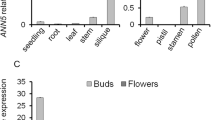
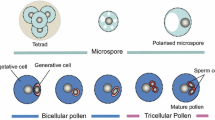
Key message
bZIP TF network in pollen.
Abstract
Transcriptional control of gene expression represents an important mechanism guiding organisms through developmental processes and providing plasticity towards environmental stimuli. Because of their sessile nature, plants require effective gene regulation for rapid response to variation in environmental and developmental conditions. Transcription factors (TFs) provide such control ensuring correct gene expression in spatial and temporal manner. Our work reports the interaction network of six bZIP TFs expressed in Arabidopsis thaliana pollen and highlights the potential functional role for AtbZIP18 in pollen. AtbZIP18 was shown to interact with three other pollen-expressed bZIP TFs—AtbZIP34, AtbZIP52, and AtbZIP61 in yeast two-hybrid assays. AtbZIP18 transcripts are highly expressed in pollen, and at the subcellular level, an AtbZIP18-GFP fusion protein was located in the nucleus and cytoplasm/ER. To address the role of AtbZIP18 in the male gametophyte, we performed phenotypic analysis of a T-DNA knockout allele, which showed slightly reduced transmission through the male gametophyte. Some of the phenotype defects in atbzip18 pollen, although observed at low penetrance, were similar to those seen at higher frequency in the T-DNA knockout of the interacting partner, AtbZIP34. To gain deeper insight into the regulatory role of AtbZIP18, we analysed atbzip18/– pollen microarray data. Our results point towards a potential repressive role for AtbZIP18 and its functional redundancy with AtbZIP34 in pollen.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe M, Kobayashi Y, Yamamoto S, Daimon Y, Yamaguchi A, Ikeda Y, Ichinoki H, Notaguchi M, Goto K, Araki T (2005) FD, a bZIP protein mediating signals from the floral pathway integrator FT at the shoot apex. Science 309:1052–1056
Alonso R, Oñate-Sánchez L, Weltmeier F, Ehlert A, Diaz I, Dietrich K, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Dröge-Laser W (2009) A pivotal role of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor bZIP53 in the regulation of Arabidopsis seed maturation gene expression based on heterodimerization and protein complex formation. Plant Cell 21:1747–1761
Amoutzias GD, Veron AS, Weiner J 3rd, Robinson-Rechavi M, Bornberg-Bauer E, Oliver SG, Robertson DL (2007) One billion years of bZIP transcription factor evolution: conservation and change in dimerization and DNA-binding site specificity. Mol Biol Evol 24:827–835
Amoutzias GD, Robertson DL, Van de Peer Y, Oliver SG (2008) Choose your partners: dimerization in eukaryotic transcription factors. Trends Biochem Sci 33:220–229
Baena-González E, Rolland F, Thevelein JM, Sheen J (2007) A central integrator of transcription networks in plant stress and energy signalling. Nature 448:938–942
Bedinger P (1992) Remarkable biology of pollen. Plant Cell 4:879–887
Bensmihen S, Rippa S, Lambert G, Jublot D, Pautot V, Granier F, Giraudat J, Parcy F (2002) The homologous ABI5 and EEL transcription factors function antagonistically to fine-tune gene expression during late embryogenesis. Plant Cell 14:1391–1403
Bokvaj P, Hafidh S, Honys D (2015) Transcriptome profiling of male gametophyte development in Nicotiana tabacum. Genom Data 3:106–111
Borg M, Brownfield L, Khatab H, Sidorova A, Lingaya M, Twell D (2011) The R2R3 MYB transcription factor DUO1 activates a male germline-specific regulon essential for sperm cell differentiation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 23(2):534–549
Borg M, Rutley N, Kagale S, Hamamura Y, Gherghinoiu M, Kumar S, Sari U, Esparza-Franco MA, Sakamoto W, Rozwadowski K, Higashiyama T, Twell D (2014) An EAR-dependent regulatory module promotes male germ cell division and sperm fertility in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26:2098–2113
Brambilla V, Battaglia R, Colombo M, Masiero S, Bencivenga S, Kater MM, Colombo L (2007) Genetic and molecular interactions between BELL1 and MADS box factors support ovule development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:2544–2556
Brownfield L, Hafidh S, Borg M, Sidorova A, Mori T, Twell D (2009) A plant germline-specific integrator of sperm specification and cell cycle progression. PLoS Genet. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000430
Causier B, Ashworth M, Guo W, Davies B (2012) The TOPLESS interactome: a framework for gene repression in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 158:423–438
Clough SJ, Benth AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Colombo M, Masiero S, Vanzulli S, Lardelli P, Kater MM, Colombo L (2008) AGL23, a type I MADS-box gene that controls female gametophyte and embryo development in Arabidopsis. Plant J 54:1037–1048
Corrêa LGG, Riaño-Pachón DM, Schrago CG, Vicentini dos Santos R, Mueller-Roeber B, Vincentz M (2008) The role of bZIP transcription factors in green plant evolution: adaptive features emerging from four founder genes. PLoS ONE 3:e2944. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002944
Dardelle F, Lehner A, Ramdani Y, Bardor M, Lerouge P, Driouich A, Mollet JC (2010) Biochemical and immunocytological characterizations of Arabidopsis pollen tube cell wall. Plant Physiol 153(4):1563–1576
Degnan BM, Vervoort M, Larroux C, Richards GS (2009) Early evolution of metazoan transcription factors. Curr Opin Genet Dev 19:591–599
Deppmann CD, Acharya A, Rishi V, Wobbes B, Smeekens S, Taparowsky EJ, Vinson C (2004) Dimerization specificity of all 67 B-ZIP motifs in Arabidopsis thaliana: a comparison to Homo sapiens B-ZIP motifs. Nucl Acids Res 32:3435–3445
Deppmann CD, Alvania RS, Taparowsky EJ (2006) Cross-species annotation of basic leucine zipper factor interactions: insight into the evolution of closed interaction networks. Mol Biol Evol 23:1480–1492
Dietrich K, Weltmeier F, Ehlert A, Weiste C, Stahl M, Harter K, Dröge-Laser W (2011) Heterodimers of the Arabidopsis transcription factors bZIP1 and bZIP53 reprogram amino acid metabolism during low energy stress. Plant Cell 23:381–395
Dupl’áková N, Reňák D, Hovanec P, Honysová B, Twell D, Honys D (2007) Arabidopsis Gene Family Profiler (aGFP): user-oriented transcriptomic database with easy-to-use graphic interface. BMC Plant Biol 7:39
Ehlert A, Weltmeier F, Wang X, Mayer CS, Smeekens S, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Dröge-Laser W (2006) Two-hybrid protein-protein interaction analysis in Arabidopsis protoplasts: establishment of a heterodimerization map of group C and group S bZIP transcription factors. Plant J 46:890–900
Fujita Y, Fujita M, Satoh R, Maruyama K, Parvez MM, Seki M, Hiratsu K, Ohme-Takagi M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2005) AREB1 is a transcription activator of novel ABRE-dependent ABA signaling that enhances drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:3470–3488
Galbiati F, Sinha Roy D, Simonini S, Cucinotta M, Ceccato L, Cuesta C, Simaskova M, Benkova E, Kamiuchi Y, Aida M, Weijers D, Simon R, Masiero S, Colombo L (2013) An integrative model of the control of ovule primordia formation. Plant J 76:446–455
Gao H, Brandizzi F, Benning C, Larkin RM (2008) A membrane-tethered transcription factor defines a branch of the heat stress response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:16398–16403
Gibalová A, Reňák D, Matczuk K, Dupl’áková N, Cháb D, Twell D, Honys D (2009) AtbZIP34 is required for Arabidopsis pollen wall patterning and the control of several metabolic pathways in developing pollen. Plant Mol Biol 70:581–601
Hafidh S, Breznenová K, Růžička P, Feciková J, Čapková V, Honys D (2012a) Comprehensive analysis of tobacco pollen transcriptome unveils common pathways in polar cell expansion and underlying heterochronic shift during spermatogenesis. BMC Plant Biol 12:24. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-12-24
Hafidh S, Breznenová K, Honys D (2012b) b. De novo post-pollen mitosis II tobacco pollen tube transcriptome. Plant Signal Behav 7:918–921
Hafidh S, Fila J, Honys D (2016) Male gametophyte development and function in angiosperms: a general concept. Plant Reprod 29(1):31–51
Honys D, Twell D (2003) Comparative analysis of Arabidopsis pollen transcriptome. Plant Physiol 132:640–652
Honys D, Twell D (2004) Transcriptome analysis of haploid male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol 5:85R
Hurst HC (1994) Transcription factors. 1: bZIP proteins. Protein Profile 1:123–168
Iven T, Strathmann A, Böttner S, Zwafink T, Heinekamp T, Guivarc’h A, Roitsch T, Dröge-Laser W (2010) Homo- and heterodimers of tobacco bZIP proteins counteract as positive or negative regulators of transcription during pollen development. Plant J 63:155–166
Iwata Y, Koizumi N (2005) An Arabidopsis transcription factor, AtbZIP60, regulates the endoplasmic reticulum stress response in a manner unique to plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5280–5285
Iwata Y, Fedoroff NV, Koizumi N (2008) Arabidopsis bZIP 60 is a proteolysis activated transcription factor involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Plant Cell 20:3107–3121
Jakoby M, Weisshaar B, Dröge-Laser W, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Tiedemann J, Kroj T, Parcy F, bZIP Research Group (2002) bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 7:106–111
Kagale S, Links MG, Rozwadowski K (2010) Genome-wide analysis of ethylene-responsive element binding factor-associated amphiphilic repression motif-containing transcriptional regulators in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 152:1109–1134
Kaminaka H, Näke C, Epple P, Dittgen J, Schütze K, Chaban C, Holt BF 3rd, Merkle T, Schäfer E, Harter K, Dangl JL (2006) bZIP10-LSD1 antagonism modulates basal defense and cell death in Arabidopsis following infection. EMBO J 20:4400–4411
Karimi M, Inzé D, Depicker A (2002) GATEWAY™ vectors for Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Trends Plant Sci 7:193–195
Kerppola TK (2006) Design and implementation of bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays for the visualization of protein interactions in living cells. Nat Prot 1(3):1278–1286
Lalanne E, Michaelidis C, Moore JM, Gagliano W, Johnson A, Patel R, Howden R, Vielle-Calzada JP, Grossniklaus U, Twell D (2004) Analysis of transposon insertion mutants highlights the diversity of mechanisms underlying male progamic development in Arabidopsis. Genetics 167:1975–1986
Lee KA (1992) Dimeric transcription factor families: it takes two to tango but who decides on partners and the venue? J Cell Sci 103:9–14
Lehner A, Dardelle F, Soret-Morvan O, Lerouge P, Driouich A, Mollet JC (2010) Pectins in the cell wall of Arabidopsis thaliana pollen tube and pistil. Plant Signal Behav 5(10):1282–1285
Li W, Jain MR, Chen C, Yue X, Hebbar V, Zhou R, Kong AN (2005) Nrf2 possesses a redox—insensitive nuclear export signal overlapping with the leucin zipper motif. J Biol Chem 280:28430–28438
Liu JX, Srivastava R, Che P, Howell SH (2007) An endoplasmic reticulum stress response in Arabidopsis is mediated by proteolytic processing and nuclear relocation of a membrane-associated transcription factor, bZIP28. Plant Cell 19:4111–4119
Llorca CM, Potschin M, Zentgraf U (2014) bZIPs and WRKYs: two large transcription factor families executing two different functional strategies. Front Plant Sci 5:169. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00169
Long JA, Ohno C, Smith ZR, Meyerowitz EM (2006) TOPLESS regulates apical embryonic fate in Arabidopsis. Science 312:1520–1523
Lozano-Sotomayor P, Chávez Montes RA, Silvestre-Vañó M, Herrera-Ubaldo H, Greco R, Pablo-Villa J, Galliani BM, Diaz-Ramirez D, Weemen M, Boutilier K, Pereira A, Colombo L, Madueño F, Marsch-Martínez N, de Folter S (2016) Altered expression of the bZIP transcription factor DRINK ME affects growth and reproductive development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. doi:10.1111/tpj.13264
Naar AM, Lemon BD, Tjian R (2001) Transcriptional coactivator complexes. Annu Rev Biochem 70:475–501
Nakagawa T, Kurose T, Hino T, Tanaka K, Kawamukai M, Niwa Y, Toyooka K, Matsuoka K, Jinbo T, Kimura T (2007) Development of series of gateway binary vectors, pGWBs, for realizing efficient construction of fusion genes for plant transformation. J Biosci Bioeng 104:34–41
Nelson BK, Cai X, Nebenführ A (2007) A multicolored set of in vivo organelle markers for co-localization studies in Arabidopsis and other plants. Plant J 51:1126–1136. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03212.x
Ohama N, Sato H, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2016) Transcriptional regulatory network of plant heat stress response. Trends Plant Sci. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2016.08.015
Oliveros JC (2009) CEL Normalizer. An interactive server for normalizing standard Affymetrix CEL files. http://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/normalize_cel
Park SK, Howden R, Twell D (1998) Arabidopsis thaliana gametophytic mutation Gemini pollen 1 disrupts microspore polarity, division asymmetry and pollen cell fate. Development 125:3789–3799
Pawar V, Poulet A, Detourne G, Tatout C, Vanrobays E, Evans DE, Graumann K (2016) A novel family of plant nuclear envelope-associated proteins. J Exp Bot. doi:10.1093/jxb/erw332
Pyo H, Demura T, Fukuda H (2006) Vascular cell expression patterns of Arabidopsis bZIP group I genes. Plant Biotechnol 23:497–501
Reňák D, Dupl’áková N, Honys D (2012) Wide-scale screening of T-DNA lines for transcription factor genes affecting male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. Sex Plant Rep 25:39–60
Rutley N, Twell D (2015) A decade of pollen transcriptomics. Plant Reprod 28(2):73–89
Schütze K, Harter K, Chaban C (2008) Post-translational regulation of plant bZIP factors. Trends Plant Sci 13:247–255. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2008.03.002
Shen H, Cao K, Wang X (2007) A conserved proline residue in the leucine zipper region of AtbZIP34 and AtbZIP61 in Arabidopsis thaliana interferes with the formation of homodimer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 362:425–430
Shen H, Cao K, Wang X (2008) AtbZIP16 and AtbZIP68, two new members of GBFs, can interact with other G group bZIPs in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMB Rep 41:132–138
Singh A, Ram H, Abbas N, Chattopadhyay S (2012) Molecular interactions of GBF1 with HY5 and HYH proteins during light-mediated seedling development in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 287:25995–26009. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.333906
Smykowski A, Zimmermann P, Zentgraf U (2010) G-Box binding factor1 reduces CATALASE2 expression and regulates the onset of leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 153:1321–1331
Strathmann A, Kuhlmann M, Heinekamp T, Dröge-Laser W (2001) BZI-1 specifically heterodimerises with the tobacco bZIP transcription factors BZI-2, BZI-3/TBZF and BZI-4, and is functionally involved in flower development. Plant J 28:397–408
Talanian RV, McKnight CJ, Kim PS (1990) Sequence-specific DNA binding by a short peptide dimer. Science 249:761–769
Tsugama D, Liu S, Takano T (2012) AbZIP protein, VIP1 is regulator of osmosensory signalingin Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 159:144–155
Verelst W, Twell D, de Folter S, Immink R, Saedler H, Münster T (2007) MADS-complexes regulate transcriptome dynamics during pollen maturation. Genome Biol 11:R249
Weigel D, Glazebrook J (2002) Arabidopsis. A laboratory handbook. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Weltmeier F, Ehlert A, Mayer CS, Dietrich K, Wang X, Schütze K, Alonso R, Harter K, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Dröge-Laser W (2006) Combinatorial control of Arabidopsis proline dehydrogenase transcription by specific heterodimerisation of bZIP transcription factors. EMBO J 25:3133–3143
Weltmeier F, Rahmani F, Ehlert A, Dietrich K, Schütze K, Wang X, Chaban C, Hanson J, Teige M, Harter K, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Smeekens S, Dröge-Laser W (2009) Expression patterns within the Arabidopsis C/S1 bZIP transcription factor network: availability of heterodimerization partners controls gene expression during stress response and development. Plant Mol Biol 69:107–119
Xu J, Yang C, Yuan Z, Zhang D, Gondwe MY, Ding Z, Liang W, Zhang D, Wilson ZA (2010) The ABORTED MICROSPORES regulatory network is required for postmeiotic male reproductive development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 22:91–107
Zhao J, Guo R, Guo C, Hou H, Wang X, Gao H (2016) Evolutionary and expression analyses of the Apple Basic Leucine Zipper transcription factor family. Front Plant Sci 7:376
Zhou D, Zhou X, Ling Y, Zhang Z, Su Z (2010) agriGO: a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community. Nucleic Acids Research 38:W64–W70 (Web Server issue)
Zhu JK (2016) Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 167(2):313–324
Zimmermann P, Hirsch-Hoffmann M, Hennig L, Gruissem W (2004) GENEVESTIGATOR. Arabidopsis microarray database and analysis toolbox. Plant Physiol 136(1):2621–2632
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from Czech Scientific Foundation (Grants Nos. 15-22720S, 14-32292S, and 13-41444P) and Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic (Grant No. LD14109). We thank Dr. Simona Masiero, Dip. Di Biologia, Universita degli Studi di Milano, Milano, Italy, for supervising the Y2H experiments and for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by David Twell.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gibalová, A., Steinbachová, L., Hafidh, S. et al. Characterization of pollen-expressed bZIP protein interactions and the role of ATbZIP18 in the male gametophyte. Plant Reprod 30, 1–17 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-016-0295-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-016-0295-5