Abstract
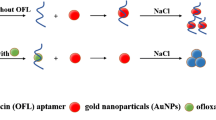
We report on a sensitive and specific method for the visual and colorimetric detection of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) in human urine by using the 8-OHdG-aptamer (Apt) as the recognition element. The aptamer was adsorbed on the surface of gold nanoparticles which enhances their stability. On addition of 8-OHdG, the conformation of the aptamer changes to form a G-quadruplex structure, thereby losing the ability to protect the nanoparticles and causing a color change from red to blue. The conformational changes were also studied by circular dichroism. The response is linearly dependent on the concentration of 8-OHdG in the range from 5.6 to 282 nM, the limit of detection is 1.7 nM, the relative standard deviation ranges from 1.1 to 4.2 % (for n = 6), and the recoveries range from 95.9 to 104.9 %. The method paves the way for visual analysis of samples without the use of costly instruments.

8-OHdG-aptamer was adsorbed onto the surface of AuNPs which enhances their stability. On addition of 8-OHdG, the conformation of 8-OHdG-aptamer changes to form a G-quadruplex structure, losing the ability to protect the AuNPs and causing a color change of the system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuo HW, Chou SY, Hu TW, Wu FY, Chen DJ (2007) Urinary 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and genetic polymorphisms in breast cancer patients. Mutat Res 631:62–68
Han YY, Donovan M, Sung FC (2010) Increased urinary 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine excretion in long-distance bus drivers in Taiwan. Chemosphere 79:942–948
Mesaros C, Arora JS, Wholer A, Vachani A, Blair IA (2012) 8-Oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine as a biomarker of tobacco-smoking-induced oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 53:610–617
Bialkowski K, Kowara R, Windorbska W, Olinski R (1996) 8-Oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine level in lymphocytes DNA of cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy. Cancer Lett 99:93–97
Isobe C, Abe T, Terayama Y (2010) Levels of reduced and oxidized coenzymeQ-10 and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with living Parkinson’s disease demonstrate that mitochondrial oxidative damage and/or oxidative DNA damage contributes to the neurodegenerative process. Neurosci Lett 469:159–163
Broedbaek K, Weimann A, Stovgaard ES, Poulsen HE (2011) Urinary 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro -2′-deoxyguanosine as a biomarker in type 2 diabetes. Free Radic Biol Med 51:1473–1479
Mei S, Yao Q, Wu C, Xu G (2005) Determination of urinary 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine by two approaches—capillary electrophoresis and GC/MS: an assay for in vivo oxidative DNA damage in cancer patients. J Chromatogr B 827:83–87
Kaneko K, Kimata T, Tsuji S, Ohashi A, Imai Y, Sudo H, Kitamura N (2012) Measurement of urinary 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2-deoxyguanosine in a novel point-of-care testing device to assess oxidative stress in children. Clin Chim Acta 413:1822–1826
Wang CJ, Yang NH, Chang CC, Liou SH, Lee HL (2011) Rapid and simple one-step membrane extraction for the determination of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine in human plasma by a combination of on-line solid phase extraction and LC–MS/MS. J Chromatogr B 879:3538–3543
Koide S, Kinoshita Y, Ito N, Kimura J, Yokoyama K, Karube I (2010) Determination of human serum 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) by HPLC-ECD combined with solid phase extraction (SPE). J Chromatogr B 878:2163–2167
Yao QH, Mei SR, Weng QF, Zhang PD, Yang Q, Wu CY, Xu GW (2004) Determination of urinary oxidative DNA damage marker 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine and the association with cigarette smoking. Talanta 63:617–623
Li B, Du Y, Dong S (2009) DNA based gold nanoparticles colorimetric sensors for sensitive and selective detection of Ag(I) ions. Anal Chim Acta 644:78–82
Chen L, Wu N, Sun B, Su H, Ai S (2013) Colorimetric detection of peroxynitrite-induced DNA damage using gold nanoparticles, and on the scavenging effects of antioxidants. Microchim Acta 180(7–8):573–580
Gu JA, Lin YJ, Chia YM, Lin HY, Huang ST (2013) Colorimetric and bare-eye determination of fluoride using gold nanoparticle agglomeration probes. Microchim Acta 180(9–10):801–806
Xu Q, Du S, Jin G, Li H, Hu XY (2011) Determination of acetamiprid by a colorimetric method based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 173(3–4):323–329
Miyaji H, Sato W, Sessler JL (2000) Naked-eye detection of anions in dichloromethane: colorimetric anion sensors based on calix. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 39:1777–1780
Cui L, Ke G, Zhang WY, Yang CJ (2011) A universal platform for sensitive and selective colorimetric DNA detection based on Exo III assisted signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2796–2800
Chen YY, Tseng CW, Chang HY, Hung YL, Huang CC (2011) Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assays for coagulation-related proteins and their inhibition reactions. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3160–3166
Zhang LP, Hu B, Wang JH (2012) Label-free colorimetric sensing of ascorbic acid based on Fenton reaction with unmodified gold nanoparticle probes and multiple molecular logic gates. Anal Chim Acta 717:127–133
Ray P, Rialon-Guevara KL, Veras E, Sullenger BA, White RR (2012) Comparing human pancreatic cell secretomes by in vitro aptamer selection identifies cyclophilin B as a candidate pancreatic cancer biomarker. J Clin Invest 122:1734–1741
Yildirim N, Long F, Gao C, He M, Shi HC, Gu AZ (2012) Aptamer-based optical biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of 17beta-estradiol in water samples. Environ Sci Technol 46:3288–3294
Duan J, Yang M, Lai Y, Yuan J, Zhan J (2012) A colorimetric and surface-enhanced Raman scattering dual-signal sensor for Hg2+ based on Bismuthiol II-capped gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 723:88–93
Miyachi Y, Shimizu N, Ogino C, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2009) Selection of a DNA aptamer that binds 8-OHdG using GMP-agarose. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:3619–3622
Li ZP, Duan XR, Liu CH, Du BA (2006) Selective determination of cysteine by resonance light scattering technique based on self-assembly of gold nanoparticles. Anal Biochem 351:18–25
Guo Y, Wang Z, Qu W, Shao H, Jiang X (2011) Colorimetric detection of mercury, lead and copper ions simultaneously using protein-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 26:4064–4069
Yang C, Wang Y, Marty JL, Yang X (2011) Aptamer-based colorimetric biosensing of Ochratoxin A using unmodified gold nanoparticles indicator. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2724–2727
Elghanian R, Storhoff JJ, Mucic RC, Letsinger RL, Mirkin CA (1997) Selective colorimetric detection of polynucleotides based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticles. Science 277:1078–1081
Zhao W, Chiuman W, Lam JCF, McManus SA, Chen W, Cui Y, Pelton R, Brook MA, Li Y (2008) DNA aptamer folding on gold nanoparticles: from colloid chemistry to biosensors. J Am Chem Soc 130:3610–3618
Zheng B, Cheng S, Liu W, Lam MHW, Liang H (2012) A simple colorimetric pH alarm constructed from DNA–gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 741:106–113
Kong DM, Wu J, Wang N, Yang W, Shen HX (2009) Peroxidase activity–structure relationship of the intermolecular four-stranded G-quadruplex–hemin complexes and their application in Hg2+ ion detection. Talanta 80:459–465
Jangir DK, Dey SK, Kundu S, Mehrotra R (2012) Assessment of amsacrine binding with DNA using UV–visible, circular dichroism and Raman spectroscopic techniques. J Photochem Photobiol B 114:38–43
Wei X, Qi L, Tan J, Liu R, Wang F (2010) A colorimetric sensor for determination of cysteine by carboxymethyl cellulose-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 671:80–84
Wu ZS, Guo MM, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2007) G-rich oligonucleotide-functionalized gold nanoparticle aggregation. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:2623–2626
Zhang SW, Xing J, Cai LS, Wu CY (2009) Molecularly imprinted monolith in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with HPLC/UV detection for determination of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine in urine. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:479–487
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21177052), the Foundation of National 863 Plan of China (No. 2012AA063501), the Science and Technology Program of Hunan Province in China (No. 2010SK3039) and the Construct Program of the Key Discipline (Public Health and Preventive Medicine) in Hunan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 594 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JC., Wang, YS., Rang, WQ. et al. Colorimetric determination of 8-hydroxy–2′-deoxyguanosine using label-free aptamer and unmodified gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 181, 903–910 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1173-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1173-1