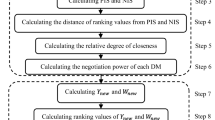
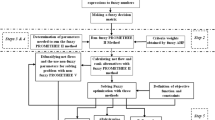
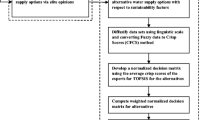
Abstract
Due to water scarcity in different regions of Iran, water supply management is a challenging task for authorities that calls for smart methods and the proper utilization of subterranean water resources. In order to handle the inherent complexity and various uncertainties in real-world scenarios, the implementation of appropriate multi-criteria decision-making techniques is required according to the challenges underlying the management of the water supply. The present study aims to propose a hybrid framework on fuzzy rough-MARCOS, which stands for measurement of alternatives and Ranking according to compromise solution. The fuzzy rough-MARCOS method provides the fuzzy rough reference points through the fuzzy rough ideal and anti-ideal solutions that offer a more precise determination of the utility degree. Throughout the evaluation process, the fuzzy rough number is employed to deal with uncertainty and imprecision in expert judgment. A case study of the village of Nohoor located in northeastern Iran is employed to illustrate how the suggested decision-making model can be used to choose the optimal method of water supply by utilizing subsurface water resources. There are four alternatives for getting water to the community of Nohoor. Our findings show that the optimal result for supplying water is through pipeline via path A. To verify the consistency of outcomes, a comparison of our suggested method with existing MCDM techniques, namely fuzzy rough-TOPSIS method, fuzzy MARCOS, rough MARCOS, is conducted.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
No data were used to support this study.
References
Akram M, Shumaiza, Arshad M (2018) J Intell Fuzzy Syst. A new approach based on fuzzy rough digraphs for decision-making 35(2):2105–2121
Akram M, Arshad M, Shumaiza (2018) Fuzzy rough graph theory with applications. Int J Comput Intel Syst 12(1):90–107
Akram M, Zafar F (2019) Rough fuzzy digraphs with applications. J Appl Math Comput 59:91–127
Akram M, Shahzadi S, Bibi R, Santos-García G (2023) Extended group decision-making methods with 2-tuple linguistic Fermatean fuzzy sets. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08158-0
Akram M, Shahzadi S, Shah SMU, Allahviranloo T (2023) An extended multi-objective transportation model based on Fermatean fuzzy sets. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08117-9
Akram M, Zafar F (2018) Multi-criteria decision-making methods under soft rough fuzzy knowledge. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 35(3):3507–3528
Akram M, Zafar F (2019) A new approach to compute measures of connectivity in rough fuzzy network models. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 36(1):449–465
Akram M, Kahraman C, Zahid K (2021) Extension of TOPSIS model to the decision-making under complex spherical fuzzy information. Soft Comput 25:10771–10795
Akram M, Khan A, Luqman A, Senapati T, Pamučar D (2023) An extended MARCOS method for MCGDM under 2-tuple linguistic q-rung picture fuzzy environment. Eng Appl Artif Intell 120:105892
Afshar A, Mariño MA, Saadatpour M, Afshar A (2011) Fuzzy TOPSIS multi-criteria decision analysis applied to Karun reservoirs system. Water Resour Manage 25:545–563
Bellman RE, Zadeh LA (1970) Decision-making in a fuzzy environment. Manage Sci 17(4):141–164
Biswas R (1994) On rough sets and fuzzy rough sets. Bull Pol Acad Sci Math 42:345–349
Biswas R (1994) On rough fuzzy sets. Bull Pol Acad Sci Math 42:352–355
Chakrabarty K, Biswas R, Nanda S (2000) Fuzziness in rough sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 110:247–251
Chen Z, Lu M, Ming X, Zhang X, Zhou T (2020) Explore and evaluate innovative value propositions for smart product service system: a novel graphics-based rough-fuzzy DEMATEL method. J Clean Prod 243:118672
Dubois D, Prade H (1990) Rough fuzzy sets and fuzzy rough sets. Int J General Syst 17:191–209
Deveci M, Pamučar D, Oguz E (2022) Floating photovoltaic site selection using fuzzy rough numbers based LAAW and RAFSI model. Appl Energy 342:119597
Deveci M, Erdogan N, Pamučar D, Kucuksari S, Cali U (2023) A rough Dombi Bonferroni based approach for public charging station type selection. Appl Energy 345:121258
Farnam M, Darehmiraki M (2022) Supply chain management problem modelling in hesitant fuzzy environment. J Fuzzy Ext Appl 3(4):317–336
Feng F, Li C, Davvaz B, Ali MI (2010) Soft sets combined with fuzzy sets and rough sets: a tentative approach. Soft Comput 14(9):899–911
Feng F (2011) Soft rough sets applied to multicriteria group decision making. Ann Fuzzy Math Inf 2(1):69–80
Feng F, Liu X, Leoreanu-Fotea V, Jun YB (2011) Soft sets and soft rough sets. Inf Sci 181(6):1125–1137
Gokasar I, Pamučar D, Deveci M, Ding W (2023) A novel rough numbers based extended MACBETH method for the prioritization of the connected autonomous vehicles in real-time traffic management. Expert Syst Appl 211:118445
Gokasar I, Deveci M, Isik M, Daim T, Zaidan AA, Smarandache F (2023) Evaluation of the alternatives of introducing electric vehicles in developing countries using Type-2 neutrosophic numbers based RAFSI model. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 192:122589
Gokasar I, Pamučar D, Deveci M, Gupta BB, Martinez L, Castillo O (2023) Metaverse integration alternatives of connected autonomous vehicles with self-powered sensors using fuzzy decision making model. Inf Sci 642:119192
Hwang CL, Yoon K (1981) Multiple attributes decision making methods and applications. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Khan A, Ahmad U, Shahzadi S (2023) A new decision analysis based on 2-tuple linguistic q-rung picture fuzzy ITARA-VIKOR method. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08263-0
Lui F, Li T, Wu J, Liu Y (2021) Modification of the BWM and MABAC method for MAGDM based on q-rung orthopair fuzzy rough numbers. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 12(9):2693–2715
Leoreanu-Fotea V (2008) The lower and upper approximations in a hypergroup. Inf Sci 178(18):3605–3615
Minatour Y, Bonakdari H, Zarghami M, Bakhshi MA (2015) Water supply management using an extended group fuzzy decision-making method: a case study in north-eastern Iran, Applied Water. Science 5:291–304
Minatour Y, Khazaie J, Ataei M (2013) Earth dam site selection using the analytic hierarchy process (AHP): a case study in the west of Iran. Arab J Geosci 6:3417–3426
Minatour Y, Khazaie J, Ataei M, Javadi AA (2015) An integrated decision support system for dam site selection. Sci Iran Trans A Civ Eng 22(2):319
Matić B, Marinković M, Jovanović S, Sremac S, Stević Ž (2022) Intelligent novel IMF D-SWARA-Rough MARCOS algorithm for selection construction machinery for sustainable construction of road infrastructure. Buildings 12(7):1059
Noori A, Bonakdari H, Hassaninia M, Morovati K, Khorshidi I, Noori A, Gharabaghi B (2022) A reliable GIS-based FAHP-FTOPSIS model to prioritize urban water supply management scenarios: a case study in semi-arid climate. Sustain Cities Soc 81:103846
Nanda S, Majumdar S (1992) Fuzzy rough sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 45:157–160
Opricovic S (1998) Multicriteria optimization of civil engineering systems. Fac Civ Eng Belgrade 2(1):5–21
Pamučar D, Petrović I, Ćirović G (2018) Modification of the Best-Worst and MABAC methods: a novel approach based on interval-valued fuzzy-rough numbers. Expert Syst Appl 91:89–106
Pamučar D, Simic V, Lazarević D, Dobrodolac M, Deveci M (2022) Prioritization of sustainable mobility sharing systems using integrated fuzzy DIBR and fuzzy-rough EDAS model. Inf Sci 82:103910
Pamučar D, Puška A, Simić V, Stojanović I, Deveci M (2023) Selection of healthcare waste management treatment using fuzzy rough numbers and Aczel-Alsina Function. Eng Appl Artif Intell 121:106025
Pamučar D, Torkayesh AE, Biswas S (2022) Supplier selection in healthcare supply chain management during the COVID-19 pandemic: a novel fuzzy rough decision-making approach. Ann Oper Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04529-2
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inform Sci 11(5):341–356
Pawlak Z (1985) Rough sets and fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 17:99–102
Pawlak Z (1996) Rough sets, rough relations and rough functions. Fund Inform 27(2):103–108
Saaty TL (1986) Axiomatic foundation of the analytic hierarchy process. Manage Sci 32(7):841–855
Srdjevic B, Medeiros YDP (2008) Fuzzy AHP assessment of water management plans. Water Resour Manage 22:877–894
Subotić M, Radičević V, Pavlović Z, Ćirović G (2021) Development of a new risk assessment methodology for light goods vehicles on two-lane road sections. Symmetry 13(7):1271
Sarwar M, Ali G, Chaudhry NR (2023) Decision-making model for failure modes and effect analysis based on rough fuzzy integrated clouds. Appl Soft Comput 136:110148
Sarwar M, Zafar F, Majeed IA, Javed S (2022) Selection of suppliers in industrial manufacturing: a fuzzy rough PROMETHEE approach. Math Probl Eng 2022:6141225
Stanković M, Stević Ž, Das DK, Subotić M, Pamučar D (2020) A new fuzzy MARCOS method for road traffic risk analysis. Mathematics 8(3):457
Simon U, Brüggemann R, Pudenz S (2004) Aspects of decision support in water management-example Berlin and Potsdam (Germany) I-spatially differentiated evaluation. Water Res 38(7):1809–1816
Stević Ž, Pamučar D, Puška A, Chatterjee P (2020) Sustainable supplier selection in healthcare industries using a new MCDM method: measurement of alternatives and ranking according to compromise solution (MARCOS). Comput Ind Eng 140:106231
Vojinović N, Sremac S, Zlatanović D (2021) A novel integrated fuzzy-rough MCDM model for evaluation of companies for transport of dangerous goods. Complexity 2021:5141611
Wang M, Zhang Y, Tian Y, Zhang K (2023) An integrated rough-fuzzy WINGS-ISM method with an application in ASSCM. Expert Syst Appl 212:118843
Wei LH, Jing LY, Wu W, Mou L (2011) Research on security assessment model of water supply system based on leakage control. Procedia Environ Sci 11:749–756
Zafar F, Akram M (2018) A novel decision making method based on rough fuzzy information. Int J Fuzzy Syst 20:1000–1014
Zaidan AA, Alsattar HA, Qahtan S, Deveci M, Pamucar D, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M (2023) Uncertainty decision modeling approach for control engineering tools to support industrial cyber-physical metaverse smart manufacturing systems. IEEE Syst J. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2023.3266842
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning-I. Inf Sci 8(3):199–249
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning-II. Inf Sci 8(4):301–357
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning-III. Inf Sci 9(1):43-80
Zhai LY, Khoo LP, Zhong ZW (2009) Design concept evaluation in product development using rough sets and grey relation analysis. Expert Syst Appl 36(3):7072–7079
Zhang K, Zhan J, Wang X (2020) TOPSIS-WAA method based on a covering-based fuzzy rough set: an application to rating problem. Inf Sci 539:397–421
Zhu GN, Hu J, Ren H (2020) A fuzzy rough number-based AHP-TOPSIS for design concept evaluation under uncertain environments. Appl Soft Comput 91:106228
Zhu GN, Ma J, Hu J (2021) Evaluating biological inspiration for biologically inspired design: an integrated DEMATEL-MAIRCA based on fuzzy rough numbers. Int J Intell Syst 36(10):6032–6065
Zhu GN, Hu J, Qi J, Gu CC, Peng YH (2015) An integrated AHP and VIKOR for design concept evaluation based on rough number. Adv Eng Inf 29(3):408–418
Zhu GN, Ma J, Hu J (2022) A fuzzy rough number extended AHP and VIKOR for failure mode and effects analysis under uncertainty. Adv Eng Inf 51:101454
Funding
There is no specific funding for this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval.
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by the author.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akram, Z., Ahmad, U. A multi-criteria group decision-making method based on fuzzy rough number for optimal water supply strategy. Soft Comput (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08942-y
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08942-y