Abstract
A lectin magnetic separation (LMS) method for Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) was developed with the aim to improve the efficiency of magnetic nanoparticles and to expand the scope of bacterial recognition. Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-mediated magnetic nanoparticles modified with streptavidin (MNP-PEG-SA) were synthesized and then applied to a two-step LMS based on the use of wheat germ agglutinin (WGA). Three specific methods for S. aureus detection (suitable for different requirements including detection time and sensitivity) were designed. The new LMS has improved anchoring efficiency (compared to two-step LMS methods) and requires a reduced number of magnetic particles. The Baird–Parker (B-P) method can detect S. aureus with a detection limit of 3 × 100 CFU·mL−1 within 15 h; the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method can be finished within 4 h, with the lowest detection limit (LOD) of 3 × 102 CFU·mL−1. The LOD of HRP-pig IgG-based colorimetric method is 3 × 105 CFU·mL−1, and the method only lasts for 2 h. If combined with specific detection methods, it meets different needs for rapid detection of S. aureus.

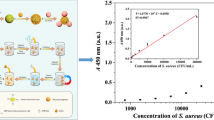
Schematic representation of lectin magnetic separation (LMS) based on biotin-wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) and poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG)-mediated streptavidin-modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNP-PEG-SA) and three different quantification strategies (including B-P culture assay, PCR assay, and colorimetric assay) for S. aureus.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen CY, Jiang YZ, Li XY, Tang M, Wu LL, Hu J, Pang DW, Zeng JB (2017) Efficient enrichment and analyses of bacteria at ultralow concentration with quick-response magnetic nanospheres. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(11):9416–9425
Olsvik O, Popovic T, Skjerve E, Cudjoe KS, Hornes E, Ugelstad J, Uhlén M (1994) Magnetic separation techniques in diagnostic microbiology. Clin Microbiol Rev 7(1):43–54
Mao Y, Huang X, Xiong S, Xu H, Aguilar ZP, Xiong Y (2016) Large-volume immunomagnetic separation combined with multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria ivanovii in lettuce. Food Control 59:601–608
Bu S, Wang K, Ju C, Han Y, Li Z, Du P, Hao Z, Li C, Liu W, Wan J (2018) A pregnancy test strip for detection of pathogenic bacteria by using concanavalin A-human chorionic gonadotropin-Cu3(PO4)2 hybrid nanoflowers, magnetic separation, and smartphone readout. Microchim Acta 185(10):464
Sun C, Hsieh YP, Ma S, Geng S, Cao Z, Li L, Lu C (2017) Immunomagnetic separation of tumor initiating cells by screening two surface markers. Sci Rep 7:40632
Brandão D, Liébana S, Campoy S, Alegret S, Pividori MI (2015) Immunomagnetic separation of Salmonella with tailored magnetic micro and nanocarriers. A comparative study. Talanta 143:198–204
Luo D, Huang X, Mao Y, Chen C, Li F, Xu H, Xiong Y (2017) Two-step large-volume magnetic separation combined with PCR assay for sensitive detection of Listeria monocytogenes in pasteurized milk. J Dairy Sci 100(10):7883–7890
Li F, Li F, Luo D, Lai W, Xiong Y, Xu H (2018) Biotin-exposure-based immunomagnetic separation coupled with nucleic acid lateral flow biosensor for visibly detecting viable Listeria monocytogenes. Anal Chim Acta 1017:48–56
Li F, Li F, Aguilar ZP, Xiong Y, Xu H (2018) Polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimer-mediated biotin amplified immunomagnetic separation method coupled with flow cytometry for viable Listeria monocytogenes detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 257:286–294
Shahdordizadeh M, Taghdisi SM, Ansari N, Langroodi FA, Abnous K, Ramezani M (2017) Aptamer based biosensors for detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Sensors Actuators B Chem 241:619–635
Meng X, Yang G, Li F, Liang T, Lai W, Xu H (2017) Sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus with vancomycin-conjugated magnetic beads as enrichment carriers combined with flow cytometry. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(25):21464–21472
Chen X, Tang M, Liu Y, Huang J, Liu Z, Tian H, Zheng Y, Lamy de la Chapelle M, Zhang Y, Fu W (2019) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering method for the identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using positively charged silver nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186(2):102
Suaifan GARY, Alhogail S, Zourob M (2017) Rapid and low-cost biosensor for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens Bioelectron 90:230–237
Qing T, Long C, Wang X, Zhang K, Zhang P, Feng BV (2019) Detection of micrococcal nuclease for identifying Staphylococcus aureus based on DNA templated fluorescent copper nanoclusters. Microchim Acta 186(4):248
Tallent SM, Sheehan JF (2018) Mitigation strategies to combat Staphylococcus aureus in the food chain: international food standards, guidelines, and codes of practice. Staphylococcus aureus 257-292
Gill AAS, Singh S, Thapliyal N, Karpoormath R (2019) Nanomaterial-based optical and electrochemical techniques for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a review. Microchim Acta 186(2):114
Neumann D, Kohlbacher O, Lenhof HP, Lehr CM (2002) Lectin–sugar interaction. Eur J Biochem 269(5):1518–1524
Mikaelyan MV, Poghosyan GG, Hendrickson OD, Dzantiev BB, Gasparyan VK (2017) Wheat germ agglutinin and Lens culinaris agglutinin sensitized anisotropic silver nanoparticles in detection of bacteria: a simple photometric assay. Anal Chim Acta 981:80–85
Yang G, Meng X, Wang Y, Yan M, Aguilar ZP, Xu H (2019) 2-step lectin-magnetic separation (LMS) strategy combined with AuNPs-based colorimetric system for S. aureus detection in blood. Sensors Actuators B Chem 279:87–94
Aycicek H, Cakiroglu S, Stevenson TH (2005) Incidence of Staphylococcus aureus in ready-to-eat meals from military cafeterias in Ankara, Turkey. Food Control 16(6):531–534
Meng X, Li F, Li F, Xiong Y, Xu H (2017) Vancomycin modified PEGylated-magnetic nanoparticles combined with PCR for efficient enrichment and detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Sensors Actuators B Chem 247:546–555
Dirk N, Claus-Michael L, Hans-Peter L, Oliver K (2004) Computational modeling of the sugar-lectin interaction. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 56(4):437–457
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No.: 2018YFC1602500), Research Foundation from State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology, Nanchang University, China (No.: SKLF-ZZB-201720), and Educational Commission of Jiangxi Province, China (No.: GJJ150014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1004 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, G., Huang, M., Wang, Y. et al. Streptavidin-exposed magnetic nanoparticles for lectin magnetic separation (LMS) of Staphylococcus aureus prior to three quantification strategies. Microchim Acta 186, 813 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3978-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3978-4