Abstract
A highly sensitive electrochemical scheme for the detection of the cancer biomarker carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is reported. An aptamer-based formation of redox-active molybdophosphate is combined with rolling circle amplification (RCA). Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were utilized as supporting matrix for the aptamer and the primer to increase the primer/aptamer loading. The formation of a sandwich structure of anti-CEA/CEA/AuNP − aptamer-primer onto a glassy carbon electrode surface enabled an effective RCA reaction. Square wave voltammetry was applied to record the current signal at a peak potential of 0.18 V vs. Ag/AgCl. Compared to the immunosensor without RCA, the sensitivity of the immunosensor with RCA is increased by about a factor of 6. In the latter case, a wider linear range was obtained for the determination of CEA (from 0.5 pg mL−1 to 1 ng mL−1) with a detection limit as low as 0.1 pg mL−1. The practical applicability of the method was studied by analyzing CEA in human serum samples. The results were found to be in good agreement with those obtained by a reference method. Conceivably, the method can be applied to other DNA amplifications and therefore has the potential of finding wide applications.

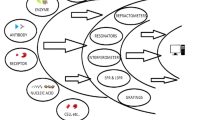
Schematic of an electrochemical aptamer based method for the detection of the cancer biomarker carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). An aptamer generated electrochemical current technique is coupled to rolling circle amplification (RCA).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gotrik MR, Feagin TA, Csordas AT, Nakamoto MA, Soh HT (2016) Advancements in Aptamer discovery technologies. Acc Chem Res 49(9):1903–1910
Kim YS, Raston NHA, Gu MB (2016) Aptamer-based nanobiosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 76:2–19
Guo Q, Li X, Shen C, Zhang S, Qi H, Li T, Yang M (2015) Electrochemical immunoassay for the protein biomarker mucin 1 and for MCF-7 cancer cells based on signal enhancement by silver nanoclusters. Microchim Acta 182(7–8):1483–1489
Quan H, Zuo C, Li T, Liu Y, Li M, Zhong M, Zhang Y, Qi H, Yang M (2015) Electrochemical detection of carcinoembryonic antigen based on silver nanocluster/horseradish peroxidase nanocomposite as signal probe. Electrochim Acta 176:893–897
Jin H, Gui R, Gong J, Huang W (2017) Aptamer and 5-fluorouracil dual-loading Ag2S quantum dots used as a sensitive label-free probe for near-infrared photoluminescence turn-on detection of CA125 antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 92:378–384
Zhang X, Zhang R, Yang A, Wang Q, Kong R, Qu F (2017) Aptamer based photoelectrochemical determination of tetracycline using a spindle-like ZnO-CdS@au nanocomposite. Microchim Acta. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2477-8
Kong R, Zhang X, Ding L, Yang D, Qu F (2017) Label-free fluorescence turn-on aptasensor for prostate-specific antigen sensing based on aggregation-induced emission–silica nanospheres. Anal Bioanal Chem 409:5757–5765
Dhiman A, Kalra P, Bansal V, Bruno JG, Sharma TK (2017) Aptamer-based point-of-care diagnostic platforms. Sensors Actuators B Chem 246:535–553
Lee J, Icoz K, Roberts A, Ellington AD, Savran CA (2010) Diffractometric detection of proteins using microbead-based rolling circle amplification. Anal Chem 82(1):197–202
Mohsen MG, Kool ET (2016) The discovery of rolling circle amplification and rolling circle transcription. Acc Chem Res 49(11):2540–2550
Tang Y, Zhang X-L, Tang L-J, Yu R-Q, Jiang J-H (2017) In situ imaging of individual mRNA mutation in single cells using ligation-mediated branched hybridization chain reaction (LigationbHCR). Anal Chem 89(6):3445–3451
Zhang S, Wang K, Li K-B, Shi W, Jia W-P, Chen X, Sun T, Han D-M (2017) A DNA-stabilized silver nanoclusters/graphene oxide-based platform for the sensitive detection of DNA through hybridization chain reaction. Biosens Bioelectron 91:374–379
Cao L, Cui X, Hu J, Li Z, Choi JR, Yang Q, Lin M, Ying H, Xu F (2017) Advances in digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) and its emerging biomedical applications. Biosens Bioelectron 90:459–474
Ali MM, Li F, Zhang Z, Zhang K, Kang D-K, Ankrum JA, Le XC, Zhao W (2014) Rolling circle amplification: a versatile tool for chemical biology, materials science and medicine. Chem Soc Rev 43(10):3324–3341
Huang J, Li X-Y, Du Y-C, Zhang L-N, Liu K-K, Zhu L-N, Kong D-M (2017) Sensitive fluorescent detection of DNA methyltransferase using nicking endonuclease-mediated multiple primers-like rolling circle amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 91:417–423
Teng J, Ye Y, Yao L, Yan C, Cheng K, Xue F, Pan D, Li B, Chen W (2017) Rolling circle amplification based amperometric aptamer/immuno hybrid biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus. Microchim Acta 184:3477–3485
Cheng X, Yu X, Chen L, ZHang H, Wu Y, Fu F (2017) Visual detection of ultra-trace levels of uranyl ions using magnetic bead-based DNAzyme recognition in combination with rolling circle amplification. Microchim Acta. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2472-0
Gu H, Hao L, Duan N, Wu S, Xia Y, Ma X, Wang Z (2017) A competitive fluorescent aptasensor for okadaic acid detection assisted by rolling circle amplification. Microchim Acta 184(8):2893–2899
Li X, Xu X, Song J, Xue Q, Li C, Jiang W (2017) Sensitive detection of T4 polynucleotide kinase activity based on multifunctional magnetic probes and polymerization nicking reactions mediated hyperbranched rolling circle amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 91:631–636
Shi H, Mao X, Chen X, Wang Z, Wang K, Zhu X (2017) The analysis of proteins and small molecules based on sterically tunable nucleic acid hyperbranched rolling circle amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 91:136–142
He Y, Yang X, Yuan R, Chai Y (2017) "off" to "on" surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy platform with padlock probe-based exponential rolling circle amplification for ultrasensitive detection of MicroRNA 155. Anal Chem 89(5):2866–2872
Li H, Xu J, Wang Z, Wu Z-S, Jia L (2016) Increasingly branched rolling circle amplification for the cancer gene detection. Biosens Bioelectron 86:1067–1073
Yang J, Tang M, Wei D, Cheng W, Zhang Y, Yan Y (2016) Electrochemical strategy for ultrasensitive detection of microRNA based on MNAzyme-mediated rolling circle amplification on a gold electrode. Microchim Acta 183:3061–3067
Shen B, Li J, Cheng W, Yan R, Tang R, Li Y, Ju H, Ding S (2015) Electrochemical aptasensor for highly sensitive determination of cocaine using a supramolecular aptamer and rolling circle amplification. Microchim Acta 182:361–367
Xu Z, Yin H, Tian Z, Zhou Y, Ai S (2014) Electrochemical immunoassays for the detection the activity of DNA methyltransferase by using the rolling circle amplification technique. Microchim Acta 181:471–477
Zhu Y, Wang H, Wang L, Zhu J, Jiang W (2016) Cascade signal amplification based on copper nanoparticle-reported rolling circle amplification for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of the prostate cancer biomarker. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(4):2573–2581
Qiu Z, Shu J, He Y, Lin Z, Zhang K, Lv S, Tang D (2017) CdTe/CdSe quantum dot-based fluorescent aptasensor with hemin/G-quadruplex DNzyme for sensitive detection of lysozyme using rolling circle amplification and strand hybridization. Biosens Bioelectron 87:18–24
Hu L, Hu S, Guo L, Shen C, Yang M, Rasooly A (2017) DNA generated electric current biosensor. Anal Chem 89(4):2547–2552
Si Z, Xie B, Chen Z, Tang C, Li T, Yang M (2017) Electrochemical aptasensor for the cancer biomarker CEA based on aptamer induced current due to formation of molybdophosphate. Microchim Acta 184(9):3215–3221
Qiu Z, Shu J, Tang D (2017) Bioresponsive release system for visual fluorescence detection of carcinoembryonic antigen from mesoporous silica nanocontainers mediated optical color on quantum dot-enzyme-impregnated paper. Anal Chem 89:5152–5160
Shen C, Li X, Rasooly A, Guo L, Zhang K, Yang M (2016) A single electrochemical biosensor for detecting the activity and inhibition of both protein kinase and alkaline phosphatase based on phosphate ions induced deposition of redox precipitates. Biosens Bioelectron 85:220–225
Shu J, Qiu Z, Lin Z, Cai G, Yang H, Tang D (2016) Semiautomated support photoelectrochemical immunosensing platform for portable and high-throughput immunoassay based on au nanocrystal decorated specific crystal facets BiVO4 photoanode. Anal Chem 88:12539–12546
Shu J, Qiu Z, Zhou Q, Lin Y, Lu M, Tang D (2016) Enzymatic Oxydate-triggered self-illuminated Photoelectrochemical sensing platform for portable immunoassay using digital multimeter. Anal Chem 88:2958–2966
Cheng W, Yan F, Ding L, Ju H, Yin Y (2010) Cascade signal amplification strategy for subattomolar protein detection by rolling circle amplification and quantum dots tagging. Anal Chem 82(8):3337–3342
Xie S, Yuan Y, Chai Y, Yuan R (2015) Tracing phosphate ions generated during loop-mediated isothermal amplification for electrochemical detection of nosema bombycis genomic DNA PTP1. Anal Chem 87(20):10268–10274
Qu F, Yang M, Rasooly A (2016) Dual signal amplification electrochemical biosensor for monitoring the activity and inhibition of the Alzheimer’s related protease β-Secretase. Anal Chem 88(21):10559–10565
Huang Y, Tang C, Liu J, Cheng J, Si Z, Li T, Yang M (2017) Signal amplification strategy for electrochemical immunosensing based on a molybdophosphate induced enhanced redox current on the surface of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184(3):855–861
Sun J, Tian D, Guo Q, Zhang L, Jiang W, Yang M (2016) A label-free electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of cancer biomarker alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) based on hydroxyapatite induced redox current. Anal Methods 8(40):7319–7323
Pal S, Bhand S (2015) Zinc oxide nanoparticle-enhanced ultrasensitive chemiluminescence immunoassay for the carcinoma embryonic antigen. Microchim Acta 182(9–10):1643–1651
Shi G-F, Cao J-T, Zhang J-J, Huang K-J, Liu Y-M, Chen Y-H, Ren S-W (2014) Aptasensor based on tripetalous cadmium sulfidegraphene electrochemiluminescence for the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Analyst 139(22):5827–5834
Wang Y-L, Cao J-T, Chen Y-H, Liu Y-M (2016) A label-free electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for carcinoembryonic antigen detection based on electrodeposited ZnS-CdS on MoS2 decorated electrode. Anal Methods 8(26):5242–5247
Xu TS, Li XY, Xie ZH, Li XG, Zhang HY (2015) Poly(o-phenylenediamine) nanosphere-conjugated capture antibody immobilized on a glassy carbon electrode for electrochemical immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen. Microchim Acta 182(15–16):2541–2549
Feng DX, Lu XC, Dong X, Ling YY, Zhang YZ (2013) Label-free electrochemical immunosensor for the carcinoembryonic antigen using a glassy carbon electrode modified with electrodeposited Prussian blue, a graphene and carbon nanotube assembly and an antibody immobilized on gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 180(9–10):767–774
Yang XM, Zhuo Y, Zhu SS, Luo YW, Feng YJ, Xu Y (2015) Selectively assaying CEA based on a creative strategy of gold nanoparticles enhancing silver nanoclusters' fluorescence. Biosens Bioelectron 64:345–351
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the support of this work by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21575165), Tianjin Clinical Research Center for Organ Transplantation Grant (No. 15ZXLCSY00070) and Science and technology fund of Tianjin Municipal Health Bureau (No. 2013 KZ034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, W., Liu, L., Zhang, L. et al. Sensitive immunosensing of the carcinoembryonic antigen utilizing aptamer-based in-situ formation of a redox-active heteropolyacid and rolling circle amplification. Microchim Acta 184, 4757–4763 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2522-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2522-7