Abstract
Conventional methods for extraction of DNA are expensive, time-consuming and tedious. To overcome these limitations, a paper-based DNA extraction device was developed that incorporates sponge-based buffer storage, a paper-based valve and channels of different length to autonomously direct the reagent and sample to the Fusion 5 disk for DNA capturing. With this device, DNA can be extracted within 2 min from only 30 μL samples of whole blood, serum, breast cancer cell, saliva, sputum and bacterial suspension. The device can also extract Hepatitis B Virus DNA from clinical blood samples and after quantification shows a detection limit as low as 104 copies⋅mL−1. This highlights its potential use in future diagnostics. The performance of the device was similar to that of the commercial QIAamp DNA micro kits and the FTA card. In our perception, this simple, inexpensive, portable and disposable device holds great promise in terms of POC testing in resource-poor settings.

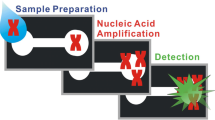
Schematic of a paper-based DNA extraction device that incorporates sponge-based on-chip reagent storage, a paper-based valve and channels of different length to autonomously direct the reagent and sample to the Fusion 5 disk for DNA capturing.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roewer L (2013) DNA fingerprinting in forensics_ past, present, future. Investig Genet 4:22–32. doi:10.1186/2041-2223-4-22
Petras ML, Lefferts JAWB, Suriawinata AA, Tsongalis GJ (2011) KRAS detection in colonic tumors by DNA extraction from FTA paper: the molecular touch-prep. Diagnostic Molecular Pathology: The American Journal of Surgical Pathology, Part B 20(4):189–193. doi:10.1097/PDM.0b013e318211d554
Thomsen PFKJ, Iversen LL, Wiuf C, Rasmussen M, Gilbert MT, Orlando L, Willerslev E (2012) Monitoring endangered freshwater biodiversity using environmental DNA. Mol Ecol 21(11):2565–2573. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05418.x
Gruentzig AWKC, Sharon A, Jeff B, Chatterjee A, Sauer-Budge AF (2011) A new DNA extraction method for automated food analysis. Anal Methods 3(7):1507. doi:10.1039/c0ay00701c
Tang R, Yang H, Choi JR, Gong Y, Hu J, Feng S, Pingguan-Murphy B, Mei Q, Xu F (2016) Improved sensitivity of lateral flow assay using paper-based sample concentration technique. Talanta 152:269–276. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2016.02.017
Choi JR, Hu J, Tang R, Gong Y, Feng S, Ren H, Wen T, Li X, Wan Abas WA, Pingguan-Murphy B, Xu F (2016) An integrated paper-based sample-to-answer biosensor for nucleic acid testing at the point of care. Lab Chip 16(3):611–621. doi:10.1039/c5lc01388g
Choi JR, Hu J, Feng S, Wan Abas WA, Pingguan-Murphy B, Xu F (2016) Sensitive biomolecule detection in lateral flow assay with a portable temperature-humidity control device. Biosens Bioelectron 79:98–107. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2015.12.005
Tang RH, Yang H, Choi JR, Gong Y, Feng SS, Pingguan-Murphy B, Huang QS, Shi JL, Mei QB, Xu F (2016) Advances in paper-based sample pretreatment for point-of-care testing. Crit Rev Biotechnol 1–18. doi:10.3109/07388551.2016.1164664
Alireza Javadi MS, Leila, Mohammadi Ziazi MP, Atosa Dorudinia SM, Seyedmehdi SK (2014) Qualification study of two genomic DNA extraction methods in different clinical samples. Tanaffos 13(4):41–47
Poh JJ, Gan SK (2014) Comparison of customized spin-column and salt-precipitation finger-prick blood DNA extraction. Biosci Rep 34(5):629–634. doi:10.1042/BSR20140105
Sirdah MM (2014) Superparamagnetic-bead based method: an effective DNA extraction from dried blood spots (DBS) for diagnostic PCR. J Clin Diagn Res: JCDR 8(4):FC01–FC04. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2014/8171.4226
Choi JRTR, Wang SQ, Wan Abas WA, Pingguan-Murphy B, Xu F (2015) Paper-based sample-to-answer molecular diagnostic platform for point-of-care diagnostics. Biosens Bioelectron 74:427–439. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2015.06.065
Hu J, Wang S, Wang L, Li F, Pingguan-Murphy B, Lu TJ, Xu F (2014) Advances in paper-based point-of-care diagnostics. Biosens Bioelectron 54:585–597. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2013.10.075
Xu Y, Liu M, Kong N, Liu J (2016) Lab-on-paper micro- and nano-analytical devices: fabrication, modification, detection and emerging applications. Microchim Acta 183(5):1521–1542. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1841-4
Wolfgramm Ede V, de Carvalho FM, Aguiar VR, Sartori MP, Hirschfeld-Campolongo GC, Tsutsumida WM, Louro ID (2009) Simplified buccal DNA extraction with FTA elute cards. Forensic Sci Int Genet 3(2):125–127. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2008.11.008
McFall SM, Wagner RL, Jangam SR, Yamada DH, Hardie D, Kelso DM (2015) A simple and rapid DNA extraction method from whole blood for highly sensitive detection and quantitation of HIV-1 proviral DNA by real-time PCR. J Virol Methods 214:37–42. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2015.01.005
Wupeng Gan BZ, Zhang P, Han J, Lid C-X, Liu P (2014) A filter paper-based microdevice for low-cost rapid, and automated DNA extraction and amplification from diverse sample types. Lab Chip 14:3719–3728. doi:10.1039/C4LC00686K
Govindarajan AVRS, Vigil GD, Yager P, Bohringer KF (2012) A low cost point-of-care viscous sample preparation device for molecular diagnosis in the developing world; an example of microfluidic origami. Lab Chip 12(1):174–181. doi:10.1039/c1lc20622b
Alidjinou EK, Ebatetou-Ataboho E, Sané F, Moukassa D, Dewilde A, Hober D (2013) Cervical samples dried on filter paper and dried vaginal tampons can be useful to investigate the circulation of high-risk HPV in Congo. J Clin Virol 57(2):161–164. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2013.02.010
Hyeran Noh STP (2010) Fluidic timers for time-dependent, point-of-care assays on paper. Anal Chem 82:8071–8078. doi:10.1021/ac1005537
Jangam SR, Yamada DH, McFall SM, DM K (2009) Rapid, point-of-care extraction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 proviral DNA from whole blood for detection by real-time PCR. J Clin Microbiol 47(8):2363–2368. doi:10.1128/JCM.r00092-09
Rui Gong SL (2014) Extraction of human genomic DNA from whole blood using a magnetic microsphere method. Int J Nanomedicine 9:3781–3789. doi:10.2147/IJN.S59545
de Man RA, Pas SD, Fries E, HGM N, Osterhaus ADME (2000) Development of a quantitative real-time detection assay for hepatitis B virus DNA and Comparison with two commercial assays. J Clin Microbiol 38:2897–2901
Esser K-H, Marx WH, Lisowsky T (2006) maxXbond: first regeneration system for DNA binding silica matrices. Nat methods 3(1). doi:10.1038/nmeth845
Zhanguo Xin JPV, Oliver MJ, Burke JJ (2003) High-throughput DNA extraction method suitable for PCR. BioTechniques 34:820–826
Al-Soud WA, Radstrom P (2001) Purification and characterization of PCR-inhibitory components in blood cells. J Clin Microbiol 39(2):485–493. doi:10.1128/JCM.39.2.485-493.2001
Queipo-Ortuno MI, Tena F, Colmenero JD, Morata P (2008) Comparison of seven commercial DNA extraction kits for the recovery of Brucella DNA from spiked human serum samples using real-time PCR. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases: Official Publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology 27(2):109–114. doi:10.1007/s10096-007-0409-y
Yeung SW, Hsing IM (2006) Manipulation and extraction of genomic DNA from cell lysate by functionalized magnetic particles for lab on a chip applications. Biosens Bioelectron 21(7):989–997. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2005.03.008
Wang C-H, Lien K-Y, Wu J-J, Lee G-B (2011) A magnetic bead-based assay for the rapid detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by using a microfluidic system with integrated loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Lab Chip 11(8):1521. doi:10.1039/c0lc00430h
Lee J-G, Cheong KH, Huh N, Kim S, Choi J-W, Ko C (2006) Microchip-based one step DNA extraction and real-time PCR in one chamber for rapid pathogen identification. Lab Chip 6(7):886. doi:10.1039/b515876a
Becker H, Maleki T, Gray BL, Fricke T, Quesenberry JT, Todd P, Leary JF (2012) Point-of-care, portable microfluidic blood analyzer system. Proc SPIE 8251:82510C–882511. doi:10.1117/12.909051
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11472224, 11672246).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, R., Yang, H., Choi, J.R. et al. Paper-based device with on-chip reagent storage for rapid extraction of DNA from biological samples. Microchim Acta 184, 2141–2150 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2225-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2225-0