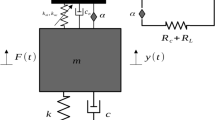
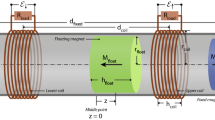
Abstract
Different architectures for vibration-based linear electromagnetic energy harvesters (EMEHs) have been developed and reported in the literature for applications in autonomous wireless sensor nodes. In the majority of the linear EMEHs the magnetic field over the coil is nonuniform. This paper presents the modeling and simulation for the electromechanical transduction of linear EMEHs with a nonuniform magnetic field configuration excited by harmonic vibrations. Models are developed based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction and the Lorentz force law. For a more accurate prediction of the performance of the EMEHs where the entire coil does not experience the same gradient of the normal component of the magnetic flux density, the analytical solution of the off-center magnetic flux density for a square magnet is used. The simulation results of the developed models show good agreement with the experimental results. Simulations of our previously developed EMEH show an improvement of load voltage and the power when the gap between the magnet and the coil is optimized. Moreover, maximizing the number of turns of the coil for the optimized gap, simulations of the optimized device predict a load voltage amplitude (90.2 mV) almost twice and a load power (40.7 μW) almost four times the experimental results obtained for the current prototype.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold DP (2007) Review of microscale magnetic power generation. IEEE Trans Magn 43:3940–3950
Beeby SP, Tudor MJ, Torah RN, Koukharenko E, Roberts S, O’Donnell T, Roy S (2006) Macro and micro scale electromagnetic kinetic energy harvesting generators. In: Proceedings of the DTIP MEMS & MOEMS
Beeby SP, Torah RN, Tudor MJ, Glynne-Jones O’Donnell T, Saha CR, Roy S (2007) A micro electromagnetic generator for vibration energy harvester. J Micromech Microeng 17:1257–1265
Berg Y, Wisland TW, Lande TS (1999) Ultra low-voltage/low-power digital floating-gate circuits. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II 46:930–936
Cook-Chennault KA, Thambi N, Sastry AM (2008) Powering MEMS portable devices-a review of non-regenerative and regenerative power supply systems with special emphasis on piezoelectric energy harvesting systems. Smart Mater Struct 17:043001
Engel-Herbert R, Hesjedal T (2005) Calculation of the magnetic stray field of a uniaxial magnetic domain. J Appl Phys 97:074504. doi:10.1063/1.1883308
Glynne-Jones P, Tudor MJ, Beeby SP, White NM (2004) An electromagnetic vibration-powered generator for intelligent sensor systems. Sens Actuators A 110:344–349
Hatipoglu G, Urey H (2010) FR4-based electromagnetic energy harvester for wireless sensor nodes. Smart Mater Struct 19:015022
Hautamaki C, Zurn S, Mantell S, Polla D (2000) Embedded microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) for measuring strain in composites. J Reinf Plast Compos 19:268–277
Huang WS, Tzeng KE, Cheng MC, Huang RS (2007) A silicon mems micro power generator for wearable micro devices. J Chin Inst Engrs 30:133–140
Khan F, Sassani F, Stoeber B (2010) Copper foil-type vibration-based electromagnetic energy harvester. J Micromech Microeng 20:125006
Khan F, Sassani F, Stoeber B (2013) Nonlinear behaviour of membrane type electromagnetic energy harvester under harmonic and random vibrations. Microsyst Technol. doi:10.1007/s00542-013-1938-1
Krantz D, Belk J, Biermann P, Dubow J, Gause L, Harjani R, Mantell S, Polla D, and Troyk P (1999) Project update: applied research on remotely-queried embedded microsensors. In: Proceedings of the SPIE 1999 3673, pp 157–164
Lee CY, Hsieh WJ, Wu GW (2008) Embedded flexible micro-sensors in MEA for measuring temperature and humidity in a micro-fuel cell. J Power Sour 181:237–243
Lukowicz P, Kirstein T, Troster G (2004) Wearable systems for health care applications. Methods Inf Med 43:232–238
Makihara K, Onoda J, Miyakawa T (2006) Low energy dissipation electric circuit for energy harvesting. Smart Mater Struct 15:1493–1498
Mitcheson PD, Green TC, Yeat EM, Holmes HS (2004) Architectures for vibration-driven micropower generators. J Microelectromech Syst 13:429–440
Mohan SS, Hershenson MDM, Boyd SP, Lee TH (1999) Simple accurate expressions for planar spiral inductances. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits 34(10):1419–1424
Pantelopoulos A, Bourbakis NG (2010) A survey on wearable sensor-based systems for health monitoring and prognosis. IEEE Tran Syst Man Cybern Part C Appl Rev 40:1–12
Priya S (2007) Advances in energy harvesting using low profile piezoelectric transducers. J Electroceram 19:167–184
Priya S, Inman DJ (2009) Energy harvesting technologies. Springer, New York
Sari I, Balkan T, Kulah H (2008) A electromagnetic micro power generator for wideband environmental vibrations. Sens Actuat A 145:405–413
Scheffler M and Hirt E (2004) Wearable devices for the emerging healthcare applications. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference (IEEE IEMBS2004), pp 3301–3304
Selvaggi JA and Selvaggi JP (1987) External and internal magnetic field equations for domain oriented permanent magnets. In: Proceedings of the Magnet Technology Conference MT-10
Serre C, Perez-Rodrıguez A, Fondevilla N, Martincic E, Morante JR, Montserrat J, Esteve J (2009) Linear and non-linear behavior of mechanical resonators for optimized inertial electromagnetic microgenerators. Microsyst Technol 15:1217–1223
Sodano HA, Inman DJ, Park G (2004) A review of power harvesting from vibration using piezoelectric materials. Shock Vib Dig 36:197–205
Srovnal V (2005) Using of embedded systems in biomedical applications. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Conference European Medical and Biological Engineering
Sterken T, Baert K, Van Hoof C, Puers R, Borghs G, Fiorini P (2004) Comparative modeling for vibration scavengers. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors Conference, pp 1249–1252
Thompson MT (1999) Inductance calculation techniques part II: approximations and handbook methods power control and intelligent motion [online]. Available from http://www.thompsonrd.com/induct2.pdf. Accessed 15 March 2014
Torah R, Glynne-Jones P, Tudor M, O’Donnell T, Roy S, Beeby S (2008) Self-powered autonomous wireless sensor node using vibration energy harvesting. Meas Sci Technol 19:125202
Torres EO, Rincon-Mora GA (2009) Electrostatic energy-harvesting and battery-charging CMOS system prototype. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I 56:1938–1948
Val C, Couderc P, Lartigues P (2009) Stacking of full rebuilt wafers for sip and abandoned sensors/applications. In: Proceedings of the Conference European Microelectronics and Packaging (EMPC2009), pp 1–9
Vullers RJM, Schaijk RV, Doms I, Hoof CV, Mertens R (2009) Micropower energy harvesting. Solid State Electron 53:684–693
Wacharasindhu T, Kwon JW (2008) A micromachined energy harvester from a keyboard using combined electromagnetic and piezoelectric conversion. J Micromech Microeng 18:104016
Wang PH, Dai XH, Fang DM, Zhao XL (2007) Design, fabrication and performance of a new vibration-based electromagnetic micro power generator. Microelectron J 38:1175–1180
Wang P, Tanaka K, Sugiyama S, Dai X, Zhao X, Liu J (2009) A micro electromagnetic low level vibration energy harvester based on MEMS technology. Microsyst Technol 15:941–951
Williams CB, Shearwood C, Harradine MA, Mellor PH, Birch TS, Yates RB (2001) Development of an electromagnetic micro-generator. In Proc IEEE Circuits Devices Syst 148:337–342
Yang B, Lee C (2010) Non-resonant electromagnetic wideband energy harvesting mechanism for low frequency vibrations. Microsyst Technol 16:961–966
Yang B, Lee C, Xiang WF, Xie J, He H, Kotlanka RK, Low SP, Feng HH (2009) Electromagnetic energy harvesting from vibrations of multiple frequencies. J Micromech Microeng 19:035001
Yuen SCL, Lee JMH, Luk MHM, Chan GMH, Lei KF, Leong PHW, Li WJ, Yam Y (2004) AA size micro power conversion cell for wireless applications. In Proceedings of the 5th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation 6, pp 5629–5634
Zhang Z (2009) Ubiquitous human motion capture using wearable micro-sensors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom2009), pp 1–2
Zhang Z, Wong LWC, Wu JK (2010) 3D Upper limb motion modeling and estimation using wearable micro-sensors. In: Proceedings of the International Conference Body Sensor Networks (BSN2010), pp 117–123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, F., Stoeber, B. & Sassani, F. Modeling of linear micro electromagnetic energy harvesters with nonuniform magnetic field for sinusoidal vibrations. Microsyst Technol 21, 683–692 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2359-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2359-5