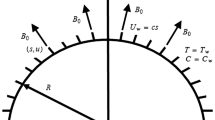
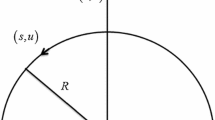
Abstract
Current determination is committed to characterize the features of curved surface for Sisko fluid in the presence of Lorentz’s forces. Heat–mass relocation exploration is conducted in the presence of homogeneous–heterogeneous processes and non-uniform heat sink/source. Similarity variables are designated to transmute nonlinear PDEs into ODEs. These intricate ordinary differential expressions assessing the flow situation are handled efficaciously by manipulating bvp4c scheme. Graphical demonstration is deliberated to scrutinize the variation in pressure, velocity, temperature and concentration profiles with respect to flow regulating parameters. Numerical data are displayed through tables in order to surmise variation in surface drag force and heat transport rate. It is noted that radius of curvature and temperature-dependent heat sink/source significantly affect heat–mass transport mechanisms for curved surface. Furthermore, graphical analysis reveals that velocity profile of Sisko magneto-fluid enhances for augmented values of curvature parameter. Additionally, it is evaluated that increasing values of heat source parameter and Lorentz’s forces, pressure profile exhibited the diminishing behavior.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- r, s :
-
Curvilinear coordinates
- \( a, b, n \) :
-
Material constants
- E, F :
-
Autocatalysts
- \( G_{a} ,G_{b} \) :
-
Concentration of chemical species E and F
- \( k_{1} ,k_{s} \) :
-
Rate coefficient of homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions
- \( G_{a0} \) :
-
Uniform concentration
- \( B_{0} \) :
-
Applied magnetic field
- R :
-
Radius of curvature
- V :
-
Velocity vector
- u,v :
-
Velocity components
- \( \rho_{\text{f}} \) :
-
Fluid density
- K :
-
Thermal conductivity
- T :
-
Temperature of fluid
- \( T_{\text{w}} \) :
-
Temperature at the wall
- \( T_{\infty } \) :
-
Ambient temperature
- \( q_{\text{r}} \) :
-
Radiative heat flux
- \( D_{A} ,D_{B} \) :
-
Diffusion coefficients of two species (E, F)
- \( q^{\prime \prime \prime } \) :
-
Heat sink/source
- C :
-
Constant
- \( \alpha_{1} \) :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- \( U_{w} \) :
-
Stretching velocity
- P :
-
Pressure
- \( A^{*} \) :
-
Space dependent
- \( B^{*} \) :
-
Temperature dependent
- \( \eta \) :
-
Dimensionless variable
- \( \psi \) :
-
Stream function
- P :
-
Dimensionless pressure
- \( R_{d} \) :
-
Radiation parameter
- F :
-
Dimensionless velocity
- \( \theta \) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \( \varphi \) :
-
Dimensionless concentration
- \( \delta \) :
-
Unsteadiness parameter
- M :
-
Magnetic parameter
- \( \varepsilon \) :
-
Diffusion coefficient
- Pr:
-
Generalized Prandtl number
- \( k_{2} \) :
-
Strength coefficient homogenous reaction
- Sc:
-
Generalized Schmidt number
- K :
-
Dimensionless radius of curvature
- A :
-
Material parameter of the Sisko fluid
- \( \gamma \) :
-
Generalized Biot number
- \( \tau_{w} \) :
-
Surface shear stress
- \( q_{w} \) :
-
Surface heat flux
- \( C_{\text{f}} \) :
-
Skin friction coefficient
- \( {\text{Nu}}_{s} \) :
-
Local Nusselt number
- \( \text{Re}_{a} ,\text{Re}_{b} \) :
-
Local Reynolds numbers
References
Ali M, Khan WA, Irfan M, Sultan F, Shahzed M, Khan M (2019a) Computational analysis of entropy generation for cross-nanofluid flow. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01038-w
Ali M, Sultan F, Khan WA, Shahzad M (2019b) Exploring the physical aspects of nanofluid with entropy generation. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01173-4
Ali M, Sultan F, Khan WA, Shahzad M, Arif H (2020) Important features of expanding/contracting cylinder for cross magneto-nanofluid flow. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 133:109656
Anwar MS, Rasheed A (2018) Joule heating in magnetic resistive flow with fractional Cattaneo–Maxwell model. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1426-8
Asghar Z, Ali N, Ahmed R, Waqas M, Khan WA (2019) A mathematical framework for peristaltic flow analysis of non-Newtonian Sisko fluid in an undulating porous curved channel with heat and mass transfer effects. Comput Methods Program Biomed 182:105040
Chaudhary MA, Merkin JH (1995) A simple isothermal model for homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions in boundary-layer flow. I. Equal diffusivities. Fluid Dyn Res 16:311–333
Deng W, Yao R, Zhao H, Yang X, Li G (2017a) A novel intelligent diagnosis method using optimal LS-SVM with improved PSO algorithm. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2940-9
Deng W, Zhao H, Zou L, Li G, Yang X, Wu D (2017b) A novel collaborative optimization algorithm in solving complex optimization problems. Soft Comput 21(15):4387–4398
Deng W, Zhao H, Yang X, Xiong J, Sun M, Li B (2017c) Study on an improved adaptive PSO algorithm for solving multi-objective gate assignment. Appl Soft Comput 59:288–302
Deng W, Xu J, Zhao H (2019) An improved ant colony optimization algorithm based on hybrid strategies for scheduling problem. IEEE Access 7:20281–20292
Haq I, Shahzad M, Khan WA, Irfan M, Mustafa S, Ali M, Sultan F (2019) Characteristics of chemical processes and heat source/sink with wedge geometry. Case Stud Therm Eng 14:100432
Hayat T, Rashid M, Alsaedi A (2018) Three dimensional radiative flow of magnetite-nanofluid with homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions. Results Phys 8:268–275
Hei Y, Zhang C, Song W, Kou Y (2019) Energy and spectral efficiency tradeoff in massive MIMO systems with multi-objective adaptive genetic algorithm. Soft Comput 23:7163–7179
Imtiaz M, Mabood F, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2019) Homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions in MHD radiative flow of second grade fluid due to a curved stretching surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf 145:118781
Irfan M, Khan M, Khan WA (2018) Interaction between chemical species and generalized Fourier’s law on 3D flow of Carreau fluid with variable thermal conductivity and heat sink/source: a numerical approach. Results Phys 10:107–117
Khan WA, Khan M, Alshomrani AS, Ahmad L (2016) Numerical investigation of generalized Fourierís and Fickís laws for Sisko fluid flow. J Mol Liq 224:1016–1021
Khan M, Irfan M, Khan WA, Alshomrani AS (2017) A new modeling for 3D Carreau fluid flow considering nonlinear thermal radiation. Results Phys 7:2692–2704
Khan M, Irfan M, Khan WA, Ayaz M (2018) Aspects of improved heat conduction relation and chemical processes on 3D Carreau fluid flow. Pramana J Phys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-018-1579-0
Khan WA, Ali M, Sultan F, Shahzad M, Khan M, Irfan M (2019a) Numerical interpretation of autocatalysis chemical reaction for nonlinear radiative 3D flow of cross magnetofluid. Pramana J Phys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-018-1678-y
Khan WA, Sultan F, Ali M, Shahzad M, Khan M, Irfan M (2019b) Consequences of activation energy and binary chemical reaction for 3D fow of Cross-nanofluid with radiative heat transfer. J Braz Soc Mech Sci 41:4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1482-0
Khan WA, Ali M, Sultan F, Shahzad M, Khan M, Irfan M (2019c) Numerical interpretation of autocatalysis chemical reaction for nonlinear radiative 3D flow of cross magnetofluid. Pramana J Phys 92:16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-018-1678-y
Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Shashikumar NS, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2018) Marangoni convection in Casson liquid flow due to an infinite disk with exponential space dependent heat source and cross-diffusion effects. Results Phys 9:78–85
Mahdy A (2019) Aspects of homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions on natural convection flow of micropolar fluid past a permeable cone. Appl Math Comput 352:59–67
Malik R, Khan M (2018) Numerical study of homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in Sisko fluid flow past a stretching cylinder. Results Phys 8:64–70
Merkin JH (1996) A model for isothermal homogenous-heterogeneous reactions in boundarylayer flow. Math Comput Model 24:125–136
Muhammad S, Ali G, Shah SIA, Irfan M, Khan WA, Ali M, Sultan F (2019) Numerical treatment of activation energy for the three-dimensional flow of a cross magnetonanoliquid with variable conductivity. Pramana J Phys 93:40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-019-1800-9
Rashid M, Hayat T, Rafique K, Alsaedi A (2019) Chemically reactive flow of thixotropic nanofluid with thermal radiation. Pramana J Phys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-019-1837-9
Shahzad M, Ali M, Sultan F, Khan WA, Hussain Z (2020) Computational investigation of magneto-cross fluid flow with multiple slip along wedge and chemically reactive species. Results Phys 16:102972
Shen M, Chen L, Zhang M, Liu F (2018) A renovated Buongiorno’s model for unsteady Sisko nanofluid with fractional Cattaneo heat flux. Int J Heat Mass Transf 126:277–286
Soomro FA, Usman M, Haq RU, Wang W (2018) Melting heat transfer analysis of Sisko fluid over a moving surface with nonlinear thermal radiation via collocation method. Int J Heat Mass Transf 126:1034–1042
Sultan F, Khan WA, Ali M, Shahzad M, Irfan M, Khan M (2019a) Theoretical aspects of thermophoresis and Brownian motion for three-dimensional flow of the cross fluid with activation energy. Pramana J Phys 92:21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-018-1676-0
Sultan F, Khan WA, Ali M, Shahzad M, Sun H, Irfan M (2019b) Importance of entropy generation and infinite shear rate viscosity for non-Newtonian nanofluid. Int J Mech Sci 41:439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1950-1
Toghraie D, Esfahani NN, Zarringhalam M, Shirani N, Rostami S (2020) Blood flow analysis inside different arteries using non-Newtonian Sisko model for application in biomedical engineering. Comput Methods Program Biomed. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105338
Waqas M (2020) A mathematical and computational framework for heat transfer analysis of ferromagnetic non-Newtonian liquid subjected to heterogeneous and homogeneous reactions. J Mag Mag Mater 493:165646
Waqas M, Jabeen S, Hayat T, Khan MI, Alsaedi A (2019) Modeling and analysis for magnetic dipole impact in nonlinear thermally radiating Carreau nanofluid flow subject to heat generation. J Magn Magn Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.03.040
Xu NL, Xu H, Raees A (2018) Homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions in flow of nanofluids near the stagnation region of a plane surface: the Buongiorno’s model. Int J Heat Mass Transf 125:604–609
Zhang S, Zhao H, Xu J, Deng W (2019) A novel fault diagnosis method based on improved adaptive VMD energy entropy and PNN. Trans Can Soc Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1139/tcsme-2018-0195
Zhao H, Deng W, Li G, Lifeng Y, Bing Y (2016) Research on a new fault diagnosis method based on WT, improved PSO and SVM for motor. Recent Patents Mech Eng 9:289–298
Zhao H, Sun D, Deng W, Yang X (2017) A new feature extraction method based on EEMD and multi-scale fuzzy entropy for motor bearing. Entropy. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19010014
Zhao H, Zheng J, Xu J, Deng W (2019a) Fault diagnosis method based on principal component analysis and broad learning system. IEEE Access 7:99263–99272
Zhao H, Liu H, Xu J, Deng W (2019b) performance prediction using high-order differential mathematical morphology gradient spectrum entropy and extreme learning machine. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2019.2948414
Zhao H, Zheng J, Deng W, Song Y (2020) Semi-supervised broad learning system based on manifold regularization and broad network. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 67(3):983–994
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the postdoctoral international exchange program for incoming postdoctoral students, at Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, M., Irfan, M., Khan, W.A. et al. Physical significance of chemical processes and Lorentz’s forces aspects on Sisko fluid flow in curved configuration. Soft Comput 24, 16213–16223 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04935-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04935-3