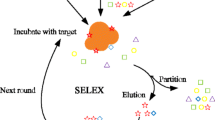
Abstract
The method referred to as “systemic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment” (SELEX) was introduced in 1990 and ever since has become an important tool for the identification and screening of aptamers. Such nucleic acids can recognize and bind to their corresponding targets (analytes) with high selectivity and affinity, and aptamers therefore have become attractive alternatives to traditional antibodies not the least because they are much more stable. Meanwhile, they have found numerous applications in different fields including food quality and safety monitoring. This review first gives an introduction into the selection process and to the evolution of SELEX, then covers applications of aptamers in the surveillance of food safety (with subsections on absorptiometric, electrochemical, fluorescent and other methods), and then gives conclusions and perspectives. The SELEX method excels by its features of in vitro, high throughput and ease of operation. This review contains 86 references.

Figure
Aptamers, novel recognition probes screened with SELEX, have been adopted as substitution to antibody in various fields and also widely applied in food safety monitoring.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346:818–822
Tuerk C, Gold L (1990) Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 249:505–510
Ciesiolka J, Gorski J, Yarus M (1995) Selection of an RNA domain that binds Zn2+. RNA 1:538–550
Wilson C, Szostak JW (1998) Isolation of a fluorophore-specific DNA aptamer with weak redox activity. J Biol Chem 5:609–617
Yang Q, Goldstein IJ, Mei HY, Engelke DRX, Affiliations A (1998) DNA ligands that bind tightly and selectively to cellobiose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:5462–5467
Famulok M, Huttenhofer A (1996) In vitro selection analysis of neomycin binding RNAs with a mutagenized pool of variants of the 16S rRNA decoding region. Biochemistry 35:4265–4270
Kraus E, James W, Barclay AN (1998) Cutting edge: Novel RNA ligands able to bind CD4 antigen and inhibit CD4+ T lymphocyte function. J Immunol 160:5209–5212
Fang XH, Tan WH (2010) Aptamers generated from cell-SELEX for molecular medicine: A chemical biology approach. Acc Chem Res 43:48–57
Mascini M, Palchetti I, Tombelli S (2010) Nucleic acid and peptide aptamers: Fundamentals and bioanalytical aspects. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:1316–1332
Jiang ZL, Fan YY, Liang AH, Wen GQ, Liu QY, Li TS (2010) Resonance scattering spectral detection of trace Pb2+ using aptamer-modified AuPd nanoalloy as probe. Plasmonics 5:375–381
Pelossof G, Tel-Vered R, Liu XQ, Willner I (2011) Amplified surface plasmon resonance based DNA biosensors, aptasensors, and Hg2+ sensors using hemin/G-quadruplexes and Au nanoparticles. Chem Eur J 17:8904–8912
Bonel L, Vidal JC, Duato P, Castillo JR (2011) An electrochemical competitive biosensor for ochratoxin A based on a DNA biotinylated aptamer. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3254–3259
Zhang JK, Zhang BB, Wu Y, Jia SR, Fan T, Zhang ZY, Zhang CZ (2010) Fast determination of the tetracyclines in milk samples by the aptamer biosensor. Analyst 135:2706–2710
Liang M, Liu R, Su RX, Qi W, Wang LB, He ZM (2012) Aptamer-based sensing technology towards food safety analysis. Progr Chem 24:1378–1387
Michaud M, Jourdan M, Ravelet C, Villet A, Ravel A, Grosset C, Peyrin E (2004) Immobilized DNA aptamers as target-specific chiral stationary phase for resolution of nucleoside and amino acid derivative enantiomers. Anal Chem 76:1015–1020
German I, Buchanan DD, Kennedy RT (1998) Aptamers as ligands in affinity probe capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem 70:4540–4545
Dick LW Jr, McGown LB (2004) Aptamer-enhanced laser desorption/ionization for affinity mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 76:3037–3041
Tombelli S, Minunni M, Mascini M (2005) Analytical application of aptamers. Biosens Bioelectron 20:2424–2434
Mehta J, Rouah-Martin E, Dorst BV, Maes B, Herrebout W, Scippo ML, Dardenne F, Blust R, Robbens J (2012) Selection and characterization of PCB-binding DNA aptamers. Anal Chem 84:1669–1676
Stoltenburg R, Reinemann C, Strehlitz B (2007) SELEX-A (r) evolutionary method to generate high-affinity nucleic acid ligands. Biomol Eng 24:381–403
Cox JC, Ellington AD (2001) Automated selection of anti-protein aptamers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9:2525–2531
Charlton J, Kirschenheuter GP, Smith D (1997) Highly potent irreversible inhibitors of neutrophil elastase generated by selection from a randomized DNA-valine phosphonate library. Biochemistry 36:3018–3026
Zimmermann GR, Wick CL, Shields TP, Jenison RD, Pardi A (2000) Molecular interactions and metal binding in the theophylline-binding core of an RNA aptamer. RNA 6:659–667
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1992) Selection in vitro of single-stranded DNA molecules that fold into specific ligand-binding structures. Nature 355:850–852
Daniels DA, Chen H, Hicke BJ, Swiderek KM, Gold L, Affiliations A (2003) A Tenascin-C aptamer identified by tumor cell SELEX: Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:15416–15421
Mendonsa SD, Bowser MT (2004) In vitro evolution of functional DNA using capillary electrophoresis. J Am Chem Soc 126:20–21
Golden MC, Collins BD, Willis MC (2000) Diagnostic potential of Photo SELEX-evolved ssDNA aptamers. J Biotechnol 81:167–178
Niazi JH, Lee SJ, Kim YS, Gu MB (2007) ssDNA aptamers that selectively bind oxytetracycline. Bioorg Med Chem 16:1261–1265
Bruno JG, Kiel L (2002) Use of magnetic beads in selection and detection of biotoxin aptamers by electrochemiluminescence and enzymatic methods. Biotechniques 32:178–183
Tok JBH, Cho J, Rando J (2000) RNA aptamers that specifically bind to a 16S ribosomal RNA decoding region construct. Nucleic Acids Res 28:2902–2910
Tuerk C, MacDougal S, Gold L (1992) RNA pseudoknots that inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:6988–6992
Boiziau C, Dausse E, Yurchenko L, Toulme JJ (1999) DNA aptamers selected against the HIV-1 trans-Activation-responsive RNA element form RNA-DNA kissing complexes. J Biol Chem 274:12730–12737
Bock LC, Griffin LC, Latham JA, Vermaas EH, Toole JJ (1992) Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin. Nature 355:564–566
Jo M, Ahn JY, Lee J, Lee S, Hong SW, Yoo JW, Kang J, Dua P, Lee DK, Hong S, King S (2011) Development of single-stranded DNA aptamers for specific bisphenol A detection. Oligonucleotides 21:85–91
Kim YS, Jung HS, Matsuura T, Lee HY, Kawai T, Gu MB (2007) Electrochemical detection of 17β-estradiol using DNA aptamer immobilized gold electrode chip. Biosens Bioelectron 22:2525–2531
Cruz-Aguado JA, Penner G (2008) Determination of ochratoxin A with a DNA aptamer. J Agric Food Chem 56:10456–10561
Chang TW, Blank M, Janardhanan P, Singh BR, Mello C, Blind M, Cai S (2010) In Vitro selection of RNA aptamers that inhibit the activity of type abotulinum neurotoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 396:854–860
McKeague M, Bradley CR, Girolamo AD, Visconti A, Miller JD, DeRoser MC (2010) Screening and initial binding assessment of fumosin B-1 aptamers. Int J Mol Sci 11:4864–4881
NeoVentures Biotechnology Inc. (2013) Aptamer catalogue. http://neoventures.ca/aptamer -database/.
Tang JJ, Xie JW, Shao NS, Yan Y (2006) The DNA aptamers that specifically recognize ricin toxin are selected by two in vitro selection methods. Electrophoresis 27:1303–1311
Joshi R, Janagama H, Dwivedi HP, Senthil Kumar TMA, Jaykus LA, Schefers J, Sreevatsan S (2009) Characterization and application of DNA aptamers for the capture and detection of Salmonella enterica serovars. Mol Cell Probes 23:20–28
Stratis-Cullum DN, McMasters S, Pellegrino PM (2009) Evaluation of relative aptamer binding to campylobacter jejuni bacteria using affinity probe capillary electrophoresis. Anal Lett 42:2389–2402
Ohk SH, Koo OK, Sen T, Yamamoto CM, Bhunia AK (2010) Antibody-aptamer functionalized fibre-optic biosensor for specific detection of Listeria monocytogenes from food. J Appl Microbiol 109:808–817
Cao X, Li S, Chen L, Ding HM, Xu H, Huang YP, Li J, Liu NL, Cao WH, Zhu YJ, Shen BF, Shao NF (2009) Combining use of a panel of ssDNA aptamers in the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Nucleic Acids Res 37:4621–4628
Camille LAH, Zhang HQ, Guan LL, Li XF, Chris LX (2008) Selection of aptamers against live bacterial cells. Anal Chem 80:7812–7819
Kim J, Kim MY, Kim HS, Hah SS (2011) Binding of uranyl ion by a DNA aptamer attached to a solid support. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21:4020–4022
Liu CW, Hsieh CW, Huang CC, Lin ZH, Chang HT (2008) Detection of mercury(II) based on Hg2+–DNA complexes inducing the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Chem Commun 19:2242–2244
Liu CW, Huang CC, Chang HT (2009) Highly selective DNA-based sensor for lead (II) and mercury (II) Ions. Anal Chem 81:2383–2387
Berens C, Thain A, Schroeder R (2001) A tetracycline binding RNA aptamer. Bioorg Med Chem 9:2549–2556
Kwon M, Chun SM, Jeong S, Yu J (2001) In vitro selection of RNA against kanamycin B. Mol Cell 11:303–311
Stead SL, Ashwin H, Johnston BH, Dallas A, Kazakov SA, Tarbin JA, Sharman M, Kay J, Keely BJ (2010) A RNA-aptamer-based assay for the detection and analysis of malachite green and leucomalachite green residues in fish tissue. Anal Chem 82:2652–2660
Joeng CB, Niazi JH, Lee SJ, Gu MB (2009) ssDNA aptamers that recognize diclofenac and 2-anilinophenylacetic acid. Bioorg Med Chem 17:5380–5387
He J, Liu Y, Fan M, Liu X (2011) Isolation and identification of the DNA aptamer target to acetamiprid. J Agric Food Chem 59:1582–1586
Lato SM, Ellington AD (1996) Screening chemical libraries for nucleic acid binding drugs by in vitro selection a test case with lividomycin. Mol Divers 21:103–110
Situ C, Buijs J, Mooney MH, Buijs J (2010) Advances in surface plasmon resonance biosensor technology towards high-throughput, food-safety analysis. Trends Anal Chem 29:1305–1315
Vallejo-Cordoba B, Gonzalez-Cordova AF (2010) Capillary electrophoresis for the analysis of contaminants in emerging food safety issues and food traceability. Electrophoresis 31:2154–2164
Hernandez F, Portoles T, Pitarch E, López FJ (2011) Gas chromatography coupled to high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry to analyze trace-level organic compounds in the environment, food safety and toxicology. Trends Anal Chem 30:388–400
Karoonuthaisiri N, Charlermroj R, Uawisetwathana U (2009) Development of antibody array for simultaneous detection of foodborne pathogens. Biosens Bioelectron 24:1641–1648
Chai F, Wang C, Wang T, Li L, Su Z (2010) Colorimetric detection of Pb2+ using glutathione functionalized gold nanoparticles. Appl Mater Interfaces 2:1466–1470
Wu LP, Zhao HW, Qin ZH, Zhao XY, Pu WD (2009) Highly selective Hg (II) ion detection based on linear blue-shift of the maximum absorption wavelength of silver nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 24:3153–3158
Wan YX, Wei TH, Jian RZ, Hong QL, Nian BL (2012) A triple-channel optical signal probe for Hg2+ detection based on acridine orange and aptamer-wrapped gold nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 22:11479–11482
Li T, Li B, Wang E, Dong S (2009) G-quadruplex-based DNAzyme for sensitive mercury detection with the naked eye. Chem Commun 24:3551–3553
Yang C, Lates V, Prieto-Simon B, Marty JL, Yang XR (2012) Aptamer-DNAzyme hairpins for biosensing of Ochratoxin A. Biosens Bioelectron 32:208–212
Yang C, Wang Y, Marty JL, Yang X (2011) Aptamer-based colorimetric biosensing of ochratoxin A using unmodified gold nanoparticles indicator. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2724–2727
Wang L, Ma WW, Chen W, Liu L, Ma W, Zhu YY, Xu LG, Kuang Y, Xu CY (2011) An aptamer-based chromatographic strip assay for sensitive toxin semi-quantitative detection. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3059–3062
Spahn CM, Prescott CD (1996) Throwing a spanner in the works: Antibiotics and the translation apparatus. Int J Mol Med 74:423–439
Jingbin W, Ndong M, Kai H, Matsuno K, Kayama F (2010) Placental transfer of melamine and its effects on rat dams and fetuses. Food Chem Toxicol 48:1791–1795
Song KM, Cho M, Jo H, Min K, Jeon SH, Kim T, Han MS, Ku JK, Ban C (2011) Gold nanoparticle based colorimetric detection of kanamycin using a DNA aptamer. Anal Biochem 415:175–181
Liang A, Zhou L, Qin H, Zhang Y, Quyang HX, Jiang ZY (2011) A highly sensitive aptamer-nanogold catalytic resonance scattering spectral assay for melamine. J Fluoresc 21:1907–1912
Babkina SS, Ulakhovich NA (2005) Complexing of heavy metals with DNA and new bioaffinity method of their determination based on amperometric DNA-based biosensor. Anal Chem 77:1815–1824
Xiao Y, Rowe AA, Plaxco KW (2007) Electrochemical detection of parts-per-billion lead via an electrode-bound DNAzyme assembly. J Am Chem Soc 129:262–263
Kim YJ, Kim YS, Niazi JH, Gu MB (2010) Electrochemical aptasensor for tetracycline detection. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 33:31–37
Shi L, Liang G, Li X, Liu X (2012) Impedimetric DNA sensor for detection of Hg2+ and Pb2+. Anal Methods 4:1036–1040
Kuang H, Chen W, Xu DH, Xu LG, Zhu YY, Liu LQ, Chu HQ, Peng CF, Xu CL, Zhu SF (2010) Fabricated aptamer-based electrochemical “signal-off” sensor of ochratoxin A. Biosens Bioelectron 26:710–716
Huang L, Wu JJ, Zheng L, Qian HS, Xue F, Wu YC, Pan DD, Adeloju SB, Chen W (2013) Rolling chain amplification (RCA) based signal enhanced electrochemical aptasensor for rapid and ultrasensitive detection of ochratoxin A. Analytical Chemistry online.
Nie DD, Wu HY, Zheng QS, Guo LQ, Ye PR, Hao YL, Li YN, Fu FF, Guo YG (2012) A sensitive and selective DNAzyme-based flow cytometric method for detecting Pb2+ ions. Chem Commun 48:1150–1152
Li CL, Liu KT, Lin YW, Chang HT (2011) Fluorescence detection of lead (II) ions through their induced catalytic activity of DNAzymes. Anal Chem 83:225–230
Won-Bo S, Hyoyoung M, Hyo-Arm J, Jack AO, Duck-Hwa C, Kim M-G (2014) Chemiluminescence competitive aptamer assay for the detection of aflatoxin B1 in corn samples. Food Control 36:30–35
Sheng L, Ren J, Miao Y, Wang J, Wang E (2011) PVP-coated graphene oxide for selective determination of ochratoxin A via quenching fluorescence of free aptamer. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3494–3499
Wang LW, Chen W, Liu L, Ma W, Zhao Y, Zhu Y, Xu L, Kuang H, Xu CL (2011) Fluorescent strip sensor for rapid determination of toxins. Chem Commun 47:1574–1576
Xu WC, Lu Y (2010) Label-free fluorescent aptamer sensor based on regulation of malachite green fluorescence. Anal Chem 82:574–578
Gilad P, Ran T-V, Willner I (2012) Amplified surface Plasmon resonance and electrochemical detection of Pb2+ ions using the Pb2+-dependent DNAzyme and hemin/G-quadruplex as a label. Anal Chem 84:3703–3709
De-los-Santos-Álvarez N, Lobo-Castanón MJ, Miranda-Ordieres AJ, Tunón-Blanco P (2009) SPR sensing of small molecules with modified RNA aptamers: Detection of neomycin B. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2547–2553
Xu S (2012) Electromechanical biosensors for pathogen detection. Microchim Acta 178:245–260
Lee HJ, Kim BC, Kim KW, Kim YK, Kim J, Oh MK (2009) A sensitive method to detect Escherichia coli based on immunomagnetic separation and real-time PCR amplification of aptamers. Biosens Bioelectron 24:3550–3555
Liu GQ, Yu XF, Xue F, Chen W, Ye YK, Yang XJ, Lian YQ, Yan Y, Zong K (2012) Screening and preliminary application of a DNA aptamer for rapid detection of Salmonella O8. Microchim Acta 178:237–244
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by the Huangshan Young Scholar Fund of Hefei University of Technology (407-037025), the National Natural Science Foundation of China with grant 31328009 and the NSF of Jiangsu Province (BK20130379, 13KJB550001), the Science and Technology Research Project of General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of P. R. China (201210127, 201310135), the 12th Five Years Key Programs (2012BAK08B01-2, 2012BAK17B10, SS2012AA101001), Suzhou Science and Technology Committee Program (SS201335) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2013HGCH0008, 2012HGCX0003).
G Liu acknowledges financial support from the National Cancer Institute (Grant number: R21CA137703) and the National Institute of General Medicine (NIGMS) (5P30 GM103332). Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jingjing Wu, Yingyue Zhu, and Feng Xue contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Zhu, Y., Xue, F. et al. Recent trends in SELEX technique and its application to food safety monitoring. Microchim Acta 181, 479–491 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1156-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1156-7