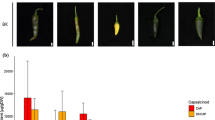
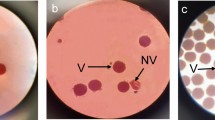
Key message
Function of Petunia PiSSK1.
Abstract
Self-incompatibility (SI), an inbreeding-preventing mechanism, is regulated in Petunia inflata by the polymorphic S-locus, which houses multiple pollen-specific S-locus F-box (SLF) genes and a single pistil-specific S-RNase gene. S 2-haplotype and S 3-haplotype possess the same 17 polymorphic SLF genes (named SLF1 to SLF17), and each SLF protein produced in pollen is assembled into an SCF (Skp1–Cullin1–F-box) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. A complete suite of SLF proteins is thought to collectively interact with all non-self S-RNases to mediate their ubiquitination and degradation by the 26S proteasome, allowing cross-compatible pollination. For each SCFSLF complex, the Cullin1 subunit (named PiCUL1-P) and Skp1 subunit (named PiSSK1), like the F-box protein subunits (SLFs), are pollen-specific, raising the possibility that they also evolved specifically to function in SI. Here we used CRISPR/Cas9-meditated genome editing to generate frame-shift indel mutations in PiSSK1 and examined the SI behavior of a T 0 plant (S 2 S 3) with biallelic mutations in the pollen genome and two progeny plants (S 2 S 2) each homozygous for one of the indel alleles and not carrying the Cas9-containing T-DNA. Their pollen was completely incompatible with pistils of seven otherwise-compatible S-genotypes, but fully compatible with pistils of an S 3 S 3 transgenic plant in which production of S3-RNase was completely suppressed by an antisense S 3-RNase gene, and with pistils of immature flower buds, which produce little S-RNase. These results suggest that PiSSK1 specifically functions in SI and support the hypothesis that SLF-containing SCF complexes are essential for compatible pollination.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abràmoff MD, Magalhães PJ, Ram SJ (2004) Image processing with imageJ. Biophotonics Int 11:36–41
Ai Y, Singh A, Coleman CE, Ioerger TR, Kheyr-Pour A, Kao T-h (1990) Self-incompatibility in Petunia inflata: isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding three S-allele-associated proteins. Sex Plant Reprod 3:130–138
Bombarely A, Moser M, Amrad A et al (2016) Insight into the evolution of the Solanaceae from the parental genomes of Petunia hybrida. Nat Plants 2:16074
Broothaerts W, Keulemans J, Van Nerum I (2004) Self-fertile apple resulting from S-RNase gene silencing. Plant Cell Rep 22:497–501
de Nettancourt D (2001) Incompatibility and incongruity in wild and cultivated plants. Springer, Berlin
Dezfulian MH, Soulliere DM, Dhaliwal RK, Sareen M, Crosby WL (2012) The SKP1-Like gene family of Arabidopsis exhibits a high degree of differential gene expression and gene product interaction during development. PLoS ONE 7:e50984
Dove KK, Kemp HA, Di KR, Reiter KH, Milburn LJ, Camacho D, Fay DS, Miller DL, Klevit RE (2017) Two functionally distinct E2/E3 pairs coordinate sequential ubiquitination of a common substrate in Caenorhabditis elegans development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:e6576–e6584. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1705060114
Eddy SR (2011) Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput Biol 7:e1002195
Engler C, Kandzia R, Marillonnet S (2008) A one pot, one step, precision cloning method with high throughput capability. PLoS ONE 3:e3647
Entani T, Kubo K, Isogai S, Fukao Y, Shirakawa M, Isogai A, Takayama S (2014) Ubiquitin-proteasome-mediated degradation of S-RNase in a solanaceous cross-compatibility reaction. Plant J 78:1014–1021
Gagne JM, Downes BP, Shiu S-HH, Durski AM, Vierstra RD (2002) The F-box subunit of the SCF E3 complex is encoded by a diverse superfamily of genes in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11519–11524
Gao Y, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Dai X, Estelle M, Zhao Y (2015) Auxin binding protein 1 (ABP1) is not required for either auxin signaling or Arabidopsis development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:2275–2280
Goldraij A, Kondo K, Lee CB, Hancock CN, Sivaguru M, Vasquez-Santana S, Kim S, Phillips TE, Cruz-Garvia F, McClure B (2006) Compartmentalization of S-RNase and HT-B degradation in self-incompatible Nicotiana. Nature 439:805–810
Gray WM, Kepinski S, Rouse D, Leyser O, Estelle M (2001) Auxin regulates SCFTIR1-dependent degradation of AUX/IAA proteins. Nature 414:271–276
Hua Z, Kao T-h (2006) Identification and characterization of components of a putative Petunia S-locus F-box-containing E3 ligase complex involved in S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. Plant Cell 18:2531–2553
Huang S, Lee H-S, Karunanandaa B, Kao T-h (1994) Ribonuclease activity of Petunia inflata S proteins is essential for rejection of self-pollen. Plant Cell 6:1021–1028
Huang J, Zhao L, Yang Q, Xue Y (2006) AhSSK1, a novel SKP1-like protein that interacts with the S-locus F-box protein SLF. Plant J 46:780–793
Kay R, Chan AMY, Daly M, McPherson J (1987) Duplication of CaMV 35S promoter sequences creates a strong enhancer for plant genes. Science 236:1299–1302
Kong H, Leebens-Mack J, Ni W, DePamphilis CW, Ma H (2004) Highly heterogeneous rates of evolution in the SKP1 gene family in plants and animals: functional and evolutionary implications. Mol Biol Evol 21:117–128
Kong H, Landherr LL, Frohlich MW, Leebens-Mack J, Ma H, DePamphilis CW (2007) Patterns of gene duplication in the plant SKP1 gene family in angiosperms: evidence for multiple mechanisms of rapid gene birth. Plant J 50:873–885
Kubo KI, Entani T, Takara A, Wang N, Fields AM, Hua Z, Toyoda M, Kawashima SI, Ando T, Isogai A, Kao T-h, Takayama S (2010) Collaborative non-self recognition system in S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. Science 330:796–799
Kubo K, Tsukahara M, Fujii S, Murase K, Wada Y, Entani T, Iwano M, Takayama S (2016) Cullin1-P is an essential component of non-self recognition system in self-incompatibility in Petunia. Plant Cell Physiol 57:2403–2416
Lai Z, Ma W, Han B, Liang L, Zhang Y, Hong G, Xue Y (2002) An F-box gene linked to the self-incompatibility (S) locus of Antirrhinum is expressed specifically in pollen and tapetum. Plant Mol Biol 50:29–41
Lee H-S, Huang S, Kao T-h (1994) S proteins control rejection of incompatible pollen in Petunia inflata. Nature 367:560–563
Li S, Sun P, Williams JS, Kao T-h (2014) Identification of the self-incompatibility locus F-box protein-containing complex in Petunia inflata. Plant Reprod 27:31–45
Li S, Williams JS, Sun P, Kao T-h (2016) All 17 types of S-locus F-box proteins of S 2- and S 3-haplotypes of Petunia inflata are assembled into similar SCF complexes with specific function in self-incompatibility. Plant J 87:606–616
Li F-C, Wang J, Wu M-M, Fan C-M, Li X, He J-M (2017) Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatases affect UV-B-induced stomatal closure via controlling NO in guard cells. Plant Physiol 173:760–770
Liu F, Ni W, Griffith ME, Huang Z, Chang C, Peng W, Ma H, Xie D (2004) The ASK1 and ASK2 genes are essential for Arabidopsis early development. Plant Cell 16:5–20
Luu DT, Qin X, Morse D, Cappadocia M (2000) S-RNase uptake by compatible pollen tubes in gametophytic self-incompatibility. Nature 407:649–651
Ma X, Chen L, Zhu Q, Chen Y, Liu YG (2015) Rapid decoding of sequence-specific nuclease-induced heterozygous and biallelic mutations by direct sequencing of PCR products. Mol Plant 8:1285–1287
Meng X, Hua Z, Sun P, Kao T-h (2011) The amino terminal F-box domain of Petunia inflata S-locus F-box protein is involved in the S-RNase-based self-incompatibility mechanism. AoB Plants 11:1–14
Minamikawa MF, Koyano R, Kikuchi S, Koba T, Sassa H (2014) Identification of SFBB-containing canonical and noncanonical SCF complexes in pollen of apple (Malus x domestica). PLoS ONE 9:e97642
Murfett J, Atherton TL, Mou B, Gasser CS, McClure B (1994) S-RNase expressed in transgenic Nicotiana causes S-allele-specific pollen rejection. Nature 367:563–566
Pierce NW, Lee JE, Liu X, Sweredoski MJ, Graham RL, Larimore EA, Rome M, Zheng N, Clurman BE, Hess S, Shan SO, Deshaies RJ (2013) Cand1 promotes assembly of new SCF complexes through dynamic exchange of F-box proteins. Cell 153:206–215
Qiao H, Wang H, Zhao L, Zhou J, Huang J, Zhang Y, Xue Y (2004) The F-box protein AhSLF-S2 physically interacts with S-RNases that may be inhibited by the ubiquitin/26S proteasome pathway of protein degradation during compatible pollination in Antirrhinum. Plant Cell 16:582–595
Risseeuw EP, Daskalchuk TE, Banks TW, Liu E, Cotelesage J, Hellmann H, Estelle M, Somers DE, Crosby WL (2003) Protein interaction analysis of SCF ubiquitin E3 ligase subunits from Arabidopsis. Plant J 34:753–767
Rossi A, Kontarakis Z, Gerri C, Nolte H, Hölper S, Krüger M, Stainier DYR (2015) Genetic compensation induced by deleterious mutations but not gene knockdowns. Nature 524:230–233
Rost B, Liu J (2003) The predictprotein server. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3300–3304
Sassa H, Kakui H, Miyamoto M, Suzuki Y, Hanada T, Ushijima K, Kusaba M, Hirano H, Koba T (2007) S locus F-box brothers: multiple and pollen-specific F-box genes with S haplotype-specific polymorphisms in apple and Japanese pear. Genetics 175:1869–1881
Schulman BA, Carrano AC, Jeffrey PD, Bowen Z (2000) Insights into SCF ubiquitin ligases from the structure of the Skp1–Skp2 complex. Nature 408:381–386
Sijacic P, Wang X, Skirpan AL, Wang Y, Dowd PE, McCubbin AG, Huang S, Kao T-h (2004) Identification of the pollen determinant of S-RNase-mediated self-incompatibility. Nature 429:302–305
Sims TL, Ordanic M (2001) Identification of a S-ribonuclease-binding protein in Petunia hybrida. Plant Mol Biol 47:771–783
Sims TL, Robbins TP (2009) Gametophytic self-incompatibility in Petunia. In: Gerats T, Strommer J (eds) Petunia: evolutionary, developmental and physiological genetics, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 85–106
Sun P, Kao T-h (2013) Self-incompatibility in Petunia inflata: the relationship between a self-incompatibility locus F-box protein and its non-self S-RNases. Plant Cell 25:470–485
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Wang N, Kao T-h (2012) Self-incompatibility in Petunia: a self/nonself-recognition mechanism employing S-locus F-box proteins and S-RNase to prevent inbreeding. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol 1:267–275
Wang X, Hughes AL, Tsukamoto T, Ando T, Kao T-h (2001) Evidence that intragenic recombination contributes to allelic diversity of the S-RNase gene at the self-incompatibility (S) locus in Petunia inflata. Plant Physiol 125:1012–1022
Williams JS, Der JP, DePamphilis CW, Kao T-h (2014) Transcriptome analysis reveals the same 17 S-Locus F-Box genes in two haplotypes of the self-incompatibility locus of Petunia inflata. Plant Cell 26:2873–2888
Williams JS, Wu L, Li S, Sun P, Kao T-h (2015) Insight into S-RNase-based self-incompatibility in Petunia: recent findings and future directions. Front Plant Sci 6:41. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00041
Xie K, Minkenberg B, Yang Y (2015) Boosting CRISPR/Cas9 multiplex editing capability with the endogenous tRNA-processing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:3570–3575
Xing H-L, Dong L, Wang Z-P, Zhang H-Y, Han C-Y, Liu B, Wang X-C, Chen Q-J (2014) A CRISPR/Cas9 toolkit for multiplex genome editing in plants. BMC Plant Biol 14:327
Xu L, Liu F, Lechner E, Genschik P, Crosby WL, Ma H, Peng W, Huang D, Xie D (2002) The SCFCOI1 ubiquitin-ligase complexes are required for jasmonate response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 14:1919–1935
Xu C, Li M, Wu J, Guo H, Li Q, Zhang Y, Chai J, Li T, Xue Y (2013) Identification of a canonical SCFSLFcomplex involved in S-RNase-based self-incompatibility of Pyrus (Rosaceae). Plant Mol Biol 81:245–257
Yuan H, Meng D, Gu Z, Li W, Wang A, Yang Q, Zhu Y, Li T (2014) A novel gene, MdSSK1, as a component of the SCF complex rather than MdSBP1 can mediate the ubiquitination of S-RNase in apple. J Exp Bot 65:3121–3131
Zhang Y, Wang C, Lin Q, Gao F, Ma Y, Zhang M, Lin Y, Ma Q, Hua X (2015) Genome-wide analysis of phylogeny, expression profile and sub-cellular localization of SKP1-like genes in wild tomato. Plant Sci 238:105–114
Zhao D, Yang M, Solava JJ, Ma H (1999) The ASK1 gene regulates development and interacts with the UFO gene to control floral organ identity in Arabidopsis. Dev Genet 25:209–223
Zhao D, Ni W, Feng B, Han T, Petrasek MG, Ma H (2003) Members of the Arabidopsis SKP1-like gene family exhibit a variety of expression patterns and may play diverse roles in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 133:203–217
Zhao L, Huang J, Zhao Z, Li Q, Sims TL, Xue Y (2010) The Skp1-like protein SSK1 is required for cross-pollen compatibility in S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. Plant J 62:52–63
Zheng N, Schulman BA, Song L, Miller JJ, Jeffrey PD, Wang P, Chu C, Koepp DM, Elledge SJ, Pagano M, Conaway RC (2002) Structure of the Cul1-Rbx1-Skp1-F-boxSkp2 SCF ubiquitin ligase complex. Nature 416:703–709
Acknowledgements
We thank Yinong Yang and Bastian Minkenberg for providing pGTR plasmid and technical advice on CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing; Ning Zheng for discussion about PiSSK1 sequence features; Shawn Burghard for greenhouse management; Hongli Hao for general laboratory help. This work was supported by Grant IOS-1645557 from the National Science Foundation to Teh-hui Kao.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Noni Franklin-Tong.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, L., Kao, Th. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of PiSSK1 reveals essential role of S-locus F-box protein-containing SCF complexes in recognition of non-self S-RNases during cross-compatible pollination in self-incompatible Petunia inflata . Plant Reprod 31, 129–143 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-017-0314-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-017-0314-1