Abstract
The authors describe a dual signal amplification strategy for improving the sensitivity of electrochemical aptasensor. Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (HAP-NPs) serve as the support for deposition of the respective aptamer. Both the HAP-NPs and the aptamer contain phosphate groups which can react with molybdate to form a redox-active molybdophosphate precipitate on the surface of a glassy carbon electrode (GCE). On applying a relatively low voltage of 0.21 V (vs. Ag/AgCl), a current is generated whose intensity depends on the concentration of the analyte. The cancer biomarker platelet-derived growth factor BB (PDGF-BB) is chosen as a model antigen (analyte). The assay works by sequential deposition of antibody against PDGF-BB, analyte (PDGF-BB) and anti-PDGF-BB aptamer modified HAP-NPs on the GCE to form a sandwich structure. The amperometric signal is linear in the 0.1 pg.mL−1 to 10 ng.mL−1 PDGF-BB concentration range, with a detection limit as low as 50 fg.mL−1. The assay was successfully applied to the determination of PDGF-BB in serum samples. In our perception, this signal amplification strategy has a wide scope in that it can be adapted to the preparation of other aptasensors for biomarkers and related species.

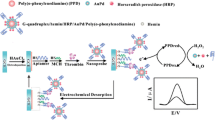
Schematic of an electrochemical aptasensor based on dual signal amplification strategy. It was applied to the detection of cancer biomarker platelet-derived growth factor BB (PDGF-BB). Hydroxyapatite (HAP) nanoparticles were chosen for the immobilization of aptamers to increase the loading of aptamers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alhadrami HA, Chinnappan R, Eissa S, Rahamn AA, Zourob M (2017) High affinity truncated DNA aptamers for the development of fluorescence based progesterone biosensors. Anal Biochem 525:78–84
Quan H, Zuo C, Li T, Liu Y, Li M, Zhong M, Zhang Y, Qi H, Yang M (2015) Electrochemical detection of carcinoembryonic antigen based on silver nanocluster/horseradish peroxidase nanocomposite as signal probe. Electrochim Acta 176:893–897
Gotrik MR, Feagin TA, Csordas AT, Nakamoto MA, Soh HT (2016) Advancements in aptamer discovery technologies. Account Chem Res 49(9):1903–1910
Dhiman A, Kalra P, Bansal V, Bruno JG, Sharma TK (2017) Aptamer-based point-of-care diagnostic platforms. Sens Actuators B Chem 246:535–553
Tang S, Lu W, Gu F, Tong P, Yan Z, Zhang L (2014) A novel electrochemical sensor for lead ion based on cascade DNA and quantum dots amplification. Electrochim Acta 134:1–7
Cui L, Wu J, Li J, Ju H (2015) Electrochemical sensor for lead cation sensitized with a DNA functionalized Porphyrinic metal–organic framework. Anal Chem 87:10635–10641
Zhang Y, Su M, Ge L, Ge S, Yu J, Song X (2013) Synthesis and characterization of graphene nanosheets attached to spiky MnO2 nanospheres and its application in ultrasensitive immunoassay. Carbon 2013(57):22–33
Sun J, Tian D, Guo Q, Zhang L, Jiang W, Yang M (2016) A label-free electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of cancer biomarker alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) based on hydroxyapatite induced redox current. Anal Methods 8(40):7319–7323
Luo J, Rasooly A, Wang L, Zeng K, Shen C, Qian P, Yang M, Qu F (2016) Fluorescent turn-on determination of the activity of peptidases using peptide templated gold nanoclusters. Microchim Acta 183(2):605–610
Tang T, Ouyang J, Hu L, Guo L, Yang M, Chen X (2016) Synthesis of peptide templated copper nanoclusters for fluorometric determination of Fe(III) in human serum. Microchim Acta 183(10):2831–2836
Guo L, Tang T, Hu L, Yang M, Chen X (2017) Fluorescence assay of Fe (III) in human serum samples based on pH dependent silver nanoclusters. Sens Actuator B Chem 241:773–778
Hu L, Hu S, Guo L, Tang T, Yang M (2016) Optical and electrochemical detection of biothiols based on aggregation of silver nanoparticles. Anal Methods 8(24):4903–4907
Shen C, Zhang K, Gao N, Wei S, Liu G, Chai Y, Yang M (2016) Colorimetric and electrochemical determination of the activity of protein kinase based on retarded particle growth due to binding of phosphorylated peptides to DNA – capped silver nanoclusters. Microchim Acta 183(11):2933–2939
Shen C, Xia X, Hu S, Yang M, Wang J (2015) Silver nanoclusters-based fluorescence assay of protein kinase activity and inhibition. Anal Chem 87(1):693–698
Kang W, Ding Y, Zhou H, Liao Q, Yang X, Yang Y, Jiang J, Yang M (2015) Monitoring the activity and inhibition of alkaline phosphatase via quenching and restoration of the fluorescence of carbon dots. Microchim Acta 182(5–6):1161–1167
Pujari-Palmer S, Chen S, Rubino S, Weng H, Xia W, Engqvist H, Tang L, Ott MK (2016) In vivo and in vitro evaluation of hydroxyapatite nanoparticle morphology on the acute inflammatory response. Biomaterials 90:1–11
Syamchand SS, Priya S, Sony G (2015) Hydroxyapatite nanocrystals dually doped with fluorescent and paramagnetic labels for bimodal (luminomagnetic) cell imaging. Microchim Acta 182:1213–1221
Abolghasemi MM, Parastari S, Yousefi V (2016) A nanoporous anodized alumina wire with a nanosized hydroxyapatite coating for headspace solid-phase microextraction of phenol and chlorophenols. Microchim Acta 183:241–247
Krenkova J, Lacher NA, Svec F (2010) Control of selectivity via Nanochemistry: monolithic capillary column containing hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for separation of proteins and enrichment of Phosphopeptides. Anal Chem 82(19):8335–8341
Lu HB, Campbell CT, Graham DJ, Ratner BD (2000) Surface characterization of hydroxyapatite and related calcium phosphates by XPS and TOF-SIMS. Anal Chem 72(13):2886–2894
Wang G, Han R, Feng X, Li Y, Lin J, Luo X (2017) A glassy carbon electrode modified with poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with nano-sized hydroxyapatite for amperometric determination of nitrite. Microchim Acta 184:1721–1727
Li J, Kuang d, Feng Y, Zhang F, Liu M (2012) Glucose biosensor based on glucose oxidase immobilized on a nanofilm composed of mesoporous hydroxyapatite, titanium dioxide, and modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 176:73–80
Syamchand SS, Sony G (2015) Multifunctional hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for drug delivery and multimodal molecular imaging. Microchim Acta 182:1567–1589
Chang H, Tang L, Wang Y, Jiang j, Li J (2010) Graphene fluorescence resonance energy transfer Aptasensor for the thrombin detection. Anal Chem 82:2341–2346
Wu S, Duan N, Zhao S, Fang C, Wang Z (2014) Simultaneous Aptasensor for multiplex pathogenic bacteria detection based on multicolor Upconversion nanoparticles labels. Anal Chem 86:3100–3107
Wu Y, Xiao F, Wu Z, Yu R (2017) Novel Aptasensor platform based on Ratiometric surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal Chem 89:2852–2858
Liu J, He D, Liu Q, He X, Wang K, Yang X, Shangguan J, Tang J, Mao Y (2016) Vertically ordered mesoporous silica film-assisted label-free and universal Electrochemiluminescence Aptasensor platform. Anal Chem 88(11707–11713)
Jo H, Gu H, Jeon W, Youn H, Her J, Kim S-K, Lee J, Shin JH, Ban C (2015) Electrochemical Aptasensor of cardiac troponin I for the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Anal Chem 87:9869–9875
Zhang X, Xiao K, Cheng L, Chen H, Liu B, Zhang S, Kong J (2014) Visual and highly sensitive detection of cancer cells by a colorimetric Aptasensor based on cell-triggered cyclic enzymatic signal amplification. Anal Chem 86:5567–5572
Shen C, Li X, Rasooly A, Guo L, Zhang K, Yang M (2016) A single electrochemical biosensor for detecting the activity and inhibition of both protein kinase and alkaline phosphatase based on phosphate ions induced deposition of redox precipitates. Biosens Bioelectron 85:220–225
Qu F, Yang M, Rasooly A (2016) Dual signal amplification electrochemical biosensor for monitoring the activity and inhibition of the Alzheimer’s related protease β-secretase. Anal Chem 88(21):10559–10565
Tang L, Liu Y, Ali MM, Kang DK, Zhao W, Li J (2012) Colorimetric and ultrasensitive bioassay based on a dual-amplification system using aptamer and DNAzyme. Anal Chem 84(11):4711–4717
Guo L, Zhao Q (2016) Determination of the platelet-derived growth factor BB by a competitive thrombin-linked aptamer-based Fluorometric assay. Microchim Acta 183:3229–3235
Zhang C, Yang J, Quan Z, Yang P, Li C, Hou Z, Lin J (2009) Hydroxyapatite Nano- and Microcrystals with multiform morphologies: controllable synthesis and luminescence properties. Crys Grow Design 9(6):2725–2733
Xie S, Yuan Y, Chai Y, Yuan R (2015) Tracing phosphate ions generated during loop-mediated isothermal amplification for electrochemical detection of nosema bombycis genomic DNA PTP1. Anal Chem 87(20):10268–10274
Hu L, Hu S, Guo L, Shen C, Yang M, Rasooly A (2017) DNA generated electric current biosensor. Anal Chem 89(4):2547–2552
Huang Y, Tang C, Liu J, Cheng J, Si Z, Li T, Yang M (2017) Signal amplification strategy for electrochemical immunosensing based on a molybdophosphate induced enhanced redox current on the surface of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184(3):855–861
Si z, Xie B, Chen Z, Tang C, Li T, Yang M (2017) Electrochemical aptasensor for the cancer biomarker CEA based on aptamer induced current due to formation of molybdophosphate. Microchim Acta 184:3215–3221
Li H, Wang M, Wang C, Li W, Qiang W, Xu D (2013) Silver nanoparticle-enhanced fluorescence resonance energy transfer sensor for human platelet-derived growth factor-BB detection. Anal Chem 85(9):4492–4499
Li H, Zhao Y, Chen Z, Xu D (2017) Silver enhanced ratiometric nanosensor based on two adjustable fluorescence resonance energy transfer modes for quantitative protein sensing. Biosens Bioelectron 87:428–432
Zhang Z, Guo C, Zhang S, He L, Wang M, Peng D, Tian J, Fang S (2017) Carbon-based nanocomposites with aptamer-templated silver nanoclusters for the highly sensitive and selective detection of platelet-derived growth factor. Biosens Bioelectron 89:735–742
He L, Zhang S, Ji H, Wang M, Peng D, Yan F, Fang S, Zhang H, Jia C, Zhang Z (2016) Protein-templated cobaltous phosphate nanocomposites for the highly sensitive and selective detection of platelet-derived growth factor-BB. Biosens Bioelectron 79:553–560
Song W, Li H, Liang H, Qiang W, Xu D (2014) Disposable electrochemical aptasensor array by using in situ DNA hybridization inducing silver nanoparticles aggregate for signal amplification. Anal Chem 86(5):2775–2783
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the support of this work by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21575165), Tianjin Clinical Research Center for Organ Transplantation Grant (No. 15ZXLCSY00070) and Science and technology fund of Tianjin Municipal Health Bureau (No. 2013 KZ034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 44 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, W., Tian, D., Zhang, L. et al. Dual signal amplification strategy for amperometric aptasensing using hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Application to the sensitive detection of the cancer biomarker platelet-derived growth factor BB. Microchim Acta 184, 4375–4381 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2471-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2471-1