Abstract
Background and Aim
miR-21, a putative tumor oncomiR, is a frequently overexpressed miRNA in a variety of tumors. Because it targets tumor-suppressor genes it has been linked to tumor progression. In this study we investigated the role of miR-21 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), and its possible mechanism.
Methods
Expression of miR-21 was detected by stem–loop RT-PCR in tissue from 76 invasive ESCC at stage I–IV and in their corresponding para-cancerous histological normal tissues (PCHNT). Thirty endoscopic esophageal mucosal biopsy specimens from non-tumor patients were used as controls. Expression of PTEN in 76 paired ESCC and PCHNT was investigated by real-time RT-PCR and an immunohistochemical method, respectively. Paired tumor and PCHNT specimens of 20 ESCC cases were randomly selected for western blot analysis. The effect of miR-21 on PTEN expression was assessed in the ESCC cell line with an miR-21 inhibitor to reduce miR-21 expression. Furthermore, the roles of miR-21 in cell biology were analyzed by use of miR-21 inhibitor-transfected cells.
Results
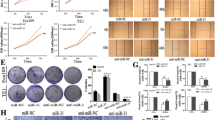
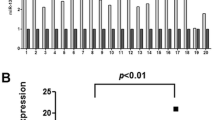
Stem–loop RT-PCR revealed miR-21 was significantly overexpressed in ESCC tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of miR-21 correlated with tumor status, lymph node metastasis, and clinical stage. We demonstrated that knockdown of miR-21 significantly increased expression of PTEN protein. Consequent PTEN expression reduced cell proliferation, invasion, and migration.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that miR-21 could be a potential oncomiR, probably by regulation of PTEN, and a novel prognostic factor for ESCC patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2137–2150.
Eslick G. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. 2009;38:17–25.
Bader F, Anwar N, Mahmood S. Geographical variation in the epidemiology of esophageal cancer in Pakistan. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2005;6:139–142.
Wu KS, Huo X, Zhu GH. Relationships between esophageal cancer and spatial environment factors by using geographic information systems. Sci Total Environ. 2008;393:219–225.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249.
Kuwano H, Kato H, Miyazaki T. Genetic alterations in esophageal cancer. Surg Today. 2005;35:7–18.
Sugimoto T, Seki N, Shimizu S, et al. The galanin signaling cascade is a candidate pathway regulating oncogenesis in human squamous cell carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2009;48:132–142.
Qin YR, Wang LD, Fan ZM, Kwong D, Guan XY. Comparative genomic hybridization analysis of genetic aberrations associated with development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Henan, China. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:1828–1835.
Davis BN, Hata A. microRNA in cancer—the involvement of aberrant microRNA biogenesis regulatory pathways. Genes Cancer. 2010;1:1100–1104.
Nicolas FE, Lopez-Martinez AF. MicroRNAs in human diseases. Recent Pat DNA Gene Seq. 2010;4:142–154.
Selcuklu SD, Donoghue MT, Spillane C. miR-21 as a key regulator of oncogenic processes. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009;37:918–925.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor-suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:647–658.
Ma WJ, Lv GD, Tuersun A, et al. Role of microRNA-21 and effect on PTEN in Kazakh’s esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38:3253–3260.
International Union Against Cancer (UICC). In: Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind Ch, eds. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 7th ed. New York: Wiley-Liss; 2010.
Noble JE, Bailey MJ. Quantitation of protein. Methods Enzymol. 2009;463:73–95.
Ge MH, Chen C, Xu JJ, Ling ZQ. Critical regions and spreading of runt-related transcription factor-3 C-phosphate-G (CpG) island methylation in human salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2011;42:1862–1872.
Mao WM, Zheng WH, Ling ZQ. Epidemiologic risk factors for esophageal cancer development. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12:2461–2466.
Lee JA, Lee HY, Lee ES, Kim I, Bae JW. Prognostic Implications of MicroRNA-21 Overexpression in Invasive Ductal Carcinomas of the Breast. J Breast Cancer. 2011;14:269–275.
Zhang Z, Li Z, Gao C, et al. miR-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab Invest. 2008;88:1358–1366.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor-suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:647–658.
Lou Y, Yang X, Wang F, Cui Z, Huang Y. MicroRNA-21 promotes the cell proliferation, invasion and migration abilities in ovarian epithelial carcinomas through inhibiting the expression of PTEN protein. Int J Mol Med. 2010;26:819–827.
Deftereos G, Corrie SR, Feng Q, et al. Expression of mir-21 and mir-143 in cervical specimens ranging from histologically normal through to invasive cervical cancer. PLoS One. 2011;6:e28423.
Nam EJ, Yoon H, Kim SW, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles in serous ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2690–2695.
Huang S, Li XQ, Chen X, Che SM, Chen W, Zhang XZ. Inhibition of microRNA-21 increases radiosensitivity of esophageal cancer cells through phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 activation. Dis Esophagus. 2012; doi:10.1111/j.1442-2050.2012.01389.x.
Sheth S, Jajoo S, Kaur T, et al. Resveratrol reduces prostate cancer growth and metastasis by inhibiting the Akt/MicroRNA-21 pathway. PLoS One. 2012;7:e51655.
Liu ZL, Wang H, Liu J, Wang ZX. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) expression promotes growth, metastasis, and chemo- or radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;372:35–45.
Zaravinos A, Radojicic J, Lambrou GI, et al. Expression of miRNAs involved in angiogenesis, tumor cell proliferation, tumor suppressor inhibition, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activation of metastasis in bladder cancer. J Urol. 2012;188:615–623.
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Tsujiura M, et al. Prognostic impact of circulating miR-21 in the plasma of patients with gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:271–276.
Hermansen SK, Dahlrot RH, Nielsen BS, Hansen S, Kristensen BW. MiR-21 expression in the tumor cell compartment holds unfavorable prognostic value in gliomas. J Neurooncol. 2013;111:71–81.
Yang M, Shen H, Qiu C, et al. High expression of miR-21 and miR-155 predicts recurrence and unfavourable survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49:604–615.
Kjaer-Frifeldt S, Hansen TF, Nielsen BS, et al. The prognostic importance of miR-21 in stage II colon cancer: a population-based study. Br J Cancer. 2012;107:1169–1174.
Zhao Y, Schetter AJ, Yang GB, et al. microRNA and inflammatory gene expression as prognostic marker for overall survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:2901–2909.
Gu J, Wang Y, Wu X. MicroRNA in the pathogenesis and prognosis of esophageal cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19:1292–1300.
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Takeshita H, et al. Prognostic impact of circulating miR-21 and miR-375 in plasma of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12:S53–S59.
Maehama T, Dixon JE. The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:13375–13378.
Leslie NR, Bennett D, Lindsay YE, Stewart H, Gray A, Downes CP. Redox regulation of PI 3-kinase signalling via inactivation of PTEN. EMBO J. 2003;22:5501–5510.
Stewart AL, Mhashilkar AM, Yang XH, et al. PI3 K blockade by Ad-PTEN inhibits invasion and induces apoptosis in radial growth phase and metastatic melanoma cells. Mol Med. 2002;8:451–461.
Tamura M, Gu J, Matsumoto K, Aota S, Parsons R, Yamada KM. Inhibition of cell migration, spreading, and focal adhesions by tumor suppressor PTEN. Science. 1998;280:1614–1617.
Castellino RC, Durden DL. Mechanisms of disease: the PI3K-Akt-PTEN signaling node-an intercept point for the control of angiogenesis in brain tumors. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2007;3:682–693.
Hu YC, Lam KY, Tang JC, Srivastava G. Mutational analysis of the PTEN/MMAC1 gene in primary oesophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Mol Pathol. 1999;52:353–356.
Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, Leal JF, Carnero A. PTEN, more than the AKT pathway. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28:1379–1386.
Reis AH, Vargas FR, Lemos B. More epigenetic hits than meets the eye: microRNAs and genes associated with the tumorigenesis of retinoblastoma. Front Genet. 2012;3:284.
Farazi TA, Hoell JI, Morozov P, Tuschl T. MicroRNAs in human cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;774:1–20.
Goeppert B, Schmezer P, Dutruel C, et al. Down-regulation of tumor suppressor A kinase anchor protein 12 in human hepatocarcinogenesis by epigenetic mechanisms. Hepatology. 2010;52:2023–2033.
Fabbri M, Calore F, Paone A, Galli R, Calin GA. Epigenetic regulation of miRNAs in cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;754:137–148.
Tanaka Y, Kamohara H, Kinoshita K, et al. Clinical impact of serum exosomal microRNA-21 as a clinical biomarker in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2013;119:1159–1167.
Alder H, Taccioli C, Chen H, et al. Dysregulation of miR-31 and miR-21 induced by zinc deficiency promotes esophageal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33:1736–1744.
Liu C, Yu J, Yu S, et al. MicroRNA-21 acts as an oncomir through multiple targets in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2010;53:98–107.
Xiong B, Cheng Y, Ma L, Zhang C. MiR-21 regulates biological behavior through the PTEN/PI-3 K/Akt signaling pathway in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2013;42:219–228.
Han M, Liu M, Wang Y, et al. Antagonism of miR-21 reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype through AKT/ERK1/2 inactivation by targeting PTEN. PLoS One. 2012;7:e39520.
Yang SM, Huang C, Li XF, Yu MZ, He Y, Li J. miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells by regulating PTEN. Toxicology. 2013;306C:162–168.
Vogt PK, Gymnopoulos M, Hart JR. PI 3-kinase and cancer: changing accents. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009;19:12–17.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University, Ministry of Education, China (NCET-11-0949), a grant from the Science and Technology General Project of Zhejiang Province (no. 2009C33143), Key Research Projects of Medicine, Ministry of Health, China (no. WKJ2010-2-004), partly by a grant from the Backbone Talent of Zhejiang Provincial Medicine and Hygiene Platform Programs (no. 2011RCA009), a grant from the Scientific and Technological Innovations Fund of Henan Province Higher Education (no. 2009HAST1T001) and a grant from the Science and Technology Key Project of the Ministry of Education, China (no. 210130).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Mao, WM., Zheng, ZG. et al. Down-Regulation of PTEN Expression Modulated by Dysregulated miR-21 Contributes to the Progression of Esophageal Cancer. Dig Dis Sci 58, 3483–3493 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-013-2854-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-013-2854-z