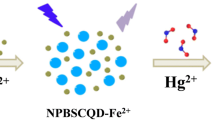
Abstract
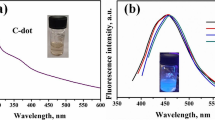
We describe a new method for synthesis of water-soluble photoluminescent carbon dots (CDs) by one-pot hydrothermal treatment of adipic acid and triammonium citrate. The CDs have excitation/emission maxima of 340/440 nm, a quantum yield of 0.13, and are shown to be a viable fluorescent probe for the determination of Hg(II). It shows a linear relationship in the 4 to 18 μM mercury ion concentration range. The detection limit is as low as 2.47 μM. The CDs were applied to intracellular sensing and imaging of Hg(II) where they showed low toxicity.

Carbon dots synthesized by hydrothermal method can be used as “turn-off” fluorescent probe Hg2+ determination. Besides, the carbon dots were applied to intracellular sensing and imaging of Hg2+.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yan FY, Zou Y, Wang M, Mu XL, Yang N, Chen L (2014) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots-based fluorescent chemosensors for sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions and application of imaging in living cells. Sensors Actuators B 192:488–495
Nolan EM, Lippard SJ (2003) A “turn-on” fluorescent sensor for the selective detection of mercuric ion in aqueous media. J Am Chem Soc 125:14270–14271
Nolan EM, Lippard SJ (2005) MS4, a seminaphthofluorescein-based chemosensorfor the ratiometric detection of Hg(II). J Mater Chem 15(27):2778–2783
Leopold K, Foulkes M, Worsfold P (2010) Methods for the determination and speciation of mercury in natural waters—a review. Anal Chim Acta 663:127–138
Gong Y, Zhang X, Chen Z, Yuan Y, Jin Z, Mei L, Zhang J, Tan W, Shen G, Yu R (2012) An efficient rhodamine thiospirolactambased fluorescent probe for detection of Hg(II) in aqueous samples. Analyst 137(4):932–938
Lin Y, Tseng WL (2010) Ultrasensitive sensing of Hg(II) and CH3Hg+ based on the fluorescence quenching of lysozyme type VI-stabilized gold nanoclusters. Anal Chem 82(22):9194–9200
Qin XY, Lu WB, Asiri AM, Al-Youbi AO, Sun XP (2013) Microwave-assisted rapid green synthesis of photoluminescent carbon nanodots from flour and their applications for sensitive and selective detection of mercury(II) ions. Sensors Actuators B 184:156–162
Barman S, Sadhukhan M (2012) Facile bulk production of highly blue fluorescent graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots and their application as highly selective and sensitive sensors for the detection of mercuric and iodide ions in aqueous media. J Mater Chem 22(41):21832–21837
Du FK, Zeng F, Ming YH, Wu SZ (2013) Carbon dots-based fluorescent probes for sensitive and selective detection of iodide. Microchim Acta 180(5):453–460
Bourlinos A, Trivizas G, Karakassides M, Baikousi M, Kouloumpis A, Gournis D, Bakandritsos A, Hola K, Kozak O, Zboril R, Papagiannouli I, Aloukos P, Couris S (2015) Green and simple route toward boron doped carbon dots with significantly enhanced non-linear optical properties. Carbon 83:173–179
Baker SN, Baker GA (2010) Luminescent carbon nanodots: emergent nanolights. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(38):6726–6744
Ahmed G, Laíño R, Calzón G, García M (2015) Highly fluorescent carbon dots as nanoprobes for sensitive and selective determination of 4-nitrophenol in surface waters. Microchim Acta 182(1):51–59
Bhaisare ML, Talib A, Khan MS, Pandey S, Wu HF (2015) Synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots via microwave carbonization of citric acid in presence of tetraoctylammonium ion, and their application to cellular bioimaging. Microchim Acta 182(13):2173–2181
Yang MM, Kong WQ, Li H, Liu J, Huang H, Liu Y, Kang ZH (2015) Fluorescent carbon dots for sensitive determination and intracellular imaging of zinc(II) ion. Microchim Acta 182(15):2443–2450
Hou JY, Dong J, Zhu HS, Teng X, Ai SY, Mang ML (2015) A simple and sensitive fluorescent sensor for methyl parathion based on L-tyrosine methyl ester functionalized carbon dots. Biosens Bioelectron 68:20–26
Zhang PJ, Xue ZJ, Luo D, Yu W, Guo ZH, Wang T (2014) Dual-Peak electrogenerated chemiluminescence of carbon dots for iron ions detection. Anal Chem 86(12):5620–5623
Zou Y, Yan FY, Zheng TC, Shi DC, Sun FZ, Yang N, Chen L (2015) Highly luminescent organosilane-functionalized carbon dots as a nanosensor for sensitive and selective detection of quercetin in aqueous solution. Talanta 135:145–148
Yang ST, Cao L, Luo PG, Lu FS, Wang X, Wang HF, Meziani MJ, Liu YF, Qi G, Sun YP (2009) Carbon dots for optical imaging in vivo. J Am Chem Soc 32:11308–11309
Wolfbeis O (2015) An overview of nanoparticles commonly used in fluorescent bioimaging. Chem Soc Rev 44(14):4743–4768
Liu HP, Ye T, Mao CD (2007) Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles derived from candle soot. Angew Chem Int Ed 46(34):6473–6475
Qiao ZA, Wang YF, Gao Y, Li HW, Dai TY, Liu YL, Huo QS (2010) Commercially activated carbon as the source for producing multicolor photoluminescent carbon dots by chemical oxidation. Chem Commun 46(46):8812–8814
Sun YP, Zhou B, Lin Y, Wang W, Fernando KAS, Pathak P, Meziani MJ, Harruff BA, Wang X, Wang HF, Luo PJG, Yang H, Kose ME, Chen BL, Veca LM, Xie SY (2006) Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J Am Chem Soc 128(24):7756–7757
Tian L, Ghosh D, Chen W, Pradhan S, Chang XJ, Chen SW (2009) Nanosized carbon particles from natural gas soot. Chem Mater 21(13):2803–2809
Hsu PC, Chang HT (2012) Synthesis of high-quality carbon nanodots from hydrophilic compounds: role of functional groups. Chem Commun 48(33):3984–3986
Sahu S, Behera B, Maiti TK, Mohapatra S (2012) Simple one-step synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots from orange juice: application as excellent bio-imaging agents. Chem Commun 48(70):8835–8837
Yang ZC, Wang M, Yong AM, Wong SY, Zhang XH, Tan H, Chang AY, Li X, Wang J (2011) Intrinsically fluorescent carbon dots with tunable emission derived from hydrothermal treatment of glucose in the presence of monopotassium phosphate. Chem Commun 47(42):11615–11617
Li HT, He XD, Kang ZH, Huang H, Liu Y, Liu JL, Lian SY, Tsang CA, Yang XB, Lee ST (2010) Water-soluble fluorescent carbon quantum dots and photocatalyst design. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(26):4430–4434
Ahmed MJ, Hossan J (1995) Spectrophotometric determination of aluminium by morin. Talanta 42:1135–1142
Li YF, Liu Y, Zhou M (2012) Synthesis and properties of a dendritic FRET donor–acceptor system with cationic iridium(III) complex core and carbazolyl periphery. Dalton Trans 41(9):2582–2591
Ray SC, Saha A, Jana NR, Sarkar R (2009) Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and bioimaging application. J Phys Chem C 113:18546–18551
Hu SL, Niu KY, Sun J, Yang J, Zhao NQ, Du XW (2009) One-step synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by laser irradiation. J Mater Chem 19(4):484–488
Chai F, Wang T, Li L, Liu H, Zhang L, Su Z, Wang C (2010) Fluorescent gold nanoprobes for the sensitive and selective detection for Hg(II). Nanoscale Res Lett 5(11):1856–1860
Wang H, Wang Y, Jin J, Yang R (2008) Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric and turn-on fluorescent probe for mercury(II) ions in aqueous solution. Anal Chem 80(23):9021–9028
Niu LY, Guan YS, Chen YZ, Wu LZ, Tung CH, Yang QZ (2012) BODIPY-based ratiometric fluorescent sensor for highly selective detection of glutathione over cysteine and homocysteine. J Am Chem Soc 134:18928–18931
Chai F, Wang CG, Wang TT, Ma ZF, Su ZM (2010) L-cysteine functionalized gold nanoparticles for the colorimetric detection of Hg(II) induced by ultraviolet light. Nanotechnology 21:025501
Paramanik B, Bhattacharyya S, Patra A (2013) Detection of Hg(II) and F− ions by using fluorescence switching of quantum dots in an Au-Cluster–CdTe QD nanocomposite. Chem Eur J 19:5980–5987
Zhou L, Lin YH, Huang ZZ, Ren JS, Qu XG (2012) Carbon nanodots as fluorescence probes for rapid, sensitive, and label-free detection of Hg(II) and biothiols in complex matrices. 48:1147–1149
Staudinger C, Borisov SM (2015) Long-wavelength analyte-sensitive luminescent probes and optical (bio) sensors. Methods Appl Fluoresc 3:042005
Acknowledgments
The work described in this manuscript was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21174103, 21374078, 51308390) and Tianjin Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology (No. 15JCYBJC18100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1.40 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, F., Kong, D., Luo, Y. et al. Carbon dots serve as an effective probe for the quantitative determination and for intracellular imaging of mercury(II). Microchim Acta 183, 1611–1618 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1788-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1788-5