Abstract
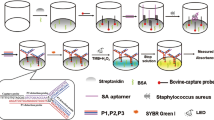
We have developed a specific method for the visual detection of Staphylococcus aureus based on aptamer recognition coupled to tyramine signal amplification technology. A biotinylated aptamer specific for S. aureus was immobilized on the surface of the wells of a microplate via biotin-avidin binding. Then, the target bacteria (S. aureus), the biotinylated-aptamer-streptavidin-HRP conjugates, biotinylated tyramine, hydrogen peroxide and streptavidin-HRP were successively placed in the wells of the microplate. After adding TMB reagent and stop solution, the intensity of the yellow reaction product can be visually inspected or measured with a plate reader. Under optimized conditions, there is a linear relationship between absorbance at 450 nm and the concentration of S. aureus in the 10 to 107 cfu mL−1 concentration range (with an R2 of 0.9976). The limit of detection is 8 cfu mL−1.

A visual detection method for Staphylococcus aureus was based on aptamer recognition coupled to tyramine signal amplification. The linear range was from 10 to 107 cfu mL-1 and the limit of detection was 8 cfu mL-1.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Francois O, Scherl A, Hochstrasserb D, Schrenzel J (2010) Proteomic approaches to study Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis. J Proteomics 73:701–708
Chakraborty SP, Mahapatra SK, Sahu SK, Chattopadhyay S, Pramanik P, Roy S (2011) Nitric oxide mediated Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis and protective role of nanoconjugated vancomycin. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 1:102–109
Atanassova V, Meindl A, Ring C (2011) Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcal enterotoxins in raw pork and uncooked smoked ham-a comparison of classical culturing detection and RFLP-PCR. Int J Food Microbial 68:105–113
Belkessam Y, Benali M, Moulessehoul S, Harrach D (2010) Polyclonal antibodies production against Staphylococcus aureus protein A: ELISA technique optimization for milk quality control. Afr J Biotechnol 9:764–769
Yazdankhah SP, Solverod L, Simonsen S (1999) Development and evaluation of an immunomagnetic separation-ELISA for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus thermostable nuclease in composite milk. Vet Microbiol 67:113–125
Pinto B, Chenoll E, Aznar R (2005) Identification and typing of food-borne Staphylococcus aureus by PCR-based techniques. Syst Appl Microbiol 28:340–352
Sabet NS, Subramaniam G, Navaratnam P, Sekaran SD (2007) Detection of methicillin- and aminoglycoside-resistant genes and simultaneous identification of S.aureus using triplex real-time PCR Taqman assay. J Microbiol Methods 68:157–162
Sowmya N, Thakur MS, Manonmani HK (2012) Rapid and simple DNA extraction method for the detection of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus directly from food samples: comparison of PCR and LAMP methods. J Appl Microbiol 133:106–113
Xu S (2012) Electromechanical biosensors for pathogen detection. Microchim Acta 178:245–260
Roda A, Mirasoli M, Roda B, Bonvicini F, Colliva C, Reschiglian P (2012) Recent developments in rapid multiplexed bioanalytical methods for foodborne pathogenic bacteria detection. Microchim Acta 178:7–28
Hamula CLA, Guthrie JW, Zhang HQ, Li XF, Le CX, Li XF (2006) Selection and analytical applications of aptamers. Trac-trend Anal Chem 25:681–691
Duan N, Sj W, Zhu CQ, Ma XY, Wang ZP, Yu Y, Jiang Y (2012) Dual-color upconversion fluorescence and aptamer-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles-based bioassay for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella Typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. Anal Chim Acta 723:1–6
Liu GQ, Yu XF, Xue F, Chen W, Ye YK, Yang XJ, Lian YQ, Yan Y, Zong K (2012) Screening and preliminary application of a DNA aptamer for rapid detection of Salmonella O8. Microchim Acta 178:237–244
Wu SJ, Duan N, Ma XY, Xia Y, Wang HX, Wang ZP (2013) A highly sensitive fluorescence resonance energy transfer aptasensor for staphylococcal enterotoxin B detection based on exonuclease-catalyzed target recycling strategy. Anal Chim Acta 782:59–66
Girolamo AD, McKeague M, Miller JD, DeRosa MC, Visconti A (2011) Determination of ochratoxin A in wheat after clean-up through a DNA aptamer-based solid phase extraction column. Food Chem 127:1378–1384
Wu SJ, Duan N, Wang ZP, Wang HX (2011) Aptamer-functionalized magnetic nanoparticle-based bioassay for the detection of ochratoxin a using upconversion nanoparticles as labels. Analyst 136:2306–2314
Chung CH, Kim JH, Jung J, Chung BH (2013) Nuclease-resistant DNA aptamer on gold nanoparticles for the simulantaneous detection of Pb2+ and Hg2+ inhuman serum. Biosens Bioelectron 41:827–832
Liang AH, Zhang J, Wen GQ, Liu QY, Li TS, Jiang ZL (2010) Aptamer-modified AuRu nanoparticle catalytic resonance scattering spectral assay for the determination of trace Pb2+. Chem J Chinese U 32:2366–2371
Liang AH, Zhou LP, Qin HM, Zhang Y, Ouyang HX, Jiang ZL (2011) A highly sensitive aptamer-nanogold catalytic resonance scattering spectral assay for melamine. J Fluoresc 21:1907–1921
Mei Z, Chu H, Chen W, Xue F, Liu J, Xu H, Zhang R, Zheng L (2013) Ultrasensitive one-step rapid visual detection of bisphenol A in water samples by label-free aptasensor. Biosens Bioelectron 39:26–30
Xue F, Wu JJ, Chu YQ, Mei ZL, Ye YK, Liu J, Zhang R, Peng CF, Zheng L, Chen W (2013) Electrochemical aptasensor for the determination of bisphenol A in drinking water. Microchim Acta 180:109–115
Wang P, Yang Y, Hong H, Zhang Y, Cai W, Fang D (2011) Aptamers as therapeutics in cardiovascular diseases. Curr Med Chem 18:4169–4174
Keefe AD, Pai S, Ellington A (2010) Aptamers as therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:537–550
Zhang Z, Kitching P (2000) A sensitive method for the detection of foot and mouth disease virus by in situ hybridisation using biotin-labelled oligodeoxynucleotides and tyramide signal amplification. J Virol Methods 88:187–192
Not F, Simon N, Biegala IC, Vaulot D (2002) Application of fluorescent in situ hybridization coupled with tyramide signal amplification (FISH-TSA) to assess eukaryotic picoplankton composition. Aquat Microb Ecol 28:157–166
Kubota K, Ohashi A, Imachi H, Harada H (2006) Visualization of mcr mRNA in a methanogen by fluorescence in situ hybridization with an oligonucleotide probeand two-pass tyramide signal amplification (two-pass TSA-FISH). J Microbiol Methods 66:521–528
Saha D, Acharya D, Roy D, Dhar TK (2007) Filtration-based tyramide amplification technique-a new simple approach for rapid detection of aflatoxin B1. Anal Chim Acta 387:1121–1130
Koda T, Aosasa MH, Nakaba H, Matsuda H (2003) Application of tyramide signal amplification for detection of N-glycolylneuraminic acid in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol 8:317–321
Strappe PM, Wang TH, McKenzie CA, Lowrie S, Simmonds P, Bell JE (1997) Enhancement of immunohistochemical detection of HIV-1 p24 antigen in brain by tyramide signal amplification. J Virol Methods 67:103–112
Cao XX, Li SH, Chen LC, Ding HM, Xu H, Huang YP, Li J, Liu N, Cao W, Zhu Y, Shen B, Shao N (2009) Combining use of a panel of ssDNA aptamers in the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Nucleic Acids Res 37:4621–4628
Hopman AH, Ramaekers FC, Speel EJ (1998) Rapid synthesis of biotin-, digoxigenin-, trinitrophenyl-, and fluorochrome-labeled tyramides and their application for in situ hybridization using CARD amplification. J Histochem Cytochem 46:771–777
Qi HJ, Chen SH, Zhang ML, Shi H, Wang SQ (2010) DNA microarrays for visual detection of human pathogenic microorganisms based on tyramine signal amplification coupled with gold label silver stain. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:2745–2750
Zaitsu K, Ohkura Y (1980) New fluorogenic substrates for horseradish peroxidase: rapid and sensitive assays for hydrogen peroxide and the peroxidase. Anal Biochem 109:109–113
Speel EJ, Anton HN (1999) Amplification methods to increase the sensitivity of in situ hybridization: play CARD(S). J Histochem Cytochem 47:281–288
Miao TT, Wang ZP, Li S, Wang X (2011) Sensitive fluorescent detection of Staphylococcus aureus using nanogold linked CdTe nanocrystals as signal amplification labels. Microchim Acta 172:431–437
Ruan M, Niu CG, Zeng GM (2011) Rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus via a sensitive DNA hybridization assay based on a long-time luminescent europium maker. Microchim Acta 178:105–112
Boujday S, Briandet R, Salmain M, Herry JM, Marnet PG, Gautier M, Pradier CM (2008) Detection of pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus bacteria by gold based immunosensors. Microchim Acta 163:203–209
Sung YJ, Suk HJ, Sung HY, Li T, Poo H, Kim MG (2013) Novel antibody/gold nanoparticle/magnetic nanoparticle nanocomposites for immunomagnetic separation and rapid colorimetric detection of Staphylococcus aureus in milk. Biosens Bioelectron 43:432–439
He Y, Liu HL, Xian MJ (2010) Detection and identification of Staphylococcus aureus in raw milk by hybridization to oligonucleotide microarray. Afr J Biotechnol 9:2284–2289
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by the S&T Supporting Project of Jiangsu (BE2011621, BE2010679, BE2012614), the National S&T Support Program of China (2012BAK08B01, 2011YQ170067), NSFC (21375049) NCET-11-0663 and JUSRP51309A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, J., Yu, Y., Li, C. et al. Visual detection and microplate assay for Staphylococcus aureus based on aptamer recognition coupled to tyramine signal amplification. Microchim Acta 181, 321–327 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1120-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1120-6