Abstract
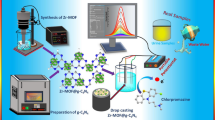
The preparation of 3 kinds of carbonaceous nanocomposites by hydrothermal treatment and subsequent calcination described. The first comprises a nanomaterial of type CuO/g-C3N4, with g-C3N4 in mass fractions of 2, 5 and 7 wt%, respectively. The second comprises CuO/porous carbon (5 wt%), and the third comprises CuO/carbon spheres (5 wt%). All of them were employed to modify a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) to obtain electrochemical sensors for glucose and dopamine. The GCE modified with CuO/g-C3N4 (5 wt%) displays the highest electrocatalytic activity towards glucose and dopamine. Figures of merit for sensing glucose (in 0.1 M NaOH solution) include a wide linear range (0.5 μM to 8.5 mM), a detection limit of 0.150 μM, and a sensitivity of 0.274 μA·μM−1·cm−2 (at a working potential of 0.60 V vs. Ag/AgCl). The respective data for dopamine (in pH 7.0 solution) are linear ranges from 0.2-16.0 μM and 16.0-78.7 μM, a lower detection limit of 60 nM, and an electrochemical sensitivity of 0.834 and 0.331 μA·μM−1·cm−2 (at a working potential of 0.22 V vs. Ag/AgCl). The good performance of the modified GCE is attributed to the synergetic interactions between CuO and the appropriate fraction of g-C3N4, and the improvement of conductivity.

Schematic presentation of a electrochemical sensor based on CuO/g-C3N4 for the determination of glucose and dopamine.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen D, Liu W, Herrmann AK, Haubold D, Holzschuh M, Simon F et al (2016) Simple and sensitive colorimetric detection of dopamine based on assembly of cyclodextrin-modified au nanoparticles. Small 12:2439–2442
Kannan P, Maiyalagan T, Marsili E, Ghosh S et al (2017) Highly active 3-dimensional cobalt oxide nanostructures on the flexible carbon substrates for enzymeless glucose sensing. Analyst 142:4299–4307
Xia YS, Ye JJ, Tan KH, Wang J, Yang G (2013) Colorimetric visualization of glucose at the submicromole level in serum by a homogenous silver nanoprism-glucose oxidase system. Anal Chem 85:6241–6247
Wang Y, Yang L, Liu Y, Zhao Q, Ding F, Zou P, Rao H, Wang X (2018) Colorimetric determination of dopamine by exploiting the enhanced oxidase mimicking activity of hierarchical NiCo2S4-rGO composites. Microchim Acta 185:496
Xu S, Chen L, Ma L (2018) Fluorometric determination of quercetin by using graphitic carbon nitride nanoparticles modified with a molecularly imprinted polymer. Microchim Acta 185:492
Krishnamoorthy K, Sudha V, Kumar SMS, Thangamuthu R (2018) Simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid using copper oxide nano-rice modified electrode. J Alloys Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.118
Fang L, Wang F, Chen Z, Qiu Y, Zhai T, Hu M, Zhang C, Huang K (2017) Flower-like MoS2 decorated with Cu2O nanoparticles for non-enzymatic amperometric sensing of glucose. Talanta 167:593–599
Yang S, Li G, Wang G, Zhao J, Gao X, Qu L (2015) Synthesis of Mn3O4 nanoparticles/nitrogen-doped graphene hybrid composite for nonenzymatic glucose sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 221:172
Reddy S, Swamy BEK, Jayadevappa H (2012) CuO nanoparticle sensor for the electrochemical determination of dopamine. Electrochim Acta 61:78–86
Dhara K, Mahapatra DR (2018) Electrochemical nonenzymatic sensing of glucose using advanced nanomaterials. Microchim Acta 185(1):49
Xu TQ, Zhang QL, Zheng JN, Lv ZY, Wei J (2014) Simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid using Pt nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide. Electrochim Acta 115:109–115
Jampaiah T, Reddy TS, Coyle VE, Nafady A, Bhargava SK (2016) Co3O4@CeO2 hybrid flower-like microspheres: a strong synergistic peroxidase-mimicking artificial enzyme with high sensitivity for glucose detection. J Mater Chem B 5:720–730
Zhang L, Gao Z, Liu C, Ren L, Tu Z, Liu R, Yang F, Zhang Y, Ye Z, Li Y, Cui L (2014) N-doped nanoporous graphene decorated three-dimensional CuO nanowire network and its application to photocatalytic degradation of dyes. RSC Adv 4:47455–47460
Ma Y, Zhao M, Cai B, Wang W, Ye Z, Huang J (2014) 3D graphene foams decorated by CuO nanoflowers for ultrasensitive ascorbic acid detection. Biosens Bioelectron 59:384–388
Li L, Hu Y, Deng D, Song H, Lv Y (2016) Highly sensitive cataluminescence gas sensors for 2-butanone based on g-C3N4 sheets decorated with CuO nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:8831–8841
Zhang H, Zhang G, Li Z, Qu K, Wang L, Zeng W, Zhang Q, Duan H (2016) Ultra-uniform CuO/cu in nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers as a stable anode for Li-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 4:10585–10592
Zhao C, Wu X, Li P, Zhao C, Qian X (2017) Hydrothermal deposition of CuO/rGO/Cu2O nanocomposite on copper foil for sensitive nonenzymatic voltammetric determination of glucose and hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 184:2341–2348
Liu B, Ouyang X, Ding Y, Luo L, Xu D, Ning Y (2016) Electrochemical preparation of nickel and copper oxides-decorated graphene composite for simultaneous determination of dopamine, acetaminophen and tryptophan. Talanta 146:114–121
Jindal K, Tomar M, Gupta V (2017) A novel low-powered uric acid biosensor based on arrayed p-n junction heterostructures of ZnO thin film and CuO microclusters. Sensors Actuators B Chem 253:566–575
Xue B, Li K, Feng L, Lu J, Zhang L (2017) Graphene wrapped porous Co3O4/NiCo2O4 double-shelled nanocages with enhanced electrocatalytic performance for glucose sensor. Electrochim Acta 239:36–44
Fang L, Xie Y, Wang Y et al (2019) Facile synthesis of hierarchical porous carbon nanorods for supercapacitors application. Appl Surf Sci 46:4479–4487
Zhao Y, Xu S, Sun X, Xu X, Gao B (2018) Unique bar-like sulfur-doped C3N4/TiO2 nanocomposite: excellent visible light driven photocatalytic activity and mechanism study. Appl Surf Sci 436:873–881
Zou J, Wu S, Liu Y, Sun Y, Cao Y, Hsu JP, Thye A, Wee S, Jiang J (2018) An ultra-sensitive electrochemical sensor based on 2D g-C3N4/CuO nanocomposites for dopamine detection. Carbon 130:652–663
Xu S, Zhu H, Cao W, Wen Z, Wang J et al (2018) Cu-Al2O3-g-C3N4 and cu-Al2O3-C-dots with dual-reaction centres for simultaneous enhancement of Fenton-like catalytic activity and selective H2O2 conversion to hydroxyl radicals. Appl Catal B-Environ 234:223-233
Shen L, Yu L, Yu XY, Zhang X, Lou XW (2015) Self-templated formation of uniform NiCo2O4 hollow spheres with complex interior structures for lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors. Angew Chem 127:1888–1892
Mao Z, Chen J, Yang Y, Wang D, Bie L, Fahlman BD (2017) Novel g-C3N4/CoO nanocomposites with significantly enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity for H evolution. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:12427–12435
Gong Y, Li M, Wang Y (2015) Carbon nitride in energy conversion and storage: recent advances and future prospects. Chem Sus Chem 8:931–946
Chen J, Liu C, Huang Y, Lee H, Feng S (2018) Study of the growth mechanisms of nanoporous ag flowers for non-enzymatic glucose detection. Microchem J. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aae363
Li Y, He X, Guo M, Lin D et al (2018) Porous NiTe2 nanosheet array: An effective electrochemical sensor for glucose detection. Sensors Actuat B:Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.07.17
He J, Jiang Y, Peng J, Li C, Yan B, Wang X (2016) Fast synthesis of hierarchical cuprous oxide for nonenzymatic glucose biosensors with enhanced sensitivity. J Mater Sci 51:9696–9704
Luan F, Zhang S, Chen D et al (2018) Ni3S2/ionic liquid-functionalized graphene as an enhanced material for the nonenzymatic detection of glucose. Microchem J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.08.046
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Ma L (2016) One-pot facile fabrication of graphene-zinc oxide composite and its enhanced sensitivity for simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sensors Actuators B Chem 227:488–496
Li B, Zhou Y, Wu W, Liu M, Mei S, Zhou Y et al (2015) Highly selective and sensitive determination of dopamine by the novel molecularly imprinted poly(nicotinamide)/CuO nanoparticles modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 67:121–128
Lian QW, Luo A, An Z, Li Z, Guo Y, Zhang D, Xue Z, Zhou X, Lu X (2015) Au nanoparticles on tryptophan-functionalized graphene for sensitive detection of dopamine. Appl Surf Sci 349:184–189
Khan MZH, Liu X, Tang Y, Zhu J, Hu W (2018) A glassy carbon electrode modified with a composite consisting of gold nanoparticle, reduced graphene oxide and poly(L-arginine) for simultaneous voltammetric determination of dopamine, serotonin and L-tryptophan. Microchim Acta 185:439
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21205030), and by key project of Hubei provincial education department (D20171001), and Hubei Key Laboratory of Ferro & Piezoelectric Materials and Devices (201710), and (111 project, B12015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 4915 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Tan, Y., Feng, C. et al. Synthesis of CuO/g-C3N4 composites, and their application to voltammetric sensing of glucose and dopamine. Microchim Acta 186, 10 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3120-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3120-z