Abstract
The authors describe a colorimetric method for the sensitive and selective detection of Pb(II). It is based on the use exonuclease I (Exo I), a Pb(II)-binding aptamer bound to gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), and a DNA strand that complementary to the aptamer. In the absence of Pb(II), the dsDNA on the AuNPs prevents aggregation of the AuNPs in the presence of NaCl. In the presence of Pb(II), however, the aptamer binds Pb(II) and complementary strand is released and digested by Exo I. As a result, the solution of AuNPs undergoes a color change from red to purple if salt is added to the sample. The assay is selective for Pb(II) and has a limit of detection as low as 2.4 nM. It was successfully applied to the determination of Pb(II) in spiked tap water.

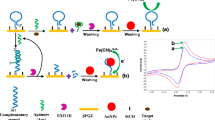
Schematic presentation of the aptamer based method for Pb2+ detection via salt-induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles and colorimetric quantitation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rom WN, Markowitz SB (2007) Environmental and occupational medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Islam E, Liu D, Li T, Yang X, Jin X, Khan MA, Mahmood Q, Hayat Y, Imtiaz M (2011) Effect of Pb toxicity on the growth and physiology of two ecotypes of Elsholtzia argyi and its alleviation by Zn. Environ Toxicol 26(4):403–416
Lo W, Chua H, Lam K-H, Bi S-P (1999) A comparative investigation on the biosorption of lead by filamentous fungal biomass. Chemosphere 39(15):2723–2736
Rastogi S (2008) Renal effects of environmental and occupational lead exposure. Indian J Occup Environ Med 12(3):103
Vaziri ND (2008) Mechanisms of lead-induced hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Am J Phys Heart Circ Phys 295(2):H454–H465
Niu R, Sun Z, Cheng Z, Li Z, Wang J (2009) Decreased learning ability and low hippocampus glutamate in offspring rats exposed to fluoride and lead. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 28(2):254–258
He Q, Chang X, Huang X, Hu Z (2008) Determination of trace elements in food samples by ICP-AES after preconcentration with p-toluenesulfonylamide immobilized on silica gel and nanometer SiO2. Microchim Acta 160(1–2):147–152
Aydin FA, Soylak M (2010) Separation, preconcentration and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometric (ICP-MS) determination of thorium (IV), titanium (IV), iron (III), lead (II) and chromium (III) on 2-nitroso-1-naphthol impregnated MCI GEL CHP20P resin. J Hazard Mater 173(1):669–674
Zhang Y, Hong H, Cai W (2011) Tumor-targeted drug delivery with aptamers. Curr Med Chem 18(27):4185–4194
Song K-M, Lee S, Ban C (2012) Aptamers and their biological applications. Sensors 12(1):612–631
Robati RY, Arab A, Ramezani M, Langroodi FA, Abnous K, Taghdisi SM (2016) Aptasensors for quantitative detection of kanamycin. Biosens Bioelectron 82:162–172
Cao X-H, Wang Q, Li J, Yi C, Li M-J (2017) Gold nanoparticles functionalized with Ru(II)bipyridyl labeled DNA as a luminescent probe for the sensitive determination of DNase I. Microchim Acta 184(9):3273–3279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2330-0
Zhao W, Lam JCF, Chiuman W, Brook MA, Li Y (2008) Enzymatic cleavage of nucleic acids on gold nanoparticles: a generic platform for facile colorimetric biosensors. Small 4(6):810–816. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200700757
Emrani A, MohammadáDanesh N, HamidáJalalian S, MohammadáTaghdisi S (2015) Sensitive and selective detection of digoxin based on fluorescence quenching and colorimetric aptasensors. Anal Methods 7(8):3419–3424
Taghdisi SM, Danesh NM, Lavaee P, Emrani AS, Ramezani M, Abnous K (2015) A novel colorimetric triple-helix molecular switch aptasensor based on peroxidase-like activity of gold nanoparticles for ultrasensitive detection of lead (II). RSC Adv 5(54):43508–43514
Taghdisi SM, Danesh NM, Lavaee P, Ramezani M, Abnous K (2015) An aptasensor for selective, sensitive and fast detection of lead (II) based on polyethyleneimine and gold nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 39(3):1206–1211
Chen Z, Huang Y, Li X, Zhou T, Ma H, Qiang H, Liu Y (2013) Colorimetric detection of potassium ions using aptamer-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 787:189–192
Zhao W, Chiuman W, Lam JC, McManus SA, Chen W, Cui Y, Pelton R, Brook MA, Li Y (2008) DNA aptamer folding on gold nanoparticles: from colloid chemistry to biosensors. J Am Chem Soc 130(11):3610–3618
Peng Y, Li L, Mu X, Guo L (2013) Aptamer-gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assay for the sensitive detection of thrombin. Sensors Actuators B Chem 177:818–825
Emrani AS, Danesh NM, Lavaee P, Ramezani M, Abnous K, Taghdisi SM (2016) Colorimetric and fluorescence quenching aptasensors for detection of streptomycin in blood serum and milk based on double-stranded DNA and gold nanoparticles. Food Chem 190:115–121
Ramezani M, Danesh NM, Lavaee P, Abnous K, Taghdisi SM (2015) A novel colorimetric triple-helix molecular switch aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of tetracycline. Biosens Bioelectron 70:181–187
Storhoff JJ, Elghanian R, Mucic RC, Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL (1998) One-pot colorimetric differentiation of polynucleotides with single base imperfections using gold nanoparticle probes. J Am Chem Soc 120(9):1959–1964
Yang C, Wang Q, Xiang Y, Yuan R, Chai Y (2014) Target-induced strand release and thionine-decorated gold nanoparticle amplification labels for sensitive electrochemical aptamer-based sensing of small molecules. Sensors Actuators B Chem 197:149–154
Sun H, Yu L, Chen H, Xiang J, Zhang X, Shi Y, Yang Q, Guan A, Li Q, Tang Y (2015) A colorimetric lead (II) ions sensor based on selective recognition of G-quadruplexes by a clip-like cyanine dye. Talanta 136:210–214
Wang Z, Chen B, Duan J, Hao T, Jiang X, Guo Z, Wang S (2015) A test strip for lead (II) based on gold nanoparticles multi-functionalized by DNAzyme and barcode DNA. J Anal Chem 70(3):339–345
Yan M, Zhu C, Huang Y, Yan J, Chen A (2017) Ultrasensitive detection of lead(II) using a turn-on probe based on the use of an aptamer and a water-soluble fluorescent perylene probe. Microchim Acta 184(7):2439–2444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2292-2
Taghdisi SM, Danesh NM, Ramezani M, Alibolandi M, Abnous K (2017) Voltammetric determination of lead(II) by using exonuclease III and gold nanoparticles, and by exploiting the conformational change of the complementary strand of an aptamer. Microchim Acta 184(8):2783–2790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2316-y
Yuan M, Song Z, Fei J, Wang X, Xu F, Cao H, Yu J (2017) Aptasensor for lead(II) based on the use of a quartz crystal microbalance modified with gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184(5):1397–1403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2135-1
Acknowledgments
Financial support of this study was provided by Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 2028 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahdordizadeh, M., Yazdian-Robati, R., Ansari, N. et al. An aptamer-based colorimetric lead(II) assay based on the use of gold nanoparticles modified with dsDNA and exonuclease I. Microchim Acta 185, 151 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2699-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2699-4