Abstract
Introduction
The objective of this study was to develop a novel, patient-specific, navigational template for thoracic pedicle screw placement.
Methods
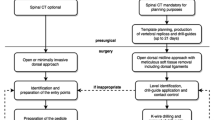
Twenty thoracic cadaver specimens were randomly divided into two groups of 10: the navigational template group and the free-hand group. A volumetric CT scan was performed on each thoracic vertebra, and a three-dimensional reconstruction model was generated. A drill template was designed with a surface that was the inverse of the posterior vertebral surface. Each drill template and its corresponding vertebra were manufactured using a rapid prototyping technique and tested for violation. Two hundred and forty screws were implanted into the thoracic spines and the positions of the screws were evaluated.
Results
Two hundred and forty thoracic screws were inserted using either the navigational template method or the free-hand method. The accuracy rate and incidence of risk for setting thoracic pedicle screws differed statistically between the two methods (P < 0.05): The navigational template method had a higher accuracy rate and a lower incidence of risk than the free-hand method. Moreover, the free-hand method had a significant learning curve, whereas a learning curve for the navigational template method was not obvious.
Conclusion
We have developed a novel, patient-specific, navigational template for thoracic pedicle screw placement with good applicability and high accuracy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Cho SK, Bridwell KH, Sides B, Blanke K (2004) Comparative analysis of pedicle screw versus hook instrumentation in posterior spinal fusion of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 29(18):2040–2048 00007632-200409150-00014
Lee SM, Suk SI, Chung ER (2004) Direct vertebral rotation: a new technique of three-dimensional deformity correction with segmental pedicle screw fixation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 29(3):343–349 00007632-200402010-00020
Liljenqvist UR, Halm HF, Link TM (1997) Pedicle screw instrumentation of the thoracic spine in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 22(19):2239–2245
Amiot LP, Lang K, Putzier M, Zippel H, Labelle H (2000) Comparative results between conventional and computer-assisted pedicle screw installation in the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spine. Spine 25(5):606
Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Cho YS, Riew KD (2004) Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine: is it safe? Spine 29(3):333
Panjabi MM, O’Holleran JD, Crisco JJ 3rd, Kothe R (1997) Complexity of the thoracic spine pedicle anatomy. Eur Spine J 6(1):19–24
Ebraheim NA, Jabaly G, Xu R, Yeasting RA (1997) Anatomic relations of the thoracic pedicle to the adjacent neural structures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 22(14):1553–1556 discussion 1557
Vaccaro AR, Rizzolo SJ, Allardyce TJ, Ramsey M, Salvo J, Balderston RA, Cotler JM (1995) Placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Part I: Morphometric analysis of the thoracic vertebrae. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77(8):1193–1199
Vaccaro AR, Rizzolo SJ, Balderston RA, Allardyce TJ, Garfin SR, Dolinskas C, An HS (1995) Placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Part II: An anatomical and radiographic assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77(8):1200–1206
Lu S, Xu YQ, Zhang YZ, Li YB, Xie L, Shi JH, Guo H, Chen GP, Chen YB (2009) A novel computer-assisted drill guide template for lumbar pedicle screw placement: a cadaveric and clinical study. Int J Med Robot 5(2):184–191
Xu R, Ebraheim NA, Ou Y, Yeasting RA (1998) Anatomic considerations of pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine. Roy-Camille technique versus open-lamina technique. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 23(9):1065–1068
Yingsakmonkol W, Karaikovic E, Gaines RW (2002) The accuracy of pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine using the “funnel technique”: Part 1 a cadaveric study. J Spinal Disord Tech 15(6):445
Kuntz IV C, Maher PC, Levine NB, Kurokawa R (2004) Prospective evaluation of thoracic pedicle screw placement using fluoroscopic imaging. J Spinal Disord Tech 17(3):206
Rajasekaran S, Vidyadhara S, Ramesh P, Shetty AP (2007) Randomized clinical study to compare the accuracy of navigated and non-navigated thoracic pedicle screws in deformity correction surgeries. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 32(2):E56–E64. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000252094.64857.ab
Mirza SK, Wiggins GC, Kuntz Iv C, York JE, Bellabarba C, Knonodi MA, Chapman JR, Shaffrey CI (2003) Accuracy of thoracic vertebral body screw placement using standard fluoroscopy, fluoroscopic image guidance, and computed tomographic image guidance: a cadaver study. Spine 28(4):402
Minor ME, Morrissey NJ, Peress R, Carroccio A, Ellozy S, Agarwal G, Teodorescu V, Hollier LH, Marin ML (2004) Endovascular treatment of an iatrogenic thoracic aortic injury after spinal instrumentation: case report. J Vasc Surg 39(4):893–896. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2003.10.056
O’Brien JR, Krushinski E, Zarro CM, Sciadini M, Gelb D, Ludwig S (2006) Esophageal injury from thoracic pedicle screw placement in a polytrauma patient: a case report and literature review. J Orthop Trauma 20(6):431–434. doi:10.1097/00005131-200607000-00012
Di Silvestre M, Parisini P, Lolli F, Bakaloudis G (2007) Complications of thoracic pedicle screws in scoliosis treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 32(15):1655–1661. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318074d604
Kakkos SK, Shepard AD (2008) Delayed presentation of aortic injury by pedicle screws: report of two cases and review of the literature. J Vasc Surg 47(5):1074–1082
Bransford R, Bellabarba C, Thompson JH, Henley MB, Mirza SK, Chapman JR (2006) The safety of fluoroscopically-assisted thoracic pedicle screw instrumentation for spine trauma. J Trauma 60(5):1047–1052. doi:10.1097/01.ta.0000215949.95089.18
Husted DS, Yue JJ, Fairchild TA, Haims AH (2003) An extrapedicular approach to the placement of screws in the thoracic spine: an anatomic and radiographic assessment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 28(20):2324–2330. doi:10.1097/01.BRS.0000085361.32600.63
White KK, Oka R, Mahar AT, Lowry A, Garfin SR (2006) Pullout strength of thoracic pedicle screw instrumentation: comparison of the transpedicular and extrapedicular techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31(12):E355–E358. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000219394.48091.d6
Upendra BN, Meena D, Chowdhury B, Ahmad A, Jayaswal A (2008) Outcome-based classification for assessment of thoracic pedicular screw placement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33(4):384–390. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181646ba1
Guzey FK, Emel E, Hakan Seyithanoglu M, Serdar Bas N, Ozkan N, Sel B, Aycan A, Alatas I (2006) Accuracy of pedicle screw placement for upper and middle thoracic pathologies without coronal plane spinal deformity using conventional methods. J Spinal Disord tech 19(6):436
Bergeson RK, Schwend RM, DeLucia T, Silva SR, Smith JE, Avilucea FR (2008) How accurately do novice surgeons place thoracic pedicle screws with the free hand technique? Spine 33(15):E501
Youkilis AS, Quint DJ, McGillicuddy JE, Papadopoulos SM (2001) Stereotactic navigation for placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Neurosurgery 48(4):771–778 discussion 778–779
Belmont PJ Jr, Klemme WR, Dhawan A, Polly DW Jr (2001) In vivo accuracy of thoracic pedicle screws. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26(21):2340–2346
Berry E, Cuppone M, Porada S, Millner PA, Rao A, Chiverton N, Seedhom BB (2005) Personalised image-based templates for intra-operative guidance. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 219(2):111–118
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr Yu-Hua Cheng for his assistance with the CT data collection. This work was supported by the Yunnan Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2010ZC183).
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, T., Xu, YQ., Cheng, YB. et al. A novel computer-assisted drill guide template for thoracic pedicle screw placement: a cadaveric study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132, 65–72 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-011-1383-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-011-1383-5