Abstract
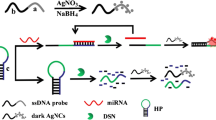
The authors report on a new gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assay for microRNA (miRNA). It is based on duplex-specific nuclease (DSN)-assisted signal amplification. Following hybridization between target miRNA and its complementary single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), the ssDNA in the DNA:RNA hybrid is selectively cleaved by DSN to produce small DNA fragments. Target microRNA is thus released and will initiate another round of hybridization and DSN digestion. In this manner, each miRNA target can specifically trigger several cycles of hybridization and DSN cleavages to yield numerous small fragments of DNA oligonucleotides. The short DNA fragments (unlike the uncleaved ssDNA probe) exhibit superior capability for stabilizing unmodified AuNP against salt-induced aggregation to the uncleaved ssDNA probe, with an accompanying color change from blue to red. These findings are exploited in a colorimetric assay for miRNA that has a 10 fmol detection limit.

A gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric strategy for the detection of microRNA has been established coupled with duplex-specific nuclease signal amplification.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li YY, Schluesener HJ, Xu SQ (2010) Gold nanoparticle-based biosensors. Gold Bull 43:29–41. doi:10.1007/BF03214964
Richards SJ, Gibson MI (2014) Optimization of the polymer coating for glycosylated gold nanoparticle biosensors to ensure stability and rapid optical readouts. ACS Macro Lett 3:1004–1008. doi:10.1021/mz5004882
Ho JA, Chang HC, Shih NY, Wu LC, Chang YF, Chen CC, Chou C (2010) Diagnostic detection of human lung cancer-associated antigen using a gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical immunosensor. Anal Chem 82:5944–5950. doi:10.1021/ac1001959
Drescher D, Giesen C, Traub H, Panne U, Kneipp J, Jakubowski N (2012) Quantitative imaging of gold and silver nanoparticles in single eukaryotic cells by laser ablation ICP-MS. Anal Chem 84:9684–9688. doi:10.1021/ac302639c
Hughes SI, Dasary SSR, Singh AK, Glenn Z, Jamison H, Ray PC, Yu HT (2013) Sensitive and selective detection of trivalent chromium using hyper Rayleigh scattering with 5,5′-dithio-bis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid)-modified gold nanoparticles. Sensors Actuators B 178:514–519. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2012.12.003
Liu JC, Guan Z, Lv ZZ, Jiang XL, Yang SM, Chen AL (2014) Improving sensitivity of gold nanoparticle based fluorescence quenching and colorimetric aptasensor by using water resuspended gold nanoparticle. Biosens Bioelectron 52:265–270. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2013.08.059
Elghanian R, Storhoff JJ, Mucic RC, Letsinger RL, Mirkin CA (1997) Selective colorimetric detection of polynucleotides based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold Nonaparticles. Science 277:1078–1081. doi:10.1126/science.277.5329.1078
Rosi NL, Mirkin CA (2005) Nanostructures in biodiagnostics. Chem Rev 105:1547–1562. doi:10.1021/cr030067f
Sato K, Hosokawa K, Maeda M (2003) Rapid aggregation of gold nanoparticles induced by non-cross-linking DNA hybridization. J Am Chem Soc 125:8102–8103. doi:10.1021/ja034876s
Sato K, Hosokawa K, Maeda M (2005) Non-cross-linking gold nanoparticle aggregation as a detection method for single-base substitutions. Nucleic Acids Res 33:e4. doi:10.1093/nar/gni007
Li HX, Rothberg L (2004) Colorimetric detection of DNA sequences based on electrostatic interactions with unmodified gold nanoparticles. PNAS 101:14036–14039. doi:10.1073/pnas.0406115101
Li HX, Rothberg LJ (2004) Label-free colorimetric detection of specific sequences in genomic DNA amplified by the polymerase chain reaction. J Am Chem Soc 126:10958–10961. doi:10.1021/ja048749n
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.035
Arenz C (2006) MicroRNAs-future drug targets ? Angew Chem Int Ed 45:5048–5050. doi:10.1002/anie.200601537
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435:834–838. doi:10.1038/nature03702
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O’Briant KC, Allen A, Lin DW, Urban N, Drescher CW, Knudsen BS, Stirewalt DL, Gentleman R, Vessella RL, Nelson PS, Martin DB, Tewari M (2008) Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. PNAS 105:10513–10518. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804549105
Cissell KA, Shrestha S, Deo SK (2007) MicroRNA detection: challenges for the analytical chemist. Anal Chem 79:4754–4761. doi:10.1021/ac0719305
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 294:853–858. doi:10.1126/science.1064921
Válóczi A, Hornyik C, Varga N, Burgyán J, Kauppinen S, Havelda Z (2004) Sensitive and specific detection of microRNAs by northern blot analysis using LNA-modified oligonucleotide probes. Nucleic Acids Res 32:e175. doi:10.1093/nar/gnh171
Thomson JM, Parker J, Perou CM, Hammond SM (2004) A custom microarray platform for analysis of microRNA gene expression. Nat Methods 1:47–53. doi:10.1038/nmeth704
Lee I, Ajay SS, Chen HM, Maruyama A, Wang NL, McInnis MG, Athey BD (2008) Discriminating single-base difference miRNA expressions using microarray probe design guru (ProDeG). Nucleic Acids Res 36:e27. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm1165
Li J, Yao B, Huang H, Wang Z, Sun CH, Fan Y, Chang Q, Li SL, Wang X, Xi JZ (2009) Real-time polymerase chain reaction microRNA detection based on enzymatic stem-loop probes ligation. Anal Chem 81:5446–5451. doi:10.1021/ac900598d
Allawi HT, Dahlberg JE, Olson S, Lund E, Olson M, Ma WP, Takova T, Neri BP, Lyamichev VI (2004) Quantitation of microRNAs using a modified invader assay. RNA 10:1153–1161. doi:10.1261/rna.5250604
Hartig JS, Grüne I, Najafi-Shoushtari SH, Famulok M (2004) Sequence-specific detection of miRNAs by signal-amplifying ribozymes. J Am Chem Soc 126:722–723. doi:10.1021/ja038822u
Cheng YQ, Zhang X, Li ZP, Jiao XX, Wang YC, Zhang YL (2009) Highly sensitive determination of microRNA using target-primed and branched rolling-circle amplification. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:3268–3272. doi:10.1002/anie.200805665
Zhang XB, Liu CH, Sun LB, Duan XR, Li ZP (2015) Lab on a single microbead: an ultrasensitive detection strategy enabling microRNA analysis at the single-molecule level. Chem Sci 6:6213–6218. doi:10.1039/c5sc02641e
Shi QN, Shi YP, Pan Y, Yue ZF, Zhang H, Yi CQ (2015) Colorimetric and bare eye determination of urinary methylamphetamine based on the use of aptamers and the salt-induced aggregation of unmodified gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:505–511. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1349-8
Lepoitevin M, Lemouel M, Bechelany M, Janot JM, Balme S (2015) Gold nanoparticles for the bare-eye based and spectrophotometric detection of proteins, polynucleotides and DNA. Microchim Acta 182:1223–1229. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1408-1
Zhou DD, Xie GM, Gao XQ, Chen XP, Zhang X (2016) Colorimetric determination of staphylococcal enterotoxin B via DNAzyme-guided growth of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1919-z
Li RD, Yin BC, Ye BC (2016) Ultrasensitive, colorimetric detection of microRNAs based on isothermal exponential amplification reaction-assisted gold nanoparticle amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 86:1011–1016. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.042
Guo S, Yang F, Zhang YL, Ning Y, Yao QF, Zhang GJ (2014) Amplified fluorescence sensing of miRNA by combination of graphene oxide with duplex-specific nuclease. Anal Methods 6:3598–3603. doi:10.1039/c4ay00345d
Liu L, Gao YP, Liu HP, Xia N (2015) An ultrasensitive electrochemical miRNAs sensor based on miRNAs-initiated cleavage of DNA by duplex-specific nuclease and signal amplification of enzyme plus redox cycling reaction. Sensors Actuators B 208:137–142. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2014.11.023
Wang Q, Li RD, Yin BC, Ye BC (2015) Colorimetric detection of sequence-specific microRNA based on duplex-specific nuclease-assisted nanoparticle amplification. Analyst 140:6306–6312. doi:10.1039/c5an01350j
Grabar KC, Freeman RG, Hommer MB, Natan MJ (1995) Preparation and characterization of Au colloid monolayers. Anal Chem 67:735–743. doi:10.1021/ac00100a008
Acknowledgments
The project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21405032) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (B2014201162 and B2016201052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 423 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Hy., Yang, L., Zhou, Xy. et al. A gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric strategy coupled to duplex-specific nuclease signal amplification for the determination of microRNA. Microchim Acta 184, 525–531 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2030-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2030-1