Abstract
Purpose
Limaprost, a prostaglandin E1 analog, has vasodilatory properties and increases blood flow of the nerve root. However, it has not been clarified whether limaprost affects pain sensation associated with radiculopathy due to lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of oral limaprost with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for radiculopathy.
Methods
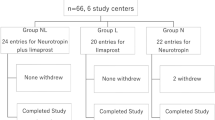
We performed a multicenter prospective randomized trial. Patients with LSS who had radicular-type neurologic intermittent claudication assessed based on a self-reported diagnostic support tool were randomized into three treatment groups. Limaprost, NSAIDs, or limaprost plus NSAIDs were administered orally for 6 weeks. Leg pain, low back pain (LBP) and the associated symptoms were assessed by a numerical rating scale (NRS) both at rest and on movement as well as the Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire (RDQ) and Short Form (SF)-36.
Results
Sixty-one patients were enrolled in the study. Each treatment finally reduced radicular pain, and the improvement was prominent in a combination treatment. There were no significant differences in radicular pain among three groups at final follow-up. LBP was not influenced by limaprost, and a significant reduction of LBP and RDQ was confirmed in a combination treatment compared with limaprost. Physical function of the SF-36 subscales after a combination treatment showed a marked alleviation compared with NSAIDs.
Conclusions
These obtained findings suggest that the effects of limaprost seem to be limited to radicular pain, not for LBP. Overall, a combination treatment might be more effective in the management of radiculopathy induced by LSS than monotherapy with either agent.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron R, Blinder A (2004) How neuropathic is sciatica? The mixed pain concept (in German). Orthopade 33:568–575
de Graaf I, Prak A, Bierma-Zeinstra S et al (2006) Diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis: a systematic review of the accuracy of diagnostic tests. Spine 31:1168–1176
Gauchan P, Andoh T, Kato A et al (2009) Effects of the prostaglandin E1 analog limaprost on mechanical allodynia caused by chemotherapeutic agents in mice. J Pharmacol Sci 109:469–472
Kanai A, Wang G, Hoshi K et al (2010) Effects of intravenous prostaglandin E1 on pain and body temperature in patients with post-herpetic neuralgia. Pain Med 11:609–616
Kikuchi S, Hoshika I, Matui T et al (1986) Neurogenic intermittent claudication in lumbar spine disease; Part 1 (in Japanese). Orthop Surg 37:1429–1438
Kobayashi S, Takeno K, Miyazaki T et al (2008) Effect of arterial ischemia and venous congestion on the lumbar nerve root in dogs. J Orthop Res 26:1533–1540
Konno S, Kayama S, Olmarker K et al (1996) Effects of OP-1206 (prostaglandin E1) on nerve-conduction velocity in the dog cauda equina subjected to acute experimental compression. J Spinal Disord 9:103–106
Konno S, Kikuchi S, Tanaka Y et al (2007) A diagnostic support tool for lumbar spinal stenosis: a self-administered, self-reported history questionnaire. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 8:102
Kurihara A, Kataoka O, Sugawara S et al (1996) Clinical benefit of OP-1206·α-CD on lumbar spinal canal stenosis: multi-center comparative double-blind clinical study (in Japanese). Rinsho Iyaku 12:511–529
Liu Y, Noguchi K, Takenobu Y et al (2002) Comparison the effect of beraprost sodium with that of limaprost alfadex in rat neuropathic intermittent claudication model (in Japanese). Jpn Pharmacol Ther 30:875–880
Liu Y, Obata K, Yamanaka H et al (2004) Activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase in dorsal horn neurons in the rat neuropathic intermittent claudication model. Pain 109:64–72
Mastudaira K, Seichi A, Kunogi J et al (2009) The efficacy of prostaglandin E1 derivative in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine 34:115–120
Murakami M, Takahashi K, Sekikawa T et al (1997) Effects of intravenous lipoprostaglandin E1 on neurogenic intermittent claudication. J Spinal Disord 10:499–504
Nakanishi K, Tanaka M, Misawa H et al (2008) Midterm results of prostaglandin E1 treatment in patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis accompanied by intermittent claudication. Spine 33:1465–1469
Roelofs PD, Deyo RA, Koes BW et al (2008) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for low back pain: an updated Cochrane review. Spine 33:1766–1774
Sawaragi H, Takenobu Y, Nonaka S et al (1996) Effect of OP-1206 α CD on the thermal hyperesthesia induced by constriction injury to the sciatic nerve in the rat (in Japanese). Kiso to Rinsho 30:237–244
Sekiguchi M, Konno S, Kikuchi S (2006) Effects on improvement of blood flow in the chronically compressed cauda equina: compression between a selective prostaglandin E receptor (EP4) agonist and a prostaglandin E1derivate. Spine 31:869–872
Tsuji H, Tamaki T, Itoh T et al (1985) Redundant nerve roots in patients with degenerative lumbar stenosis. Spine 10:72–82
Uratsuji M, Kurihara A, Iguchi T et al (1996) The optimal dose for OP-1206·α-CD on lumbar spinal canal stenosis: multi-center comparative double-blind clinical study [in Japanese]. Rinsho Iyaku 12:489–509
Yamamoto T, Shimoyama N, Asano H et al (1995) OP-1206, a prostaglandin E1 derivative, attenuates the thermal hyperesthesia induced by constriction injury to the sciatic nerve in the rat. Anesth Analg 80:515–520
Yoshida K, Sekiguchi M, Otani K et al (2011) A validation study of the Brief Scale for Psychiatric problems in Orthopaedic Patients (BS-POP) for patients with chronic low back pain (verification of reliability, validity, and reproducibility). J Orthop Sci 16:7–13
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge medical staffs in 12 affiliated hospitals (Sukagawa hospital, Fukushima prefectural Aizu general hospital, Minamisoma municipal general hospital, Iwaki municipal kyouritsu hospital, Futaba kosei hospital, Fukushima prefectural Minamiaizu hospital, Fukushima prefectural Ono hospital, Shirakawa kosei general hospital, Fukushima red cross hospital, Ohara general hospital, Iwase general hospital, and Fukushima medical university hospital) and 1 private clinic (Ichiro orthopaedic clinic) that participated in the study.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onda, A., Kikuchi, Si., Yabuki, S. et al. Limaprost alfadex and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for sciatica due to lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J 22, 794–801 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2551-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2551-1