Abstract
Study design
Systematic review.
Objectives
The aims of this systematic review were: (1) to determine the most commonly used methods for assessing pedicle screw placement accuracy, and (2) assess the difference in pedicle screw placement accuracy between navigation and free-hand techniques according to the classification method.
Background data
Pedicle screw fixation and spine surgery have almost become synonymous. However, there is currently no gold standard method to assess pedicle screw placement accuracy. We reviewed the literature to determine current techniques used by spine surgeons for the assessment of pedicle screw accuracy.
Methods
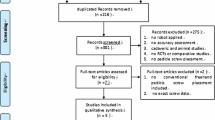
We systematically reviewed the medical literature (OVID Medline, Embase, PubMed) to identify all articles published between 2010 and 2013 that have assessed pedicle screw placement accuracy in humans. Two independent reviewers with a third independent mediator performed study screening, selection and data extraction using a blinded and objective protocol.
Results
A total of 68 relevant articles were included in this systematic review, for a total of 3442 patients, 60 cadavers and 43,305 pedicle screws. The most widely used method (37 articles) was based on 2 mm breach increments measured on computer tomography images. The second most widely used method consisted of an “in” or “out” classification system (16 articles). The remaining 15 articles used variable classification systems. Our result suggests that an average of 91.4 % of pedicle screws placed with free-hand or fluoroscopy technique where within the safe zone (<2 mm breach) in comparison to an average of 97.3 % of pedicle screws using navigation (p < 0.001) for the 2 mm increment method. Similarly, the in or out classification also showed statistically significant difference between free-hand and navigated techniques (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
The grading system based on 2 mm increments seems to be the most widely accepted method for determining pedicle screw placement accuracy. All grading systems were based on imaging alone without taking into account the direction of the breach or patient’s symptoms.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Obernauer J, Kavakebi P, Quirbach S, Thome C (2014) Pedicle-Based Non-fusion Stabilization Devices: a Critical Review and Appraisal of Current Evidence. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg 41:131–142. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-01830-0_6
Boos N, Webb JK (1997) Pedicle screw fixation in spinal disorders: a European view. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 6:2–18
Roy-Camille R, Saillant G, Mazel C (1986) Internal fixation of the lumbar spine with pedicle screw plating. Clin Orthop Relat Res 213:7–17
Roy-Camille R, Saillant G, Mazel C (1986) Plating of thoracic, thoracolumbar, and lumbar injuries with pedicle screw plates. Orthop Clin North Am 17:147–159
Magerl FP (1984) Stabilization of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine with external skeletal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 189:125–141
Krag MH, Weaver DL, Beynnon BD, Haugh LD (1988) Morphometry of the thoracic and lumbar spine related to transpedicular screw placement for surgical spinal fixation. Spine 13:27–32
Yahiro MA (1994) Review of the “Historical Cohort Study of Pedicle Screw Fixation in Thoracic, Lumbar, and Sacral Spinal Fusions” report. Spine 19:2297s–2299s
Esses SI, Sachs BL, Dreyzin V (1993) Complications associated with the technique of pedicle screw fixation. A selected survey of ABS members. Spine 18:2231–2238 (discussion 2238–2239)
Soultanis KC, Sakellariou VI, Starantzis KA, Papagelopoulos PJ (2013) Late diagnosis of perforation of the aorta by a pedicle screw. Acta Orthop Belg 79:361–367
Li G, Lv G, Passias P, Kozanek M, Metkar US, Liu Z, Wood KB, Rehak L, Deng Y (2010) Complications associated with thoracic pedicle screws in spinal deformity. Eur Spine J 19:1576–1584. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1316-y
Harimaya K, Lenke LG, Son-Hing JP, Bridwell KH, Schwend RM, Luhmann SJ, Koester LA, Sides BA (2011) Safety and accuracy of pedicle screws and constructs placed in infantile and juvenile patients. Spine 36:1645–1651. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318225b8f9
Hu XO, Donna D, Lieberman Isador H (2013) Robotic-assisted pedicle screw placement: lessons learned from the first 102 patients. Eur Spine J 22:661–666. doi:10.1007/s00586-012-2499-1
Abe Y, Ito M, Abumi K, Kotani Y, Sudo H, Minami A (2011) A novel cost-effective computer-assisted imaging technology for accurate placement of thoracic pedicle screws. J Neurosurg Spine 15:479–485. doi:10.3171/2011.6.spine10721
Costa F, Cardia A, Ortolina A, Fabio G, Zerbi A, Fornari M (2011) Spinal navigation: standard preoperative versus intraoperative computed tomography data set acquisition for computer-guidance system radiological and clinical study in 100 consecutive patients. Spine 36:2094–2098. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318201129d
Cui G, Wang Y, Kao TH, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Liu B, Li J, Zhang X, Zhu S, Lu N, Mao K, Wang Z, Zhang X, Yuan X, Dong T, Xiao S (2012) Application of intraoperative computed tomography with or without navigation system in surgical correction of spinal deformity a preliminary result of 59 consecutive human cases. Spine 37:891–900. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31823aff81
Devito DP, Kaplan L, Dietl R, Pfeiffer M, Horne D, Silberstein B, Hardenbrook M, Kiriyanthan G, Barzilay Y, Bruskin A, Sackerer D, Alexandrovsky V, Stüer C, Burger R, Maeurer J, Donald GD, Schoenmayr R, Friedlander A, Knoller N, Schmieder K, Pechlivanis I, Kim IS, Meyer B, Shoham M (2010) Clinical acceptance and accuracy assessment of spinal implants guided with SpineAssist surgical robot retrospective study. Spine 35:2109–2115. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181d323ab
Dinesh SK, Tiruchelvarayan R, Ng I (2012) A prospective study on the use of intraoperative computed tomography (iCT) for image-guided placement of thoracic pedicle screws. Br J Neurosurg 26:838–844. doi:10.3109/02688697.2012.690917
Fan Chiang CY, Tsai TT, Chen LH, Lai PL, Fu TS, Niu CC, Chen WJ (2012) Computed tomography-based navigation-assisted pedicle screw insertion for thoracic and lumbar spine fractures. Chang Gung Med J 35:332–338
Kuraishi S, Takahashi J, Hirabayashi H, Hashidate H, Ogihara N, Mukaiyama K, Kato H (2013) Pedicle morphology using computed tomography-based navigation system in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech 26:22–28. doi:10.1097/BSD.0b013e31823162ef
Lu S, Zhang YZ, Wang Z, Shi JH, Chen YB, Xu XM, Xu YQ (2012) Accuracy and efficacy of thoracic pedicle screws in scoliosis with patient-specific drill template. Med Biol Eng Comput 50:751–758. doi:10.1007/s11517-012-0900-1
Ma T, Xu YQ, Cheng YB, Jiang MY, Xu XM, Xie L, Lu S (2012) A novel computer-assisted drill guide template for thoracic pedicle screw placement: a cadaveric study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132:65–72. doi:10.1007/s00402-011-1383-5
Modi HN, Suh SW, Hong JY, Yang JH (2010) Accuracy of thoracic pedicle screw using ideal pedicle entry point in severe scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:1830–1837. doi:10.1007/s11999-010-1280-1
Ravi B, Zahrai A, Rampersaud R (2011) Clinical accuracy of computer-assisted two-dimensional fluoroscopy for the percutaneous placement of lumbosacral pedicle screws. Spine 36:84–91. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181cbfd09
Ringel F, Stüer C, Reinke A, Preuss A, Behr M, Auer F, Stoffel M, Meyer B (2012) Accuracy of robot-assisted placement of lumbar and sacral pedicle screws a prospective randomized comparison to conventional freehand screw implantation. Spine 37:E496–E501. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31824b7767
Rodrigues LM, Nicolau RJ, Milani C (2011) Computed tomographic evaluation of thoracic pedicle screw placement in idiopathic scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop B 20:195–198. doi:10.1097/BPB.0b013e328344105c
Schizas C, Thein E, Kwiatkowski B, Kulik G (2012) Pedicle screw insertion: robotic assistance versus conventional C-arm fluoroscopy. Acta Orthop Belg 78:240–245
Shin BJ, Njoku IU, Tsiouris AJ, Härtl R (2013) Navigated guide tube for the placement of mini-open pedicle screws using stereotactic 3D navigation without the use of K-wires technical note. J Neurosurg Spine 18:178–183. doi:10.3171/2012.10.spine12569
Takahashi J, Hirabayashi H, Hashidate H, Ogihara N, Kato H (2010) Accuracy of multilevel registration in image-guided pedicle screw insertion for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 35:347–352. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181b77f0a
Waschke A, Walter J, Duenisch P, Reichart R, Kalff R, Ewald C (2013) CT-navigation versus fluoroscopy-guided placement of pedicle screws at the thoracolumbar spine: single center experience of 4,500 screws. Eur Spine J 22:654–660. doi:10.1007/s00586-012-2509-3
Wu ZX, Huang LY, Sang HX, Ma ZS, Wan SY, Cui G, Lei W (2011) Accuracy and safety assessment of pedicle screw placement using the rapid prototyping technique in severe congenital scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech 24:444–450. doi:10.1097/BSD.0b013e318201be2a
Amato V, Giannachi L, Irace C, Corona C (2010) Accuracy of pedicle screw placement in the lumbosacral spine using conventional technique: computed tomography postoperative assessment in 102 consecutive patients. J Neurosur Spine 12:306–313. doi:10.3171/2009.9.spine09261
Bai YS, Niu YF, Chen ZQ, Zhu XD, Gabriel LK, Wong HK, Li M (2013) Comparison of the pedicle screws placement between electronic conductivity device and normal pedicle finder in posterior surgery of scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech 26:316–320. doi:10.1097/BSD.0b013e318247f21d
Cho JY, Chan CK, Lee SH, Lee HY (2012) The accuracy of 3D image navigation with a cutaneously fixed dynamic reference frame in minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Comput Aided Surg 17:300–309. doi:10.3109/10929088.2012.728625
Kim MC, Chung HT, Cho JL, Kim DJ, Chung NS (2011) Factors affecting the accurate placement of percutaneous pedicle screws during minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J 20:1635–1643. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1892-5
Oertel MF, Hobart J, Stein M, Schreiber V, Scharbrodt W (2011) Clinical and methodological precision of spinal navigation assisted by 3D intraoperative O-arm radiographic imaging Technical note. J Neurosurg Spine 14:532–536. doi:10.3171/2010.10.spine091032
Bai YS, Zhang Y, Chen ZQ, Wang CF, Zhao YC, Shi ZC, Li M, Liu KP (2010) Learning curve of computer-assisted navigation system in spine surgery. Chin Med J 123:2989–2994. doi:10.3760/cmaj.issn.0366-6999.2010.21.007
Chan CY, Kwan MK, Saw LB (2010) Safety of thoracic pedicle screw application using the funnel technique in Asians: a cadaveric evaluation. Eur Spine J 19:78–84. doi:10.1007/s00586-009-1157-8
Erkan S, Hsu B, Wu C, Mehbod AA, Perl J, Transfeldt EE (2010) Alignment of pedicle screws with pilot holes: can tapping improve screw trajectory in thoracic spines? Eur Spine J 19:71–77. doi:10.1007/s00586-009-1063-0
Parker SL, McGirt MJ, Farber SH, Amin AG, Rick AM, Suk I, Bydon A, Sciubba DM, Wolinsky JP, Gokaslan ZL, Witham TF (2011) Accuracy of free-hand pedicle screws in the thoracic and lumbar spine: analysis of 6816 consecutive screws. Neurosurgery 68:170–178. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e3181fdfaf4
Liang H, Zhang C, Yan M, Zhou J (2005) Data Correction for Gantry-tilted Local CT. Conf Proc Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc Annu Conf 2:1798–1801. doi:10.1109/iembs.2005.1616797
Alhabib H, Nataraj A, Khashab M, Mahood J, Kortbeek F, Fox R (2011) Pedicle screw insertion in the thoracolumbar spine: comparison of 4 guidance techniques in the intact cadaveric spine. J Neurosurg Spine 14:664–669. doi:10.3171/2010.11.spine10177
Youkilis AS, Quint DJ, McGillicuddy JE, Papadopoulos SM (2001) Stereotactic navigation for placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Neurosurgery 48:771–778 (discussion 778–779)
Han W, Gao ZL, Wang JC, Li YP, Peng X, Rui J, Jun W (2010) Pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine: a comparison study of computer-assisted navigation and conventional techniques. Orthopedics 33(8):201–205. doi:10.3928/01477447-20100625-14
Houten JK, Nasser R, Baxi N (2012) Clinical assessment of percutaneous lumbar pedicle screw placement using the O-arm multidimensional surgical imaging system. Neurosurgery 70:990–995. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e318237a829
Iampreechakul P, Chongchokdee C, Tirakotai W (2011) The accuracy of computer-assisted pedicle screw placement in degenerative lumbrosacral spine using single-time, paired point registration alone technique combined with the surgeon’s experience. J Med Assoc Thai (Chotmaihet thangphaet) 94:337–345
Kakarla UK, Little AS, Chang SW, Sonntag VK, Theodore N (2010) Placement of percutaneous thoracic pedicle screws using neuronavigation. World Neurosurg 74:606–610. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2010.03.028
Lieberman IHH, Mitchell A, Wang Jeffrey C, Guyer Richard D (2012) Assessment of pedicle screw placement accuracy, procedure time, and radiation exposure using a miniature robotic guidance system. J Spinal Disord Tech 25:241–248. doi:10.1097/BSD.0b013e318218a5ef
Lotfinia I, Sayahmelli S, Gavami M (2010) Postoperative computed tomography assessment of pedicle screw placement accuracy. Turk Neurosurg 20:500–507
Merc M, Drstvensek I, Vogrin M, Brajlih T, Recnik G (2013) A multi-level rapid prototyping drill guide template reduces the perforation risk of pedicle screw placement in the lumbar and sacral spine. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 133:893–899. doi:10.1007/s00402-013-1755-0
Raley DA, Mobbs RJ (2012) Retrospective computed tomography scan analysis of percutaneously inserted pedicle screws for posterior transpedicular stabilization of the thoracic and lumbar spine accuracy and complication rates. Spine 37:1092–1100. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31823c80d8
Rampersaud YR, Pik JH, Salonen D, Farooq S (2005) Clinical accuracy of fluoroscopic computer-assisted pedicle screw fixation: a CT analysis. Spine 30:E183–E190 (00007632-200504010-00026 [pii])
Shin MH, Ryu KS, Park CK (2012) Accuracy and Safety in Pedicle Screw Placement in the Thoracic and Lumbar Spines: Comparison Study between Conventional C-Arm Fluoroscopy and Navigation Coupled with O-Arm (R) Guided Methods. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 52:204–209. doi:10.3340/jkns.2012.52.3.204
Sugimoto Y, Ito Y, Tomioka M, Shimokawa T, Shiozaki Y, Mazaki T, Tanaka M (2010) Clinical accuracy of three-dimensional fluoroscopy (IsoC-3D)-assisted upper thoracic pedicle screw insertion. Acta Medica Okayama 64:209–212
Rao G, Brodke DS, Rondina M, Bacchus K, Dailey AT (2003) Inter- and intraobserver reliability of computed tomography in assessment of thoracic pedicle screw placement. Spine 28:2527–2530. doi:10.1097/01.BRS.0000092341.56793.F1
Watanabe K, Matsumoto M, Tsuji T, Ishii K, Takaishi H, Nakamura M, Toyama Y, Chiba K (2010) Ball tip technique for thoracic pedicle screw placement in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis Technical note. J Neurosurg Spine 13:246–252. doi:10.3171/2010.3.spine09497
Wang VYC, Cynthia T, Lu Daniel C, Smith Justin S, Chou Dean (2010) Free-hand thoracic pedicle screws placed by neurosurgery residents: a CT analysis. Eur Spine J 19:821–827. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1293-1
Learch TJ, Massie JB, Pathria MN, Ahlgren BA, Garfin SR (2004) Assessment of pedicle screw placement utilizing conventional radiography and computed tomography: a proposed systematic approach to improve accuracy of interpretation. Spine 29:767–773 (00007632-200404010-00011 [pii])
Wu H, Gao ZL, Wang JC, Li YP, Xia P, Jiang R (2010) Pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine: a randomized comparison study of computer-assisted navigation and conventional techniques. Chin J Traumatol (Zhonghua chuang shang za zhi/Chinese Medical Association) 13:201–205
Yang BP, Wahl MM, Idler CS (2012) Percutaneous lumbar pedicle screw placement aided by computer-assisted fluoroscopy-based navigation perioperative results of a prospective, comparative, multicenter study. Spine 37:2055–2060. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31825c05cd
Braga BP, de Morais JV, Vilela MD (2010) Free-hand placement of high thoracic pedicle screws with the aid of fluoroscopy evaluation of positioning by CT scans in a four-year consecutive series. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 68:390–395. doi:10.1590/s0004-282x2010000300012
Chang KW, Wang YF, Zhang GZ, Cheng CW, Chen HY, Leng X, Chen YY (2012) Tai Chi (sic) pedicle screw placement for severe scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech 25:E67–E73. doi:10.1097/BSD.0b013e31823db498
Idler CR, Kevin W, Gorek Josef E (2010) Accuracy of percutaneous lumbar pedicle screw placement using the oblique or “owl’s-eye” view and novel guidance technology. J Neurosurg Spine 13:509–515. doi:10.3171/2010.4.spine09580
Lee CS, Park SA, Hwang CJ, Kim DJ, Lee WJ, Kim YT, Lee MY, Yoon SJ, Lee DH (2011) A novel method of screw placement for extremely small thoracic pedicles in scoliosis. Spine 36:E1112–E1116. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181ffeea2
Neal CJR, Michael K (2010) Resident learning curve for minimal-access transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in a military training program. Neurosurg Focus 28:E21. doi:10.3171/2010.1.focus1011
Samdani AF, Ranade A, Saldanha V, Yondorf MZ (2010) Learning curve for placement of thoracic pedicle screws in the deformed spine. Neurosurgery 66:290–294. doi:10.1227/01.neu.0000363853.62897.94
Samdani AF, Ranade A, Saldanha V, Yondorf MZ (2010) Learning curve for placement of thoracic pedicle screws in the deformed spine. Neurosurgery 66:290–294. doi:10.1227/01.neu.0000363853.62897.94
Su P, Zhang W, Peng Y, Liang A, Du K, Huang D (2012) Use of computed tomographic reconstruction to establish the ideal entry point for pedicle screws in idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 21:23–30. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1962-8
Su P, Zhang W, Peng Y, Liang A, Du K, Huang D (2012) Use of computed tomographic reconstruction to establish the ideal entry point for pedicle screws in idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 21:23–30. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1962-8
Tohtz SW, Rogalla P, Taupitz M, Perka C, Winkler T, Putzier M (2010) Inter- and intraobserver variability in the postoperative evaluation of transpedicular stabilization: computed tomography versus magnetic resonance imaging. Spine J 10:285–290. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2009.12.020
Van de Kelft E, Costa F, Van der Planken D, Schils F (2012) A prospective multicenter registry on the accuracy of pedicle screw placement in the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral levels with the use of the O-arm imaging system and StealthStation navigation. Spine 37:E1580–E1587. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318271b1fa
Abul-Kasim K, Ohlin A, Strömbeck A, Maly P, Sundgren PC (2010) Radiological and clinical outcome of screw placement in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: evaluation with low-dose computed tomography. Eur Spine J 19:96–104. doi:10.1007/s00586-009-1203-6
Abul-Kasim K, Ohlin A (2011) The rate of screw misplacement in segmental pedicle screw fixation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Acta Orthop 82:50–55. doi:10.3109/17453674.2010.548032
Allam Y, Silbermann J, Riese F, Greiner-Perth R (2013) Computer tomography assessment of pedicle screw placement in thoracic spine: comparison between free hand and a generic 3D-based navigation techniques. Eur Spine J 22:648–653. doi:10.1007/s00586-012-2505-7
Ammirati M, Salma A (2013) Placement of thoracolumbar pedicle screws using O-arm-based navigation: technical note on controlling the operational accuracy of the navigation system. Neurosurg Rev 36:157–162. doi:10.1007/s10143-012-0421-2
Gang C, Haibo L, Fancai L, Weishan C, Qixin C (2012) Learning curve of thoracic pedicle screw placement using the free-hand technique in scoliosis: how many screws needed for an apprentice? Eur Spine J 21:1151–1156. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-2065-2
Harimaya K, Lenke LG, Son-Hing JP, Bridwell KH, Schwend RM, Luhmann SJ, Koester LA, Sides BA (2011) Safety and accuracy of pedicle screws and constructs placed in infantile and juvenile patients. Spine 36:1645–1651. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318225b8f9
Kantelhardt SR, Martinez R, Baerwinkel S, Burger R, Giese A, Rohde V (2011) Perioperative course and accuracy of screw positioning in conventional, open robotic-guided and percutaneous robotic-guided, pedicle screw placement. Eur Spine J 20:860–868. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1729-2
Sethi A, Lee A, Vaidya R (2012) Lumbar pedicle screw placement: Using only AP plane imaging. Indian J Orthop 46:434–438. doi:10.4103/0019-5413.98832
Scheufler KM, Cyron D, Dohmen H, Eckardt A (2010) Less invasive surgical correction of adult degenerative scoliosis, Part I: technique and radiographic results. Neurosurgery 67:696–710. doi:10.1227/01.neu.0000377851.75513.fe
Xu R, Ebraheim NA, Shepherd ME, Yeasting RA (1999) Thoracic pedicle screw placement guided by computed tomographic measurements. J Spinal Disord 12:222–226
Silbermann J, Riese F, Allam Y, Reichert T, Koeppert H, Gutberlet M (2011) Computer tomography assessment of pedicle screw placement in lumbar and sacral spine: comparison between free-hand and O-arm based navigation techniques. Eur Spine J 20:875–881. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1683-4
Ughwanogho E, Patel NM, Baldwin KD, Sampson NR, Flynn JM (2012) Computed tomography-guided navigation of thoracic pedicle screws for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis results in more accurate placement and less screw removal. Spine 37:E473–E478. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318238bbd9
von Jako R, Finn MA, Yonemura KS, Araghi A, Khoo LT, Carrino JA, Perez-Cruet M (2011) Minimally invasive percutaneous transpedicular screw fixation: increased accuracy and reduced radiation exposure by means of a novel electromagnetic navigation system. Acta Neurochir 153:589–596. doi:10.1007/s00701-010-0882-4
Yson SC, Sembrano JN, Sanders PC, Santos ER, Ledonio CG, Polly DW Jr (2013) Comparison of cranial facet joint violation rates between open and percutaneous pedicle screw placement using intraoperative 3-D CT (O-arm) computer navigation. Spine 38:E251–E258. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31827ecbf1
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aoude, A.A., Fortin, M., Figueiredo, R. et al. Methods to determine pedicle screw placement accuracy in spine surgery: a systematic review. Eur Spine J 24, 990–1004 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3853-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3853-x