Abstract
A nanohybrid electrode was prepared by functionalizing reduced graphene oxide nanosheets (GNs) with gold nanoparticles (AuNP), CoS2, and an ionic liquid. It is shown to enable voltammetric determination of dopamine (DA). The AuNPs were electrodeposited onto the electrode that was first modified with CoS2 and the IL-GNs to obtain a well-defined 3-dimensional and porous structure. The nanohybrid material displays high catalytic activity and an ultrasensitive cyclic voltammetric response to DA. The peak current (best measured at a working voltage of 0.17 V vs. Ag/AgCl) increases linearly in the 0.1 to 400 μM DA concentration range, with a 40 nM detection limit (at S/N = 3). The electrode was successfully applied to the determination of DA in spiked serum samples.

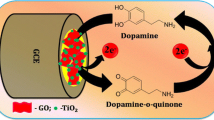
Schematic of the preparation of a nanohybrid electrode odified with graphene oxide nanosheets functionalized with gold nanoparticles/CoS2/ionic liquid by electrodeposition. The electrode exhibits excellent electrocatalytic performance with respect to the electrochemical detection of dopamine. The determination of the DPV curves provides satisfactory results which can be characterized by a linear response for DA concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 400.0 μM with a 40 nM detection limit (at S/N = 3).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hammami A, Sahli R, Raouafi N (2016) Indirect amperometric sensing of dopamine using a redox-switchable naphthoquinone-terminated self-assembled monolayer on gold electrode. Microchim Acta 183:1137–1144
Hsieh YS, Hong BD, Lee CL (2016) Non-enzymatic sensing of dopamine using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of palladium nanocubes supported on reduced graphene oxide in a nafion matrix. Microchim Acta 183:905–910
Taleb M, Ivanov R, Bereznev S, Kazemi SH, Hussainova I (2017) Ultra-sensitive voltammetric simultaneous determination of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid based on a graphene-coated alumina electrode. Microchim Acta 184:4603–4610
Cudjoe E, Pawliszyn J (2014) Optimization of solid phase microextraction coatings for liquid chromatography mass spectrometry determination of neurotransmitters. J Chromatogr A 1341:1–7
Musshoff F, Schmidt P, Dettmeyer R, Priemer F, Jachau K, Madea B (2000) Determination of dopamine and dopamine-derived (R)−/(S)-salsolinol and norsalsolinol in various human brain areas using solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci Int 113:359–366
Qian T, Yu C, Zhou X, Ma P, Wu S, Shen LX (2014) Ultrasensitive dopamine sensor based on novel molecularly imprinted polypyrrole coated carbon nanotubes. Biosens Bioelectron 58:237–241
Schumacher F, Chakraborty S, Kleuser B, Gulbins E, Schwerdtle T, Aschner M, Bornhorst J (2015) Highly sensitive isotope-dilution liquid-chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem-mass spectrometry approach to study the drug-mediated modulation of dopamine and serotonin levels in Caenorhabditis elegans. Talanta 144:71–79
Pozo MD, Mejías J, Hernández P, Quintana C (2014) Cucurbit uril-based electrochemical sensors as detectors in flow injection analysis. Application to dopamine determination in serum samples. Sensors Actuators B Chem 193:62–69
Wu HP, Cheng TL, Tseng WL (2007) Phosphate-modified TiO2 nanoparticles for selective detection of dopamine, levodopa, adrenaline, and catechol based on fluorescence quenching. Langmuir 23:7880–7885
Numan A, Shahid MM, Omar FS, Ramesh K, Ramesh S (2017) Facile fabrication of cobalt oxide nanograin-decorated reduced graphene oxide composite as ultrasensitive platform for dopamine detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 238:1043–1051
Li Y, Gu Y, Zheng B, Luo L, Li C, Yan X, Zhang T, Lu N, Zhang Z (2017) A novel electrochemical biomimetic sensor based on poly(Cu-AMT) with reduced graphene oxide for ultrasensitive detection of dopamine. Talanta 162:80–89
Hawley MD, Tatawawadi SV, Adams SPN (1967) Electrochemical studies of the oxidation pathways of catecholamines. J Am Chem Soc 89:447–450
Yusoff N, Pandikumar A, Ramaraj R, Ngee LH, Huang NM (2015) Gold nanoparticle based optical and electrochemical sensing of dopamine. Microchim Acta 182:2091–2114
Liu J, Xie Y, Wang K, Zeng Q, Liu R, Liu X (2017) A nanocomposite consisting of carbon nanotubes and gold nanoparticles in an amphiphilic copolymer for voltammetric determination of dopamine, paracetamol and uric acid. Microchim Acta 184:1739–1745
Zachek MK, Hermans A, Wightman RM, McCarty GS (2008) Electrochemical dopamine detection: comparing gold and carbon fiber microelectrodes using background subtracted fast scan cyclic voltammetry. J Electroanal Chem 614:113–120
Zhang MR, Chen XQ, Pan GB (2017) Electrosynthesis of gold nanoparticles/porous GaN electrode for non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 240:142–147
Numan A, Shahid MM, Omar FS, Rafique S, Bashir S, Ramesh K, Ramesh S (2017) Binary nanocomposite based on Co3O4 nanocubes and multiwalled carbon nanotubes as an ultrasensitive platform for amperometric determination of dopamine. Microchim Acta 184:2739–2748
Zhang H, Li Y, Zhang G, Wan P, Xu T, Wu X, Sun X (2014) Highly crystallized cubic cattierite CoS2 for electrochemically hydrogen evolution over wide pH range from 0 to 14. Electrochim Acta 148:170–174
Faber MS, Dziedzic R, Lukowski MA, Kaiser NS, Ding Q, Jin S (2014) High-performance electrocatalysis using metallic cobalt pyrite (CoS2) micro- and nanostructures. J Am Chem Soc 136:10053–10061
Xing Z, Wang L, Yang X (2016) Cobalt disulfide nanowires as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for DNA detection. J Mater Chem B 4:2860–2863
Lu L, Guo L, Kang T, Cheng S (2017) A gold electrode modified with a three-dimensional graphene-DNA composite for sensitive voltammetric determination of dopamine. Microchim Acta 184:2949–2957
Song H, Xue G, Zhang J, Wang G, Ye BC, Sun S, Li Y (2017) Simultaneous voltammetric determination of dopamine and uric acid using carbon-encapsulated hollow Fe3O4 nanoparticles anchored to an electrode modified with nanosheets of reduced graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 184:843–853
Yang G, Zhao F, Zeng B (2014) Facile fabrication of a novel anisotropic gold nanoparticle-chitosan-ionic liquid/graphene modified electrode for the determination of theophylline and caffeine. Talanta 127:116–127
Zhuang XM, Wang HH, He T, Chen LX (2016) Enhanced voltammetric determination of dopamine using a glassy carbon electrode modified with ionic liquid-functionalized graphene and carbon dots. Microchim Acta 183:3177–3182
Kumar MK, Prataap RV, Mohan S, Jha SK (2016) Preparation of electro-reduced graphene oxide supported walnut shape nickel nanostructures, and their application to selective detection of dopamine. Microchim Acta 183:1759–1768
Qiu B, Zhao X, Xia D (2013) In situ synthesis of CoS2/RGO nanocomposites with enhanced electrode performance for lithium-ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 579:372–376
Lian J, Duan X, Ma J, Peng P, Kim T, Zheng W (2009) Hematite (α-Fe2O3) with various morphologies: ionic liquid-assisted synthesis, formation mechanism, and properties. ACS Nano 3:3749–3761
Chakraborty I, Malik PK, Moulik SP (2006) Preparation and characterisation of CoS2 nanomaterial in aqueous cationic surfactant medium of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). J Nanopart Res 8:889–897
Guo S, Wen D, Zhai Y, Dong S, Wang E (2011) Ionic liquid-graphene hybrid nanosheets as an enhanced material for electrochemical determination of trinitrotoluene. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3475–3481
Thanh TD, Balamurugan J, Lee SH, Kim NH, Lee JH (2016) Effective seed-assisted synthesis of gold nanoparticles anchored nitrogen-doped graphene for electrochemical detection of glucose and dopamine. Biosens Bioelectron 81:259–267
Laviron E (1979) General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial 101:19–28
Shu H, Cao L, Chang G, He H, Zhang Y, He Y (2014) Direct electrodeposition of gold nanostructures onto glassy carbon electrodes for non-enzymatic detection of glucose. Electrochim Acta 132:524–532
Wang Y, Li Y, Tang L, Lu J, Li J (2009) Application of graphene-modified electrode for selective detection of dopamine. Electrochem Commun 11:889–892
Li SJ, He JZ, Zhang MJ, Zhang RX, Lv XL, Li SH, Pang H (2013) Electrochemical detection of dopamine using water-soluble sulfonated grapheme. Electrochim Acta 102:58–65
Tong Y, Li Z, Lu X, Yang L, Sun W, Nie G, Wang Z, Wang C (2013) Electrochemical determination of dopamine based on electrospun CeO2/Au composite nanofibers. Electrochim Acta 95:12–17
Ahn M, Kim J (2012) Electrochemical behavior of dopamine and ascorbic acid at dendritic Au rod surfaces: selective detection of dopamine in the presence of high concentration of ascorbic acid. J Electroanal Chem 683:75–79
Ali A, Jamal R, Abdiryim T, Huang X (2017) Synthesis of monodispersed PEDOT/Au hollow nanospheres and its application for electrochemical determination of dopamine and uric acid. J Electroanal Chem 787:110–117
Xing L, Ma Z (2016) A glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of MoS2 and reduced graphene oxide for electrochemical simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Microchim Acta 183:257–263
Rao D, Zhang X, Sheng Q, Zheng J (2016) Highly improved sensing of dopamine by using glassy carbon electrode modified with MnO2, graphene oxide, carbon nanotubes and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 183:2597–2604
Mei LP, Feng JJ, Wu L, Chen JR, Shen L, Xie Y, Wang AJ (2016) A glassy carbon electrode modified with porous Cu2O nanospheres on reduced graphene oxide support for simultaneous sensing of uric acid and dopamine with high selectivity over ascorbic acid. Microchim Acta 183:2039–2046
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21778047, 21675138, 21575159).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2418 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuang, X., Chen, D., Zhang, S. et al. Reduced graphene oxide functionalized with a CoS2/ionic liquid composite and decorated with gold nanoparticles for voltammetric sensing of dopamine. Microchim Acta 185, 166 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2712-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2712-y