Abstract
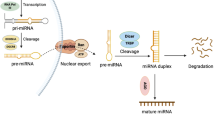
MicroRNAs (miRNA) are 22-nucleotide non-coding RNAs that post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression by base pairing to partially complementary sequences in the 3′-untranslated region of their target messenger RNA. Altered miRNA expression also changes the expression of oncogenes and tumor suppressors, affecting the proliferation, apoptosis, motility and invasibility of gastrointestinal cancer cells, including the cells of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). It has been suggested that various miRNA expression profiles may provide useful biomarkers and therapeutic targets, but to date few studies have been published on the role of miRNA in ESCC. In this review we summarize the identification and characterization of miRNAs involved in ESCC and discuss their potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c-MYC:
-
Myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog
- CAF:
-
Cancer-associated fibroblast
- CDK:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- ESCC:
-
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- KRAS:
-
V-Myc Avian v-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- miRNA:
-
microRNAs
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- PDCD4:
-
Programmed cell death protein 4
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- SOX4:
-
SRY-related HMG-box 4
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor beta
- TS-miRs:
-
Tumor-suppressive miRNAs
- ZEB1:
-
Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1
References
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2241–52.
Allum WH, Stenning SP, Bancewicz J, et al. Long-term results of a randomized trial of surgery with or without preoperative chemotherapy in esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5062–7.
Gertler R, Stein HJ, Langer R, et al. Long-term outcome of 2920 patients with cancers of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction: evaluation of the New Union Internationale Contre le Cancer/American Joint Cancer Committee staging system. Ann Surg. 2011;253:689–98.
He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–31.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20.
Alvarez-Garcia I, Miska EA. MicroRNA functions in animal development and human disease. Development. 2005;132:4653–62.
Xiao C, Rajewsky K. MicroRNA control in the immune system: basic principles. Cell. 2009;136:26–36.
Song JH, Meltzer SJ. MicroRNAs in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of gastroesophageal cancers. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(35–47):e2.
Guo Y, Chen Z, Zhang L, et al. Distinctive microRNA profiles relating to patient survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2008;68:26–33.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–8.
Kano M, Seki N, Kikkawa N, et al. miR-145, miR-133a and miR-133b: tumor-suppressive miRNAs target FSCN1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2804–14.
He L, He X, Lim LP, et al. A microRNA component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature. 2007;447:1130–4.
Yao L, Zhang Y, Zhu Q, et al. Downregulation of microRNA-1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma correlates with an advanced clinical stage and its overexpression inhibits cell migration and invasion. Int J Mol Med. 2015;35:1033–41.
Fu HL, de Wu P, Wang XF, et al. Altered miRNA expression is associated with differentiation, invasion, and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) in patients from Huaian, China. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;67:657–68.
Yang M, Liu R, Sheng J, et al. Differential expression profiles of microRNAs as potential biomarkers for the early diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2013;29:169–76.
Ren LH, Chen WX, Li S, et al. MicroRNA-183 promotes proliferation and invasion in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting programmed cell death 4. Br J Cancer. 2014;111:2003–13.
Liu R, Gu J, Jiang P, et al. DNMT1-microRNA126 epigenetic circuit contributes to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth via ADAM9-EGFR-AKT signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:854–63.
Liu M, Wang Z, Yang S, et al. TNF-alpha is a novel target of miR-19a. Int J Oncol. 2011;38:1013–22.
Harada K, Baba Y, Ishimoto T, et al. Suppressor microRNA-145 is epigenetically regulated by promoter hypermethylation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2015;35:4617–24.
Miska EA. How microRNAs control cell division, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005;15:563–8.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74.
Liu R, Liao J, Yang M, et al. The cluster of miR-143 and miR-145 affects the risk for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through co-regulating fascin homolog 1. PLoS One. 2012;7:e33987.
Kong KL, Kwong DL, Chan TH, et al. MicroRNA-375 inhibits tumour growth and metastasis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma through repressing insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Gut. 2012;61:33–42.
Nie J, Ge X, Geng Y, et al. miR-34a inhibits the migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Yin Yang-1. Oncol Rep. 2015;34:311–7.
Qi Y, Li X, Zhao S. miR-29b inhibits the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting MMP-2. Neoplasma. 2015;62:384–90.
Koumangoye RB, Andl T, Taubenslag KJ, et al. SOX4 interacts with EZH2 and HDAC3 to suppress microRNA-31 in invasive esophageal cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:24.
Hiyoshi Y, Kamohara H, Karashima R, et al. MicroRNA-21 regulates the proliferation and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:1915–22.
Li P, Mao WM, Zheng ZG, et al. Down-regulation of PTEN expression modulated by dysregulated miR-21 contributes to the progression of esophageal cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58:3483–93.
Liu F, Zheng S, Liu T, et al. MicroRNA-21 promotes the proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in Eca109 via activating ERK1/2/MAPK pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;381:115–25.
Meng H, Wang K, Chen X, et al. MicroRNA-330-3p functions as an oncogene in human esophageal cancer by targeting programmed cell death 4. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5:1062–75.
Nouraee N, Van Roosbroeck K, Vasei M, et al. Expression, tissue distribution and function of miR-21 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 2013;8:e73009.
Ni Y, Meng L, Wang L, et al. MicroRNA-143 functions as a tumor suppressor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gene. 2013;517:197–204.
Cheng Y, Li Y, Nian Y, et al. STAT3 is involved in miR-124-mediated suppressive effects on esophageal cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:306.
Zhu L, Wang Z, Fan Q, et al. microRNA-27a functions as a tumor suppressor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting KRAS. Oncol Rep. 2014;31:280–6.
Jiang Y, Duan Y, Zhou H. MicroRNA-27a directly targets to inhibit cell proliferation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2015;9:471–7.
Yu T, Cao R, Li S, et al. MiR-130b plays an oncogenic role by repressing PTEN expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:29.
Lin C, Liu A, Zhu J, et al. miR-508 sustains phosphoinositide signalling and promotes aggressive phenotype of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4620.
Zhang K, Dai L, Zhang B, et al. miR-203 is a direct transcriptional target of E2F1 and causes G1 arrest in esophageal cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230:903–10.
Ding DP, Chen ZL, Zhao XH, et al. miR-29c induces cell cycle arrest in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating cyclin E expression. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32:1025–32.
Li H, Zheng D, Zhang B, et al. Mir-208 promotes cell proliferation by repressing SOX6 expression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Transl Med. 2014;12:196.
Yang M, Liu R, Li X, et al. miRNA-183 suppresses apoptosis and promotes proliferation in esophageal cancer by targeting PDCD4. Mol Cells. 2014;37:873–80.
Zhang J, Cheng C, Yuan X, et al. microRNA-155 acts as an oncogene by targeting the tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:602–10.
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer development and its clinical significance. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:293–9.
Song Y, Li J, Zhu Y, et al. MicroRNA-9 promotes tumor metastasis via repressing E-cadherin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2014;5:11669–80.
Zhang Y, Pan T, Zhong X, et al. Nicotine upregulates microRNA-21 and promotes TGF-beta-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition of esophageal cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:7063–72.
Xu X, Chen Z, Zhao X, et al. MicroRNA-25 promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;421:640–5.
Chen ZL, Zhao XH, Wang JW, et al. microRNA-92a promotes lymph node metastasis of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via E-cadherin. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:10725–34.
Zhang N, Fu H, Song L, et al. MicroRNA-100 promotes migration and invasion through mammalian target of rapamycin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2014;32:1409–18.
Harazono Y, Muramatsu T, Endo H, et al. miR-655 is an EMT-suppressive microRNA targeting ZEB1 and TGFBR2. PLoS One. 2013;8:e62757.
Yokobori T, Suzuki S, Tanaka N, et al. MiR-150 is associated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via targeting the EMT inducer ZEB1. Cancer Sci. 2013;104:48–54.
Matsushima K, Isomoto H, Yamaguchi N, et al. MiRNA-205 modulates cellular invasion and migration via regulating zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Transl Med. 2011;9:30.
Zhang HF, Zhang K, Liao LD, et al. miR-200b suppresses invasiveness and modulates the cytoskeletal and adhesive machinery in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via targeting Kindlin-2. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:292–301.
Fu MG, Li S, Yu TT, et al. Differential expression of miR-195 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and miR-195 expression inhibits tumor cell proliferation and invasion by targeting of Cdc42. FEBS Lett. 2013;587:3471–9.
Blower PE, Verducci JS, Lin S, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles for the NCI-60 cancer cell panel. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:1483–91.
Huang S, Li XQ, Chen X, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-21 increases radiosensitivity of esophageal cancer cells through phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 activation. Dis Esophagus. 2013;26:823–31.
Kurashige J, Kamohara H, Watanabe M, et al. Serum microRNA-21 is a novel biomarker in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2012;106:188–92.
Hamano R, Miyata H, Yamasaki M, et al. Overexpression of miR-200c induces chemoresistance in esophageal cancers mediated through activation of the Akt signaling pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:3029–38.
Xia H, Chen S, Chen K, et al. MiR-96 promotes proliferation and chemo- or radioresistance by down-regulating RECK in esophageal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2014;68:951–8.
Chen G, Peng J, Zhu W, et al. Combined downregulation of microRNA-133a and microRNA-133b predicts chemosensitivity of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma undergoing paclitaxel-based chemotherapy. Med Oncol. 2014;31:263.
Imanaka Y, Tsuchiya S, Sato F, et al. MicroRNA-141 confers resistance to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by targeting YAP1 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Hum Genet. 2011;56:270–6.
Tanaka K, Miyata H, Sugimura K, et al. miR-27 is associated with chemoresistance in esophageal cancer through transformation of normal fibroblasts to cancer-associated fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis. 2015;36:894–903.
Dong W, Li B, Wang Z, et al. Clinical significance of microRNA-24 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasma. 2015;62:250–8.
Chen X, Guo J, Xi RX, et al. MiR-210 expression reverses radioresistance of stem-like cells of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Clin Oncol. 2014;5:1068–77.
Wu C, Wang C, Guan X, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic implications of a serum miRNA panel in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 2014;9:e92292.
Tanaka K, Miyata H, Yamasaki M, et al. Circulating miR-200c levels significantly predict response to chemotherapy and prognosis of patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy for esophageal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20[Suppl 3]:S607–15.
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Takeshita H, et al. Prognostic impact of circulating miR-21 and miR-375 in plasma of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12[Suppl 1]:S53–9.
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Takeshita H, et al. Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2011;105:104–11.
Wu C, Li M, Hu C, et al. Clinical significance of serum miR-223, miR-25 and miR-375 in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41:1257–66.
Tanaka Y, Kamohara H, Kinoshita K, et al. Clinical impact of serum exosomal microRNA-21 as a clinical biomarker in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2013;119:1159–67.
Yu H, Duan B, Jiang L, et al. Serum miR-200c and clinical outcome of patients with advanced esophageal squamous cancer receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. Am J Transl Res. 2013;6:71–7.
Huang SD, Yuan Y, Zhuang CW, et al. MicroRNA-98 and microRNA-214 post-transcriptionally regulate enhancer of zeste homolog 2 and inhibit migration and invasion in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2012;11:51.
Wang X, Li M, Wang Z, et al. Silencing of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 by miR-101 and miR-217 inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:3925–35.
Li H, Meng F, Ma J, et al. Insulin receptor substrate-1 and Golgi phosphoprotein 3 are downstream targets of miR126 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2014;32:1225–33.
Akanuma N, Hoshino I, Akutsu Y, et al. MicroRNA-133a regulates the mRNAs of two invadopodia-related proteins, FSCN1 and MMP14, in esophageal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2014;110:189–98.
Suzuki S, Yokobori T, Tanaka N, et al. CD47 expression regulated by the miR-133a tumor suppressor is a novel prognostic marker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2012;28:465–72.
Gong H, Song L, Lin C, et al. Downregulation of miR-138 sustains NF-kappaB activation and promotes lipid raft formation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:1083–93.
Liu R, Yang M, Meng Y, et al. Tumor-suppressive function of miR-139-5p in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 2013;8:e77068.
Li W, Jiang G, Zhou J, et al. Down-regulation of miR-140 induces EMT and promotes invasion by targeting Slug in esophageal cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34:1466–76.
Yuan Y, Zeng ZY, Liu XH, et al. MicroRNA-203 inhibits cell proliferation by repressing DeltaNp63 expression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:57.
Yu X, Jiang X, Li H, et al. miR-203 inhibits the proliferation and self-renewal of esophageal cancer stem-like cells by suppressing stem renewal factor Bmi-1. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23:576–85.
Wang T, Chen T, Niu H, et al. MicroRNA-218 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting BMI1. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36:93–102.
Isozaki Y, Hoshino I, Nohata N, et al. Identification of novel molecular targets regulated by tumor suppressive miR-375 induced by histone acetylation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2012;41:985–94.
Zhang R, Chen X, Zhang S, et al. Upregulation of miR-494 inhibits cell growth and invasion and induces cell apoptosis by targeting cleft lip and palate transmembrane 1-like in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60:1247–55.
Wang Z, Qiao Q, Chen M, et al. miR-625 down-regulation promotes proliferation and invasion in esophageal cancer by targeting Sox2. FEBS Lett. 2014;588:915–21.
Wang Y, Zang W, Du Y, et al. Mir-655 up-regulation suppresses cell invasion by targeting pituitary tumor-transforming gene-1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Transl Med. 2013;11:301.
Liu Q, Lv GD, Qin X, et al. Role of microRNA let-7 and effect to HMGA2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39:1239–46.
Zhu Y, Xia Y, Niu H, et al. MiR-16 induced the suppression of cell apoptosis while promote proliferation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33:1340–8.
Harata K, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, et al. MicroRNA-34b has an oncogenic role in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2010;1:685–9.
Li J, Shan F, Xiong G, et al. Transcriptional regulation of miR-146b by C/EBPbeta LAP2 in esophageal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;446:267–71.
Lee KH, Goan YG, Hsiao M, et al. MicroRNA-373 (miR-373) post-transcriptionally regulates large tumor suppressor, homolog 2 (LATS2) and stimulates proliferation in human esophageal cancer. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315:2529–38.
Yuan X, He J, Sun F, et al. Effects and interactions of MiR-577 and TSGA10 in regulating esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;6:2651–67.
Xu Y, He J, Wang Y, et al. miR-889 promotes proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinomas through DAB2IP. FEBS Lett. 2015;589:1127–35.
Jiang L, Wang Y, Rong Y, et al. miR-1179 promotes cell invasion through SLIT2/ROBO1 axis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:319–27.
Li M, He XY, Zhang ZM, et al. MicroRNA-1290 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:3245–55.
Li J, Li X, Li Y, et al. Cell-specific detection of miR-375 downregulation for predicting the prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by miRNA in situ hybridization. PLoS One. 2013;8:e53582.
Zhao Y, Schetter AJ, Yang GB, et al. microRNA and inflammatory gene expression as prognostic marker for overall survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:2901–9.
Ge C, Wu S, Wang W, et al. miR-942 promotes cancer stem cell-like traits in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6:10964–77.
Zhou S, Yang B, Zhao Y, et al. Prognostic value of microRNA-100 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Surg Res. 2014;192:515–20.
Kurashige J, Watanabe M, Iwatsuki M, et al. Overexpression of microRNA-223 regulates the ubiquitin ligase FBXW7 in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2012;106:182–8.
Xiang Z, Dong X, Sun Q, et al. Clinical significance of up-regulated miR-181a in prognosis and progression of esophageal cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2014;46:1007–10.
Xu XL, Jiang YH, Feng JG, et al. MicroRNA-17, microRNA-18a, and microRNA-19a are prognostic indicators in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;97:1037–45.
Sun J, Chen Z, Tan X, et al. MicroRNA-99a/100 promotes apoptosis by targeting mTOR in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oncol. 2013;30:411.
Sun N, Ye L, Chang T, et al. microRNA-195-Cdc42 axis acts as a prognostic factor of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:6871–9.
Lin RJ, Xiao DW, Liao LD, et al. MiR-142-3p as a potential prognostic biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2012;105:175–82.
Liu K, Li L, Rusidanmu A, et al. Down-regulation of MiR-1294 is related to dismal prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma hrough elevating C-MYC expression. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36:100–10.
Zhang BJ, Gong HY, Zheng F, et al. Up-regulation of miR-335 predicts a favorable prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:6213–8.
Zhang M, Yang Q, Zhang L, et al. miR-302b is a potential molecular marker of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting ErbB4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014;33:10.
Qi B, Lu JG, Yao WJ, et al. Downregulation of microRNA-382 is associated with poor outcome of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:6884–91.
Ogawa R, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, et al. Expression profiling of micro-RNAs in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using RT-PCR. Med Mol Morphol. 2009;42:102–9.
Zhang M, Zhou S, Zhang L, et al. miR-518b is down-regulated, and involved in cell proliferation and invasion by targeting Rap1b in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 2012;586:3508–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harada, K., Baba, Y., Ishimoto, T. et al. The role of microRNA in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 51, 520–530 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-016-1161-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-016-1161-9