Abstract
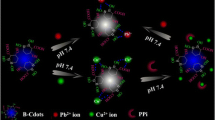
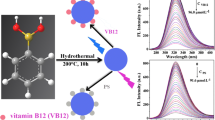
We report on the hydrothermal synthesis of boron-doped carbon dots (B-CDs) starting from glucose and boric acid. Doping of the CDs with boron was confirmed by Fourier transform infrared and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The B-CDs have an average diameter of about 4 nm and display blue fluorescence which is dynamically quenched by Fe(III) ions. This finding was exploited to design a method for the determination of Fe(III) in water. The relative fluorescence intensity at 359 nm in the presence and of absence ions is inversely proportional to the concentration of Fe(III) ions, and a Stern-Volmer calibration plot is linear in the concentration range of 0–16 μM, with a 242 nM detection limit. The assay is sensitive, robust and selective.

The stable blue fluorescent boron-doped carbon dots (B-CDs) were obtained by hydrothermal method. The fluorescence of B-CDs was effectively quenched by Fe(III). The B-CDs probe was able to discriminate Fe(III) from other metal ions. The probe shows high sensitivity to Fe(III) ions with low limit of detection.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Y, Hu A (2014) Carbon quantum dots: synthesis, properties and applications. J Mater Chem C 2:6921–6939
Tao H, Yang K, Ma Z, Wan J, Zhang Y, Kang Z, Liu Z (2012) In vivo NIR fluorescence imaging, biodistribution, and toxicology of photoluminescent carbon dots produced from carbon nanotubes and graphite. Small 8:281–290
Yang ZC, Wang M, Yong AM, Wong SY, Zhang X-H, Tan H, Chang AY, Li X, Wang J (2011) Intrinsically fluorescent carbon dots with tunable emission derived from hydrothermal treatment of glucose in the presence of monopotassium phosphate. Chem Commun 47:11615–11617
Zhu C, Zhai J, Dong S (2012) Bifunctional fluorescent carbon nanodots: green synthesis via soy milk and application as metal-free electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. Chem Commun 48:9367–9369
Zhu S, Meng Q, Wang L, Zhang J, Song Y, Jin H, Zhang K, Sun H, Wang H, Yang B (2013) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:3953–3957
Hu Y, Yang J, Tian J, Jia L, Yu JS (2014) Waste frying oil as a precursor for one-step synthesis of sulfur-doped carbon dots with pH-sensitive photoluminescence. Carbon 77:775–782
Yang Z, Nie H, Xa C, Chen X, Huang S (2013) Recent progress in doped carbon nanomaterials as effective cathode catalysts for fuel cell oxygen reduction reaction. J Power Sources 236:238–249
Zhang YQ, Ma DK, Zhuang Y, Zhang X, Chen W, Hong LL, Yan QX, Yu K, Huang SM (2012) One-pot synthesis of N-doped carbon dots with tunable luminescence properties. J Mater Chem 22:16714–16718
Ma Z, Ming H, Huang H, Liu Y, Kang Z (2012) One-step ultrasonic synthesis of fluorescent N-doped carbon dots from glucose and their visible-light sensitive photocatalytic ability. New J Chem 36:861–864
Dong Y, Pang H, Yang HB, Guo C, Shao J, Chi Y, Li CM, Yu T (2013) Carbon-based dots co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur for high quantum yield and excitation-independent emission. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:7800–7804
Jahan S, Mansoor F, Naz S, Lei J, Kanwal S (2013) Oxidative synthesis of highly fluorescent boron/nitrogen co-doped carbon nanodots enabling detection of photosensitizer and carcinogenic dye. Anal Chem 85:10232–10239
Zhang R, Chen W (2014) Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots: facile synthesis and application as a “turn-off” fluorescent probe for detection of Hg2+ ions. Biosens Bioelectron 55:83–90
Qin C, Cheng Y, Wang L, Jing X, Wang F (2008) Phosphonate-functionalized polyfluorene as a highly water-soluble iron(III) chemosensor. Macromolecules 41:7798–7804
Ajlec R, Stupar J (1989) Determination of iron species in wine by ion-exchange chromatography-flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Analyst 114:137–142
Wu J, Boyle EA (1998) Determination of iron in seawater by high-resolution isotope dilution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after Mg(OH)2 coprecipitation. Anal Chim Acta 367:183–191
Bobrowski A, Nowak K, Zarębski J (2005) Application of a bismuth film electrode to the voltammetric determination of trace iron using a Fe(III)–TEA–BrO3− catalytic system. Anal Bioanal Chem 382:1691–1697
Bhalla V, Sharma N, Kumar N, Kumar M (2013) Rhodamine based fluorescence turn-on chemosensor for nanomolar detection of Fe3+ ions. Sensors Actuators B Chem 178:228–232
Singh A, Sinha S, Kaur R, Kaur N, Singh N (2014) Rhodamine based organic nanoparticles for sensing of Fe3+ with high selectivity in aqueous medium: application to iron supplement analysis. Sensors Actuators B Chem 204:617–621
Qu K, Wang J, Ren J, Qu X (2013) Carbon dots prepared by hydrothermal treatment of dopamine as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for the label-free detection of iron(III) ions and dopamine. Chem Eur J 19:7243–7249
Shen C, Sun Y, Wang J, Lu Y (2014) Facile route to highly photoluminescent carbon nanodots for ions detection, pH sensors and bioimaging. Nanoscale 6:9139–9147
Gong X, Lu W, Paau MC, Hu Q, Wu X, Shuang S, Dong C, Choi MMF (2015) Facile synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots for Fe3+ sensing and cellular imaging. Anal Chim Acta 861:74–84
Xu J, Zhou Y, Liu S, Dong M, Huang C (2014) Low-cost synthesis of carbon nanodots from natural products used as a fluorescent probe for the detection of ferrum(III) ions in lake water. Anal Methods 6:2086–2090
Yang X, Zhuo Y, Zhu S, Luo Y, Feng Y, Dou Y (2014) Novel and green synthesis of high-fluorescent carbon dots originated from honey for sensing and imaging. Biosens Bioelectron 60:292–298
Ananthanarayanan A, Wang X, Routh P, Sana B, Lim S, Kim D-H, Lim KH, Li J, Chen P (2014) Facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots from 3D graphene and their application for Fe3+ sensing. Adv Funct Mater 24:3021–3026
Zhou Z, Zhou M, Gong A, Zhang Y, Li Q (2015) Synthesis of highly photoluminescent carbon dots via citric acid and Tris for iron (III) ions sensors and bioimaging. Talanta 143:107–113
Li L, Li L, Wang C, Liu K, Zhu R, Qiang H, Lin Y (2015) Synthesis of nitrogen-doped and amino acid-functionalized graphene quantum dots from glycine, and their application to the fluorometric determination of ferric ion. Microchim Acta 182:763–770
Shen P, Xia Y (2014) Synthesis-modification integration: one-step fabrication of boronic acid functionalized carbon dots for fluorescent blood sugar sensing. Anal Chem 86:5323–5329
Zhang L, Zhang ZY, Liang RP, Li YH, Qiu JD (2014) Boron-doped graphene quantum dots for selective glucose sensing nased on the “abnormal” aggregation-induced photoluminescence enhancement. Anal Chem 86:4423–4430
Bourlinos AB, Stassinopoulos A, Anglos D, Zboril R, Georgakilas V, Giannelis EP (2008) Photoluminescent carbogenic dots. Chem Mater 20:4539–4541
Zhu H, Wang XL, Li YL, Wang ZJ, Yang F, Yang XR (2009) Microwave synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles with electrochemiluminescence properties. Chem Commun 5118–5120
Fan LJ, Zhang Y, Murphy CB, Angell SE, Parker MFL, Flynn BR, Jones WE (2009) Fluorescent conjugated polymer molecular wire chemosensors for transition metal ion recognition and signaling. Coord Chem Rev 253:410–422
Dwivedi AK, Saikia G, Iyer PK (2011) Aqueous polyfluorene probe for the detection and estimation of Fe3+ and inorganic phosphate in blood serum. J Mater Chem 21:2502–2507
Liu JM, Lin LP, Wang XX, Lin SQ, Cai WL, Zhang LH, Zheng ZY (2012) Highly selective and sensitive detection of Cu2+ with lysine enhancing bovine serum albumin modified-carbon dots fluorescent probe. Analyst 137:2637–2642
Wang F, Gu Z, Lei W, Wang W, Xia X, Hao Q (2014) Graphene quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing platform for highly efficient detection of copper(II) ions. Sensors Actuators B Chem 190:516–522
Mu X, Qi L, Dong P, Qiao J, Hou J, Nie Z, Ma H (2013) Facile one-pot synthesis of l-proline-stabilized fluorescent gold nanoclusters and its application as sensing probes for serum iron. Biosens Bioelectron 49:249–255
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the Program for NCET-12-0629, Ph.D. Program Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (No.20133219110018), Qing Lan Project and Six Major Talent Summit (XNY-011), the Science and Technology Support Plan (No. BE2013126), and PAPD of Jiangsu Province, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 2453 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Hao, Q., Zhang, Y. et al. Fluorescence quenchometric method for determination of ferric ion using boron-doped carbon dots. Microchim Acta 183, 273–279 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1650-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1650-1