disease patients. Mov Disord 21:1703–1708
Chinta SJ, Andersen JK (2008) Redox imbalance in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Acta 1780:1362–1367
Choi J, Levey AI, Weintraub ST, Rees HD, Gearing M, Chin LS, Li L (2004) Oxidative modifications and down-regulation of ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1 associated with idiopathic Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. J Biol Chem 279:13256–13264
Choi J, Rees HD, Weintraub ST, Levey AI, Chin LS, Li L (2005) Oxidative modifications and aggregation of Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase associated with Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. J Biol Chem 280:11648–11655
Chu Y, Dodiya H, Aebischer P, Olanow CW, Kordower JH (2009) Alterations in lysosomal and proteasomal markers in Parkinson’s disease: relationship to alpha-synuclein inclusions. Neurobiol Dis 35:385–398
Chung KK, Thomas B, Li X, Pletnikova O, Troncoso JC, Marsh L, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2004) S-Nitrosylation of parkin regulates ubiquitination and compromises Parkin’s protective function. Science 304:1328–1331
Cuervo AM, Stefanis L, Fredenburg R, Lansbury PT, Sulzer D (2004) Impaired degradation of mutant alpha-synuclein by chaperone-mediated autophagy. Science 305:1292–1295
Dalfó E, Ferrer I (2008) Early α-synuclein lipoxidation in neocortex in Lewy body diseases. Neurobiol Aging 29:408–417
Dalfó E, Barrachina M, Rosa JL, Ambrosio S, Ferrer I (2004) Abnormal α-synuclein interactions with rab3a and rabphilin in diffuse Lewy body disease. Neurobiol Dis 16:92–97
Dalfó E, Portero-Otín M, Ayala V, Martínez A, Pamplona R, Ferrer I (2005) Evidence of oxidative stress in the neocortex in incidental Lewy body disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:1–13
Daniel SE, Hawkes CH (1992) Preliminary diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease by olfactory bulb pathology. Lancet 340:186
Del Tredici K, Rüb U, De Vos RA, Bohl JR, Braak H (2002) Where does Parkinson disease pathology begin in the brain? J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:413–426
DelleDonne A, Klos KJ, Fujishiro H, Ahmed Z, Parisi JE, Josephs KA, Frigerio R, Burnett M, Wszolek ZK, Uiti RJ, Ahlskog JE, Dickson DW (2008) Incidental Lewy body disease and preclinical Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 65:1074–1080
Dexter DT, Sian J, Rose S, Hindmarsh JG, Mann VM, Cooper JM, Wells FR, Daniel SE, Lees AJ, Schapira AH (1994) Indices of oxidative stress and mitochondrial function in individuals with incidental Lewy body disease. Ann Neurol 35:38–44
Dickson DW (2001) Alpha-synuclein and the Lewy body disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 14:423–432
Dickson DW, Fujishiro H, DelleDonne A, Menke J, Ahmed Z, Klos KJ, Josephs KA, Frigerio R, Burnett M, Parisi JE, Ahlskog JE (2008) Evidence that incidental Lewy body disease is pre-symptomatic Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 115:437–444
Dickson DW, Uchikado H, Fujishiro H, Tsuboi Y (2010) Evidence in favor of Braak staging of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 25(Suppl 1):S78–S82
Digicaylioglu M, Bichet S, Marti HH, Wenger RH, Rivas LA, Bauer C, Gassmann M (1995) Localization of specific erythropoietin binding sites in defined areas of the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3717–3720
Double KL (2006) Functional effects of neuromelanin and synthetic melanin in model systems. J Neuarl Transm 113:751–756
Double KL, Halliday GM (2006) New face of neuromelanin. J Neural Transm Suppl 70:119–123
Duda JE, Giasson BI, Chen Q, Gur TL, Hurtig HI, Stern MB, Gollomp SM, Ischiropoulos H, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2000) Widespread nitration of pathological inclusions in neurodegenerative synucleinopathies. Am J Pathol 157:1439–1445
ECh Wolters, Braak H (2006) Parkinson’s disease: pre-motor clinico-pathological correlations. J Neural Transm Suppl 70:309–319
Engelender S (2008) Ubiquitination of alpha synuynucelin and autophagy in Parkinson’s disease. Autophagy 4:372–374
Fasano M, Bergamasco B, Lopiano L (2006) Modifications of the iron-neuromelanin system in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 96:909–916
Fernandez A, de Ceballos ML, Rose S, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1996) Alterations in peptide levels in Parkinson’s disease and incidental Lewy body disease. Brain 119:823–830
Ferrer I (2009a) Early involvement of the cerebral cortex in Parkinson’s disease: convergence of multiple metabolic defects. Progr Neurobiol 88:89–103
Ferrer I (2009b) Altered mitochondria, energy metabolism, voltage-dependent anion channel, and lipid rafts converge to exhaust neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. J Bioenerg Biomembr 41:425–431
Ferrer I, Blanco R, Carmona M, Puig B, Barrachina M, Gómez C, Ambrosio S (2001) Active, phosphorylation-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK/ERK), stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAPK/JNK), and p38 kinase expression in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. J Neural Transm 108:1383–1396
Forno LS (1996) Neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:259–272
Frigerio R, Fujishiro H, Maraganore DM, Klos KJ, DelleDonne A, Heckman MG, Crook JE, Josephs KA, Parisi JE, Boeve BF, Dickson DW, Ahlskog JE (2009) Comparison of risk factor profiles in incidental Lewy body disease and Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 66:1114–1119
Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Dohmae N, Kawashima A, Masliah E, Goldberg MS, Shen J, Takio K, Iwatsubo T (2002) α-synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat Cell Biol 4:160–164
Fuxe K, Marcellino D, Genedani S, Agnati L (2007) Adenosine A(2A) receptors, dopamine D(2) receptors and their interactions in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 22:1990–2017
García-Arencibia M, García C, Fernández-Ruiz J (2009) Cannabinoids and Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 8:432–439
Gerlach M, Double KL, Youdim MB, Riederer P (2006) Potential sources of increased iron in the substantia nigra of parkinsonian patients. J Neural Transm Suppl 70:133–142
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Murray IV, Chen Q, Souza JM, Hurtig HI, Ischiropuolos H, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (2000) Oxidative damage linked to neurodegeneration by selective α-synuclein nitration in synucleinopathy lesions. Science 290:985–989
Goedert M (2001) Parkinson’s disease and other α-synucleinopathies. Clin Chem Lab Med 39:308–312
Gómez A, Ferrer I (2009) Increased oxidation of certain glycolysis and energy metabolism enzymes in the frontal cortex in Lewy body diseases. J Neurosci Res 87:1002–1013
Halliday GM, Ophof A, Broe M, Jensen PH, Kettle E, Fedorow H, Cartwright MI, Griffiths FM, Shepherd CE, Double KL (2005) Alpha-synuclein redistributes to neuromelanin lipid in the substantia nigra early in Parkinson's disease. Brain 128:2654–2664
Hashimoto M, Masliah E (1999) α-synuclein in Lewy body disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol 9:707–720
Herting B, Schulze S, Reichmann H, Haehner A, Hummel T (2008) A longitudinal study of olfactory function in patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 255:367–370
Hirsch EC (2006) Altered regulation of iron transport and storage in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 71:201–204
Hoozemans JJ, van Haastert ES, Eikelenboom P, de Vos RA, Rozemuller JM, Scheper W (2007) Activation of the unfolded protein response in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354:707–711
Hubbard PS, Esiri MM, Reading M, McShane R, Nagy Z (2007) α-synuclein pathology in the olfactory pathways of dementia patients. J Anat 211:117–124
Iranzo A, Molinuevo JL, Santamaria J, Serradell M, Marti MJ, Vallderiola F, Tolosa E (2006) Rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder as an early marker for a neurodegenerative disorder: a descriptive study. Lancet Neurol 5:572–577
Ishii A, Nonaka T, Taniguchi S, Saito T, Arai T, Mann D, Iwatsubo T, Hisanaga S, Goedert M, Hasegawa M (2007) Casein kinase 2 is the major enzyme in brain that phosphorylates Ser129 of human alpha-synuclein: implication for alpha-synucleinopathies. FEBS Lett 581:4711–4717
Iwanaga K, Wakabayashi K, Yoshimoto M, Tomita I, Satoh H, Takashima H, Satoh M, Tsujihara M, Takahashi H (1999) Lewy body-type degeneration in cardiac plexus in Parkinson’s and incidental Lewy body disease. Neurology 52:1269–1271
Jellinger KA (2004) Lewy body-related synucleinopathy in the aged human brain. J Neural Transm 111:1219–1235
Jellinger KA (2008) A critical reappraisal of current staging of Lewy-related pathology in human brain. Acta Neuropathol 116:1–16
Jellinger KA (2009) A critical evaluation of current staging of alpha-synuclein pathology in Lewy body disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:730–740
Jellinger KA (2010) Prevalence and impact of cerebrovascular lesions in Alzheimer and Lewy body diseases. Neurodegener Dis 7:112–115
Jellinger K, Mizuno Y (2003) Parkinson’s disease. In: Dickson D (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropathol Press, Bassel, pp 159–187
Jenner P (1993) Altered mitochondrial function, iron metabolism and glutathione levels in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 146:6–13
Jenner P (1998) Oxidative mechanisms in nigral cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 13:24–34
Jenner P, Dexter DT, Sian J, Schapira AH, Marsden CD (1992) Oxidative stress as a cause of nigral cell death in Parkinson’s disease and incidental Lewy body disease. The Royal Kings and Queens Parkinson’s Disease Research Group. Ann Neurol 32:S82–S87
Keeney PM, Xie J, Capaldi RA, Bennett JP (2006) Parkinson’s disease brain mitochondrial complex I has oxidatively damaged subunits and is functionally impaired and misassembled. J Neurosci 26:5256–5264
Kingsbury AE, Daniel SE, Sangha H, Eisen S, Lees AJ, Foster OJ (2004) Alteration in alpha-synuclein mRNA expression in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 19:162–170
Klionsky DJ, Abeliovich H, Agostinis P, Agrawal DK, Aliev G, Askew DS et al (2008) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy in higher eukaryotes. Autophagy 4:151–175
Koziorowski D, Friedman A, Arosio P, Santambrogio P, Dziewulska D (2007) ELISA reveals a difference in the structure of substantia nigra ferritin in Parkinson’s disease and incidental Lewy body compared to control. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 13:214–218
Kuusisto E, Parkkinen L, Alafuzoff I (2003) Morphogenesis of Lewy bodies: dissimilar incorporation of alpha-synuclein, ubiquitin, and p62. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:1241–1253
Leverenz JB, Umar I, Wang Q, Montine TJ, McMillan PJ, Tsuang DW, Jin J, Pan C, Shin J, Zhu D, Zhang J (2007) Proteomic identification of novel proteins in cortical Lewy bodies. Brain Pathol 17:139–145
Li W, West N, Colla E, Pletnikova O, Troncoso JC, Marsh L, Dawson TM, Jakala P, Hartmann T, Price DL, Lee MK (2005) Aggregation promoting C-terminal truncation of alpha-synuclein is a normal cellular process and is enhanced by the familial Parkinson’s disease-linked mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2162–2167
Mak SK, McCormack AL, Manning-Bog AB, Cuervo AM, Di Monte DA (2010) Lysosomal degradation of α-synuclein in vivo. J Biol Chem 285:13621–13629
Markesbery WR, Jicha GA, Liu H, Schmitt FA (2009) Lewy body pathology in normal elderly subjects. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 68:816–822
Martínez A, Portero-Otin M, Pamplona R, Ferrer I (2010) Protein targets of oxidative damage in human neurodegenerative diseases with abnormal protein aggregates. Brain Pathol 20:281–297
Martínez-Vicente M, Talloczy Z, Kaushik S, Massey AC, Mazzulli J, Mosharov EV, Hodara R, Fredenburg R, Wu DC, Follenzi A, Dauer W, Przedborski S, Ischiropoulos H, Lansbury PT, Sulzer D, Cuervo AM (2008) Dopamine-modified alpha-synuclein blocks chaperone-mediated autophagy. J Clin Invest 118:777–788
Matsuda S, Okano M, Yamagishi K, Nagao M, Ueda M, Sasaki R (1994) A novel site of erythropoietin production. Oxygen-dependent production in cultured rat astrocytes. J Biol Chem 269:19488–19493
McKinlay A, Grace RC, Dalrymple-Alford JC, Roger D (2009) Cognitive characteristics associated with mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 28:121–129
Mizuno Y, Ohta S, Tanaka M, Takamiya S, Suzuki K, Sato T, Oya H, Ozawa T, Kagawa Y (1989) Deficiencies in complex I subunits of the respiratory chain in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163:1450–1455
Muntané G, Ferrer I, Martínez-Vicente M α-Synuclein phosphorylation and lysosomal-mediated α-synuclein truncation are normal events in the adult human brain (in preparation)
Muntané G, Dalfó E, Martinez A, Ferrer I (2008) Phosphorylation of tau and alpha-synuclein in synaptic-enriched fractions of the frontal cortex in Alzheimer’s disease, and in Parkinson’s disease and related α-synucleinopathies. Neuroscience 152:913–923
Murray IV, Giasson BI, Quinn SM, Koppaka V, Axelsen PH, Ischiropoulos H, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2003) Role of alpha-synuclein carboxy-terminus on fibril formation in vitro. Biochemistry 42:8530–8540
Nakaso K, Yoshimoto Y, Nakano T, Takeshima T, Fukuhara Y, Yasui K, Araga S, Yanagawa T, Ishii T, Nakashima K (2004) Transcriptional activation of p62/A170/ZIP during the formation of the aggregates: possible mechanisms and the role in Lewy body formation in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1012:42–51
Natale G, Pasquali L, Riuggieri S, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2008) Parkinson’s disease and the gut: a well known clinical association in need of an effective cure and explanation. Neurogastroenterol Motil 20:741–749
Navarro A, Boveris A, Bández MJ, Sánchez-Pino MJ, Gómez C, Muntané G, Ferrer I (2009) Human brain cortex: mitochondrial oxidative damage and adaptive response in Parkinson disease and in dementia with Lewy bodies. Free Radic Biol Med 46:1574–1580
Oakley AE, Collingwood JF, Dobson J, Love G, Perrott HR, Edwardson JA, Elstner M, Morris CM (2007) Individual dopaminergic neurons show raised iron levels in Parkinson disease. Neurology 68:1820–1825
Olanow CW, McNaught KS (2006) Ubiquitin-proteasome system and Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 21:1806–1823
Onyango IG (2008) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Res 33:589–597
Pan T, Kondo S, Le W, Jankovic J (2008) The role of autophagy-lysosome pathway in neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131:1969–1978
Parker WD, Boyson SJ, Parks JK (1989) Abnormalities of the electron transport chain in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 26:719–723
Parkkinen L, Kauppinen T, Pirttilä T, Autere JM, Alafuzoff I (2005) α-Synuclein pathology does not predict extrapyramidal symptoms or dementia. Ann Neurol 57:82–91
Parkkinen L, Pirttilä T, Alafuzoff I (2008) Applicability of current staging/categorization of α-synuclein pathology and their clinical relevance. Acta Neuropathol 115:399–407
Pearce RK, Hawkes CH, Daniel SE (1995) The anterior olfactory nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 10:283–287
Pedersen KF, Alves G, Aarsland D, Larsen JP (2009) Occurrence and risk factors for apathy in Parkinson disease: a 4-year prospective longitudinal study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80:1279–1782
Poewe W (2007) Dysautonomia and cognitive dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord Suppl 17:S374–S378
Poewe W (2008) Non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurol 15(Suppl 1):14–20
Postuma RB, Lang AE, Massicotte-Marquez J, Montplaisir J (2006) Potential early markers of Parkinson disease in idiopathic REM sleep behavioral disorder. Neurology 66:845–851
Richter F, Meurers BH, Zhu C, Medvedeva VP (2009) Neurons express haemoglobin α- and β-chains in rat and human brains. J Comp Neurol 515:538–547
Rockenstein E, Hansen LA, Mallory M, Trojanowski JQ, Galasko D, Masliah E (2001) Altered expression of the synuclein family mRNA in Lewy body and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 914:48–56
Ross GW, Petrovitch H, Abbott RD, Tanner CM, Popper J, Masaki K, Launer L, White LR (2008) Association of olfactory dysfunction with risk for future Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 63:167–173
Ryu MY, Kim DW, Arima K, Mouradian MM, Kim SU, Lee G (2008) Localization of CKII beta subunits in Lewy bodies of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 266:9–12
Saito Y, Ruberu NN, Sawabe M, Arai T, Kazama H, Hosoi T, Yamanouchi H, Murayama S (2004) Lewy body-related α-synucleinopathy in aging. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:742–749
Salazar J, Mena N, Núñez MT (2006) Iron dyshomeostasis in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 71:205–213
Schapira AH (2008) Mitochondria in the aetiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 7:97–109
Schults CW (2006) Lewy bodies. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 103:1661–1668
Shamoto-Nagai M, Maruyama W, Hashizume Y, Yoshida M, Osawa T, Riederer P, Naoi M (2007) In parkinsonian substantia nigra, α-synuclein is modified by acrolein, a lipid-peroxidation product, and accumulates in the dopamine neurons with inhibition of the proteasome activity. J Neural Transm 114:1559–1567
Siderowf A, Stern MB (2008) Premotor Parkinson’s disease: clinical features, detection, and prospects for treatment. Ann Neurol 64(Suppl 2):S139–S147
Solano SM, Miller DW, Augood SJ, Young AB, Penney JB Jr (2000) Expression of alpha-synuclein, parkin, and ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 mRNA in human brain: genes associated with familial Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 47:201–210
Spillantini MG, Schmidt M, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Kaques R, Goedert M (1997) α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840
Srivastava G, Singh K, Tiwari MN, Singh MP (2010) Proteomics in Parkinson’s disease: current trends, translational snags and future possibilities. Expert Rev Proteomics 7:127–139
Stefanis L, Larsen KE, Rideout HJ, Sulzer D, Greene LA (2001) Expression of A53T mutant but not wild-type alpha-synuclein in PC12 cells induces alterations of the ubiquitin-dependent degradation system, loss of dopamine release, and autophagic cell death. J Neurosci 21:9549–9560
Stiasny-Kolster K, Doerr Y, Möller JC, Höffken H, Behr TM, Oertel WH, Mayer G (2005) Combination of idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder and olfactory dysfunction as possible indicator for alpha-synucleinopathy demonstrated by dopamine transporter FP-CIT-SPECT. Brain 128:126–137
Tang CC, Poston KL, Dhawan V, Eidelberg D (2010) Abnormalities in metabolic network activity precede the onset of motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 30:1049–1056
Tolosa E, Compta Y, Gaig C (2007) The premotor phase of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Rel Disord 13:S2–S7
Tribl F, Marcus K, Meyer HE, Bringmann G, Gerlach M, Riederer P (2006) Subcellular proteomics reveals neuromelanin granules to be a lysosome-related organelle. J Neural Transm 113:741–749
Tribl F, Asan E, Arzberger T, Tatschner T, Langenfeld E, Meyer HE, Bringmann G, Riederer P, Gerlach M, Marcus K (2009) Identification of L-ferritin in neuromelanin granules of the human substantia nigra: a targeted proteomics approach. Mol Cell Proteomics 8:1832–1838
Varani K, Vincenzi F, Tosi A, Gessi S, Casetta I, Granieri G, Fazio P, Leung E, MacLennan S, Granieri E, Borea PA (2010) A2A adenosine receptor overexpression and functionality, as well as TNF-alpha levels, correlate with motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J 24:587–598
Vogiatzi T, Xilouri M, Vekrellis K, Stefanis L (2008) Wild type α-synuclein is degraded by chaperone-mediated autophagy and macroautophagy in neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 283:23542–23556
Wakabayashi K, Matsumoto K, Takayama K, Yoshimoto M, Takahashi H (1997) NACP, a presynaptic protein, immunoreactivity in Lewy bodies in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 249:180–182
Wakabayashi K, Tanji K, Mori F, Takahashi H (2007) The Lewy body in Parkinson’s disease: molecules implicated in the formation and degradation of α-synuclein aggregates. Neuropathology 27:494–506
Wang HQ, Takahashi R (2007) Expanding insights on the involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress in Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 9:553–561
Wang R, Qing H, Liu XQ, Zheng XL, Deng YL (2008) Iron contributes to the formation of catechol isoquinolines and oxidative toxicity induced by overdose dopamine in dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci Bull 24:125–132
Waxman EA, Giasson BI (2008) Specificity and regulation of casein kinase-mediated phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:402–416
Weisman D, Cho M, Taylor C, Adame A, Thal LJ, Hansen LA (2007) In dementia with Lewy bodies, Braak stage determines phenotype, not Lewy body distribution. Neurology 69:356–359
Wirdefeldt K, Bogdanovic N, Westerberg L, Payami H, Schalling M, Murdoch G (2001) Expression of alpha-synuclein in the human brain: relation to Lewy body disease. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 92:58–65
Wypijewska A, Galazka-Friedman J, Bauminger ER, Wszolek ZK, Schweitzer KJ, Dickson DW, Jaklewicz A, Elbaum D, Friedman A (2010) Iron and reactive oxygen species activity in parkinsonian substantia nigra. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 16:329–333
Xia Q, Liao L, Cheng D, Duong DM, Gearing M, Lah JJ, Levey AI, Peng J (2008) Proteomic identification of novel proteins associated with Lewy bodies. Front Biosci 13:3850–3856
Xilouri M, Vogiatzi T, Vekrellis K, Stefanis L (2008) alpha-synuclein degradation by autophagic pathways: a potential key to Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Autophagy 4:917–919
Youdim MB (2008) Brain iron deficiency and excess; cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration with involvement of striatum and hippocampus. Neurotox Res 14:45–56
Zecca L, Lucca FA, Albertini A, Rizzio E, Fariello RG (2006) A proposed dual role of neuromelanin in the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease. Neurology 67(Suppl 2):S8–S11
Zecca L, Casella L, Albertini A, Bellei C, Zucca FA, Engelen M, Zadlo A, Szewczyk G, Zareba M, Sarna T (2008) Neuromelanin can protect against iron-mediated oxidative damage in system modeling iron overload of brain aging and Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 106:1866–1875
Zeevalk GD, Razmpour R, Bernard LP (2008) Glutathione and Parkinson’s disease: is this the elephant in the room? Biomed Pharmacother 62:236–249
Ziemssen T, Reichmann H (2007) Non-motor dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Rel Disord 13:323–332
Acknowledgments
Work carried out in the Institute of Neuropathology was partially funded by grants from the Spanish Ministry of Health, Instituto de Salud Carlos III PI05/1570, PI05/2214 and PI08/0582, and supported by the European Commission: BrainNet Europe II, LSHM-CT-2004-503039 and INDABIP FP6-2005-LIFESCIHEALTH-7 Molecular Diagnostics. Thanks to T. Yohannan for editorial help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrer, I., Martinez, A., Blanco, R. et al. Neuropathology of sporadic Parkinson disease before the appearance of parkinsonism: preclinical Parkinson disease. J Neural Transm 118, 821–839 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-010-0482-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-010-0482-8