Abstract
We report on the voltammetric determination of the flavonoid Baicalein by using a carbon paste electrode that was doped with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. The resulting sensor exhibits excellent redox activity towards Baicalein due to the large surface area and good conductivity of the electrode. Cyclic voltammetry at various scan rates was used to investigate the redox properties of Baicalein. At the optimum conditions, the sensor displays a linear current response to Baicalein in the 0.02–10 μM concentration range, with a limit of detection of 4.2 n M. The method was successfully applied to the determination of Baicalein in spiked human blood serum samples and in a Chinese oral liquid.

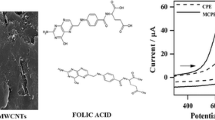
We construct a new voltammetric sensor, based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) doped Carbon paste electrode(CPE), The proposed electrode can improve the oxidation of Baicalein intensively, which can applied to the quantitative determination of Baicalein with wide linear response and low detection limit.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen Y-C, Chiou W-F, Chou Y-C et al (2003) Mechanisms in mediating the anti-inflammatory effects of baicalin and baicalein in human leukocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 465:171–181
Tanaka R, Tsujii H, Yamada T et al (2009) Novel 3a-methoxyserrat-14-en-21b-ol (PJ-1) and 3b-methoxyserrat-14-en-21b-ol (PJ-2)-curcumin, kojic acid, quercetin, and baicalein conjugates as HIV agents. Bioorg Med Chem 17:5238–5246
Chan F-L, Choi H-L, Chen Z-Y et al (2000) Induction of apoptosisin prostate cancer cell lines by a flavonoid, baicalin. Cancer Lett 160:219–228
Ikemoto S, Sugimura K, Yoshida N et al (2000) Antitumor effects of Scutellariae radix and its components baicalein, baicalin, and wogonin on bladder cancer cell lines. Urology 55:951–955
Li-Weber M (2009) New therapeutic aspects of flavones: the anticancer properties of Scutellaria and its main active constituents Wogonin, Baicalein and Baicalin. Cancer Treat Rev 35:57–68
Matsuzaki Y, Korokawa N, Terai S et al (1996) Cell death induced by baicalein in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Jpn J Cancer Res 87:170–177
Gao Z-H, Huang K-X, Yang X-L et al (1999) Free radical scavenging and antioxidant activities of £avonoids extracted from the radix of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. Biochim Biophys Acta 1472:643–650
Hamada H, Hiramatsu M, Edamatsu R, Mori A (1933) Free radical scavenging action of Baicalein. Arch Biochem Biophys 306:261–266
Li B-X, Guo L-L, Xu C-L, Ma L-M (2008) Flow-injection chemiluminescence determination of chrysin and baicalein assisted by theoretical prediction of chemiluminescence behavior of chrysin and baicalein. Spectrochimica Acta Part A 71:892–897
Okamoto M, Ohta M, Kakamu H, Omori T (1993) Evaluation of phenyldimethylethoxysilane treated high-performance thin-layer chromatographic plates. Application to analysis of flavonoids in Scutellariae radix. Chromatographia 35:281–284
Kotani A, Kojima S, Hakamata H, Kusu F (2006) HPLC with electrochemical detection to examine the pharmacokinetics of baicalin and baicalein in rat plasma after oral administration of a Kampo medicine. Anal Biochem 350:99–104
Zhang L, Lin G, Zuo Z (2004) High-performance liquid chromatographic method for simultaneous determination of baicalein and baicalein 7-glucuronide in rat plasma. J Pharm Biomed Anal 36:637–641
Chen G, Zhang H-W, Ye J-N (2000) Determination of baicalein, baicalin and quercetin in Scutellariae Radix and its preparations by capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection. Talanta 53:471–479
Peng Y-Y, Ding X-H, Chu Q-C et al (2003) Determination of Baicalein, Baicalin, and chlorogenic acid in Yinhuang oral liquid by capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection. Anal Lett 36:2793–2803
Iijima S (1991) Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354:56–58
Wildgoose G-G, Banks C-E, Leventis H-C, Compton R-G (2006) Chemically modified carbon nanotubes for use in electroanalysis. Microchim Acta 152:187–214
Viry L, Derre A, Poulin P et al (2010) Discrimination of dopamine and ascorbic acid using carbon nanotube fiber microelectrodes. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:9993–9995
Bhambi M, Sumana G, Malhotra B-D, Pundir C-S (2010) An amperomertic uric acid biosensor based on immobilization of uricase onto polyaniline-multiwalled carbon nanotube composite film. Artif Cell Blood Substit Bio 38:178–185
Rubianes M-D, Rivas G-A (2003) Carbon nanotubes paste electrode. Electrochem Commun 5:689–694
Park J-A, Kim B-K, Choi H-N et al (2010) Electrochemical determination of dopamine based on carbon nanotube-sol–gel titania-nafion composite film modified electrode. Bull Kor Chem Soc 31:3123–3127
Manso J, Mena M-L, Yáñez-Sedeño P et al (2007) Electrochemical biosensors based on colloidal gold–carbon nanotubes composite electrodes. J Electroanal Chem 603:1–7
Adams R-N (1958) Carbon paste electrodes. Anal Chem 30:1576–1576
Wang F, Zhao F-Y, Zhang Y-Z et al (2011) Sensitive voltammetric determination of baicalein at DNA Langmuir–Blodgett film modified glassy carbon electrode. Talanta 84:160–168
Anson F-C (1964) Application of potentiostatic current integration to the study of the adsorption of cobalt (III)-(Ethylenedinitrilo (tetraacetate) on mercury electrodes. Anal Chem 36:932–934
Yang B, Hu F-D, Wei J-P, Wang C-M (2009) Electrochemical study on Baicalein at poly-l-lysine modified glass carbon electrode. Acta Chimica Sinica 67:2585–2591
Acknowledgments
The authors really appreciate for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 20875083 & 20775073) and the Innovation Scientists & Technicians Troop Construction Projects of Zhengzhou City (10LJRC192).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Wang, F., Zhang, K. et al. Electrochemical sensor for Baicalein using a carbon paste electrode doped with carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 178, 179–186 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0812-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0812-7