Abstract
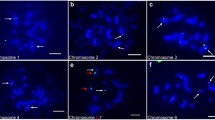
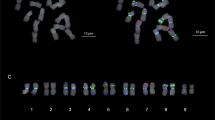
Non-heading Chinese cabbage [Brassica rapa L. ssp. chinensis (L.) Hanelt] is one of the most popular leafy vegetables. Despite the economic importance of non-heading Chinese cabbage, little attention has been given to its cytogenetic profile. This study reveals the karyotype of non-heading Chinese cabbage. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with 45S and 5S rDNA probes was performed on mitotic metaphase complementary regions. We located 45S rDNA on the centromeric or adjacent region of chromosomes A1 and A2, with the largest on the satellite of chromosome A5. Meanwhile, 5S rDNA co-localized with 45S rDNA on chromosomes A2 and A5, and on the telomeric region of chromosome A10. We performed DAPI fluorescence banding on the same metaphase chromosomes to identify homologous chromosomes. The DAPI fluorescence pattern was observed mainly on the centromeric heterochromatin regions of each chromosome. However, the lengths of chromosomes A2 and A6 were completely stained, except for their telomeric regions. Meiotic diakinesis chromosomes as new substrates in FISH-developed karyotype were revealed for the first time. The karyotype of non-heading Chinese cabbage reveals that it contains eight submetacentric chromosomes, one subtelocentric chromosome (bearing satellite), and one telocentric chromosome. Diakinetic chromosome pairing can overcome the difficulty of unlabeled chromosome identification. This study provided valuable information for cytogenetic research and molecular breeding of non-heading Chinese cabbage by using the combination of FISH and DAPI fluorescence patterns on mitotic and meiotic chromosomes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- rDNA (RNA):
-
Ribosomal DNA (RNA)
- BDB:
-
Blenched DAPI band
- NOR:
-
Nucleolus organizing region
- M:
-
Metacentric
- SM:
-
Submetacentric
- ST:
-
Subtelocentric
- T:
-
Telocentric
References
Abd El-Twab MH, Kondo K (2012) Physical mapping of 5S and 45S rDNA in Chrysanthemum and related genera of the Anthemideae by FISH, and species relationships. J Genet 91:245–249
Ali HBM, Lysak MA, Schubert I (2005) Chromosomal localization of rDNA in the Brassicaceae. Genome 48:341–346
Appels R, Gerlach WL, Dennis ES, Swift H, Peacock WJ (1980) Molecular and chromosomal organization of DNA sequences coding for the ribosomal RNAs in cereals. Chromosoma 78:293–311
Baeza C, Schrader O, Budahn H (2007) Characterization of geographically isolated accessions in five Alstroemeria L. species (Chile) using FISH of tandemly repeated DNA sequences and RAPD analysis. Plant Syst Evol 269:1–14
Cao JS, Cao SC, Song CY (1994) Studies on chromosome G-banding in 10-chromosome of Brassica. Acta Horticulturae Sinica 21(23):257–263 (in Chinese)
Eroglu HE, Simsek N, Koc M, Hamzaoglu E (2013) Karyotype analysis of some Minuartia L. (Caryophyllaceae) taxa. Plant Syst Evol 299(1):67–73
Feitoza LL, Martins MIG, Castro A, Felix LP, Carvalho R (2010) Cytogenetics of Alismataceae and Limnocharitaceae: CMA/DAPI banding and 45S rDNA sites. Plant Syst Evol 286:199–208
Felix WJP, Felix LP, Melo NF, Dutilh JHA, Carvalho R (2011) Cytogenetics of Amaryllidaceae species: heterochromatin evolution in different ploidy levels. Plant Syst Evol 292:215–221
Fukui K, Nakayama S, Ohmido N, Yoshiaki H, Yamabe M (1998) Quantitative karyotyping of three diploid Brassica species by imaging methods and localization of 45s rDNA loci on the identified chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 96:325–330
Gladis TH, Hammer K (1992) The Gatersleben Brassica collection—Brassica juncea, B. napus, B. nigra and B. rapa (Germ., Engl. summary). Feddes Repert 103:469–507
Hasterok R, Maluszynska J (2000) Cytogenetic analysis of diploid Brassica species. Acta Biologica Cracoviensia Series Botanica 42:145–153
Hasterok R, Jenkins G, Langdon T, Jones RN, Maluszynska J (2001) Ribosomal DNA is an effective marker of Brassica chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 103:486–490
Hasterok R, Wolny E, Hosiawa M, Kowalczyk M, Kulak-Ksiazczyk S, Ksiazczyk T, Heneen WK, Maluszynska J (2006) Comparative analysis of rDNA distribution in chromosomes of various species of Brassicaceae. Ann Bot 97:205–216
Howell EC, Kearsey MJ, Jones GH, King GJ, Armstrong SJ (2008) A and C genome distinction and chromosome identification in Brassica napus by sequential fluorescence in situ hybridization and genomic in situ hybridization. Genetics 180(4):1849–1857
Kim H, Choi SR, Bae J, Hong CP, Lee SY, Hossain MJ, Van Nguyen D, Jin M, Park BS, Bang JW, Bancroft I, Lim YP (2009) Sequenced BAC anchored reference genetic map that reconciles the ten individual chromosomes of Brassica rapa. BMC Genomics 10
Koo DH, Plaha P, Lim YP, Hur Y, Bang JW (2004) A high-resolution karyotype of Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis revealed by pachytene analysis and multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 109:1346–1352
Kwon JK, Kim BD (2009) Localization of 5S and 25S rRNA genes on somatic and meiotic chromosomes in Capsicum species of chili pepper. Mol Cells 27:205–209
Lavania UC, Kushwaha JS, Lavania S, Basu S (2010) Chromosomal localization of rDNA and DAPI bands in solanaceous medicinal plant Hyoscyamus niger L. J Genet 89:493–496
Levan A, Fredga K, Sandberg AA (1964) Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes Hereditas 52(2):201–220
Lim KB, de Jong H, Yang TJ, Park JY, Kwon SJ, Kim JS, Lim MH, Kim JA, Jin M, Jin YM, Kim SH, Lim YP, Bang JW, Kim HI, Park BS (2005) Characterization of rDNAs and tandem repeats in the heterochromatin of Brassica rapa. Mol Cells 19:436–444
Lysak MA, Lexer C (2006) Towards the era of comparative evolutionary genomics in Brassicaceae. Plant Syst Evol 259:175–198
Maluszynska J, Heslopharrison JS (1993) Physical mapping of rDNA loci in Brassica species. Genome 36:774–781
Martinez J, Vargas P, Luceno M, Cuadrado A (2010) Evolution of Iris subgenus Xiphium based on chromosome numbers, FISH of nrDNA (5S, 45S) and trnL-trnF sequence analysis. Plant Syst Evol 289(3–4):223–235
Matoba H, Uchiyama H (2009) Physical mapping of 5S rDNA, 18S rDNA and telomere sequences in three species of the genus Artemisia (Asteraceae) with distinct vasic chromosome numbers. Cytologia 74:115–123
Nagaharu U (1935) Genome analysis in Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Jpn J Bot 7:389–452
Novotnά J, Havelka J, Stary P, Koutecky P, Vitkova M (2011) Karyotype analysis of the Russian wheat aphid, Diuraphis noxia (Kurdjumov) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) reveals a large X chromosome with rRNA and histone gene families. Genetica 139:281–289
Snowdon RJ (2007) Cytogenetics and genome analysis in Brassica crops. Chromosome Res 15:85–95
Snowdon RJ, Köhler W, Köhler A (1997) Chromosomal localization and characterization of rDNA loci in the Brassica A and C genomes. Genome 40:582–587
Snowdon RJ, Friedrich T, Friedt W, Kohler W (2002) Identifying the chromosomes of the A- and C-genome diploid Brassica species B. rapa (syn. campestris) and B. oleracea in their amphidiploid B. napus. Theor Appl Genet 104:533–538
Tang X, Szinay D, Lang C, Ramanna MS, van der Vossen EAG, Datema E, Lankhorst RK, de Boer J, Peters SA, Bachem C, Stiekema W, Visser RGF, de Jong H, Bai Y (2008) Cross-species bacterial artificial chromosome-fluorescence in situ hybridization painting of the tomato and potato chromosome 6 reveals undescribed chromosomal rearrangements. Genetics 180:1319–1328
Tantravahi R, Miller DA, Dev VG, Miller OJ (1976) Detection of nucleolus organizer regions in chromosomes of human, chimpanzee, gorilla, orangutan and gibbon. Chromosoma 56:15–27
Vanzela ALL, Cuadrado A, Guerra M (2003) Localization of 45S rDNA and telomeric sites on holocentric chromosomes of Rhynchospora tenuis Link (Cyperaceae). Genet Mol Biol 26(2):199–201
Viehoever A (1920) Studies in mustard seeds and substitutes: I. Chinese colza (Brassica campestris chinoleifera VIEHOEVER). J Agric Res Wash 20(2):117–140
Wang YJ, Cao SC (1988) A study on the karyotype of non-heading Chinese cabbage. J Nanjing Agric Univ 11(3):133–135 (in Chinese)
Wang K, Guo W, Yang Z, Hu Y, Zhang W, Zhou B, Stelly DM, Chen ZJ, Zhang T (2010) Structure and size variations between 12A and 12D homoeologous chromosomes based on high-resolution cytogenetic map in allotetraploid cotton. Chromosoma 119:255–266
Wang XW, Wang HZ, Wang J, Sun RF, Wu J, Liu SY, Bai YQ, Mun JH, Bancroft I, Cheng F, Huang SW, Li XX, Hua W, Wang JY, Wang XY, Freeling M, Pires JC, Paterson AH, Chalhoub B, Wang B, Hayward A, Sharpe AG, Park BS, Weisshaar B, Liu BH, Li B, Liu B, Tong CB, Song C, Duran C, Peng CF, Geng CY, Koh CS, Lin CY, Edwards D, Du DS, Shen D, Soumpourou E, Li F, Fraser F, Conant G, Lassalle G, King GJ, Bonnema G, Tang HB, Wang HP, Belcram H, Zhou HL, Hirakawa H, Abe H, Guo H, Wang H, Jin HZ, Parkin IAP, Batley J, Kim JS, Just J, Li JW, Xu JH, Deng J, Kim JA, Li JP, Yu JY, Meng JL, Wang JP, Min JM, Poulain J, Hatakeyama K, Wu K, Wang L, Fang L, Trick M, Links MG, Zhao MX, Jin MN, Ramchiary N, Drou N, Berkman PJ, Cai QL, Huang QF, Li RQ, Tabata S, Cheng SF, Zhang S, Zhang SJ, Huang SM, Sato S, Sun SL, Kwon SJ, Choi SR, Lee TH, Fan W, Zhao X, Tan X, Xu X, Wang Y, Qiu Y, Yin Y, Li YR, Du YC, Liao YC, Lim Y, Narusaka Y, Wang YP, Wang ZY, Li ZY, Wang ZW, Xiong ZY, Zhang ZH (2011) The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nature Genet 43:1035–1157
Xiong ZY, Pires JC (2011) Karyotype and identification of all homologous chromosomes of allopolyploid Brassica napus and its diploid progenitors. Genetics 187:37–49
Zhao D, Zhang SN, Zheng JS, Liu HJ, Hou XL (2011) Karyotype analysis for pollen mother cells meiosis diakinesis of Apium graveolens L. J Nanjing Agric Univ 34(1):25–28 (in Chinese)
Zheng JS, Zhang SN, Sun CZ, Wang JJ, Hou XL (2012) Karyotype analysis of diploid and autotetraploid non-heading Chinese cabbage. J Nanjing Agric Univ 35(1):131–134 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by grants from: 1. National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, No. 2012AA100101); 2. the project supported by China Agriculture Research System (CARS-25-A-12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Js., Sun, Cz., Zhang, Sn. et al. Karyotype of mitotic metaphase and meiotic diakinesis in non-heading Chinese cabbage. Plant Syst Evol 300, 295–302 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-013-0882-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-013-0882-y