Abstract
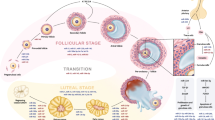
The mammalian ovary is a dynamic organ. The coordination of follicle recruitment, selection, and ovulation and the timely development and regression of the corpus luteum are essential for a functional ovary and fertility. Deregulation of any of these processes results in ovarian dysfunction and potential infertility. MicroRNA (miRNA) are short noncoding RNA that regulate developmental processes and time-sensitive functions. The expression of miRNA in the ovary varies with cell type, function, and stage of the estrous cycle. miRNA are involved in the formation of primordial follicles, follicular recruitment and selection, follicular atresia, oocyte-cumulus cell interaction, granulosal cell function, and luteinization. miRNA are differentially expressed in luteal cells at the various stages of the estrous cycle and during maternal recognition of pregnancy, suggesting a role in luteal development, maintenance, and regression. An understanding of the patterns of expression and functions of miRNA in the ovary will lead to novel therapeutics to treat ovarian dysfunction and improve fertility and, potentially, to the development of better contraceptives.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El Naby WS, Hagos TH, Hossain MM, Salilew-Wondim D, Gad AY, Rings F, Cinar MU, Tholen E, Looft C, Schellander K, Hoelker M, Tesfaye D (2011) Expression analysis of regulatory microRNAs in bovine cumulus oocyte complex and preimplantation embryos. Zygote 21:31–51
Ahn HW, Morin RD, Zhao H, Harris RA, Coarfa C, Chen ZJ, Milosavljevic A, Marra MA, Rajkovic A (2010) MicroRNA transcriptome in the newborn mouse ovaries determined by massive parallel sequencing. Mol Hum Reprod 16:463–471
Assou S, Al-edani T, Haouzi D, Philippe N, Lecellier C-H, Piquemal D, Commes T, Ait-Ahmed O, Dechaud H, Hamamah S (2013) MicroRNAs: new candidates for the regulation of the human cumulus-oocyte complex. Hum Reprod 28:3038–3049
Atli MO, Bender RW, Mehta V, Bastos MR, Luo W, Vezina CM, Wiltbank MC (2012) Patterns of gene expression in the bovine corpus luteum following repeated intrauterine infusions of low doses of prostaglandin F2alpha. Biol Reprod 86:130
Baley J, Li J (2012) MicroRNAs and ovarian function. J Ovarian Res 5:8
Bartel DP (2004) MicrorNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bernstein E, Kim SY, Carmell MA, Murchison EP, Alcorn H, Li MZ, Mills AA, Elledge SJ, Anderson KV, Hannon GJ (2003) Dicer is essential for mouse development. Nat Genet 35:215–217
Brennecke J, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM (2005) Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol 3:e85
Cannon MJ, Pate JL (2006) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase participates in the interferon-gamma-induced cell death process in cultured bovine luteal cells. Biol Reprod 74:552–559
Cao R, Wu WJ, Zhou XL, Xiao P, Wang Y, Liu HL (2015) Expression and preliminary functional profiling of the let-7 family during porcine ovary follicle atresia. Mol Cells 38:304–311
Carletti MZ, Christenson LK (2009) MicroRNA in the ovary and female reproductive tract. J Anim Sci 87(14 Suppl):E29–E38
Carletti MZ, Fiedler SD, Christenson LK (2010) MicroRNA21 blocks apoptosis in mouse periovulatory granulosa cells. Biol Reprod 83:286–295
Chen PH, Shih CM, Chang WC, Cheng CH, Lin CW, Ho KH, Su PC, Chen KC (2014) MicroRNA-302b-inhibited E2F3 transcription factor is related to all trans retinoic acid-induced glioma cell apoptosis. J Neurochem 131:731–742
Christenson LK (2010) MicroRNA control of ovarian function. Anim Reprod 7:129–133
Czech B, Hannon GJ (2010) Small RNA sorting: matchmaking for Argonautes. Nat Rev Genet 12:19–31
Da Silveira JC, de Andrade GM, Nogueira MF, Meirelles FV, Perecin F (2015) Involvement of miRNAs and cell-secreted vesicles in mammalian ovarian antral follicle development. Reprod Sci (in press)
Dai L, Xu J, Liu S, Ma T, Zhu Y, Xu F, Gao Y, Yuan B, Wang S, Zhang Y, Sun G, Zhang J (2014) Characterization of miR-126-3p and its target Talin2 in the bovine corpus luteum during the oestrus cycle. Reprod Domest Anim 49:913–919
Di R, He J, Song S, Tian D, Liu Q, Liang X, Ma Q, Sun M, Wang J, Zhao W, Cao G, Wang J, Yang Z, Ge Y, Chu M (2014) Characterization and comparative profiling of ovarian microRNAs during ovine anestrus and the breeding season. BMC Genomics 15:899
Donadeu FX, Schauer SN (2013) Differential miRNA expression between equine ovulatory and anovulatory follicles. Domest Anim Endocrinol 45:122–125
Donadeu FX, Schauer SN, Sontakke SD (2012) Involvement of miRNA in ovarian follicular and luteal development. J Endocrinol 215:323–334
Du T, Zamore PD (2005) MicroPrimer: the biogenesis and function of microRNA. Development 132:4645–4652
Esau C, Davis S, Murray SF, Yu XX, Pandey SK, Pear M, Watts L, Booten SL, Graham M, McKay R, Subramaniam A, Propp S, Lollo BA, Freier S, Bennett CF, Bhanot S, Monia BP (2006) miR-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab 3:87–98
Espey LL (1980) Ovulation as an inflammatory reaction: a hypothesis. Biol Reprod 22:73–106
Fairchild DL, Pate JL (1989) Interferon-gamma induction of major histocompatibility complex antigens on cultured bovine luteal cells. Biol Reprod 40:453–457
Fiedler SD, Carletti MZ, Hong X, Christenson LK (2008) Hormonal regulation of microRNA expression in periovulatory mouse mural granulosa cells. Biol Reprod 79:1030–1037
Fischer S, Handrick R, Aschrafi A, Otte K (2015) Unveiling the principle of microRNA-mediated redundancy in cellular pathway regulation. RNA Biol 12:238–247
Flemr M, Malik R, Franke V, Nejepinska J, Sedlacek R, Vlahovicek K, Svoboda P (2013) A retrotransposon-driven dicer isoform directs endogenous small interfering RNA production in mouse oocytes. Cell 155:807–816
Ge T, Yin M, Yang M, Liu T, Lou G (2014) MicroRNA-302b suppresses human epithelial ovarian cancer cell growth by targeting RUNX1. Cell Physiol Biochem 34:2209–2220
Gonzalez G, Behringer RR (2009) Dicer is required for female reproductive tract development and fertility in the mouse. Mol Reprod Dev 76:678–688
Ha M, Kim VN (2014) Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:509–524
Hasuwa H, Ueda J, Ikawa M, Okabe M (2013) miR-200b and miR-429 function in mouse ovulation and are essential for female fertility. Science 341:71–73
Hawkins SM, Matzuk MM (2010) Oocyte-somatic cell communication and microRNA function in the ovary. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 71:144–148
Hong X, Luense LJ, McGinnis LK, Nothnick WB, Christenson LK (2008) Dicer1 is essential for female fertility and normal development of the female reproductive system. Endocrinology 149:6207–6212
Hossain MM, Ghanem N, Hoelker M, Rings F, Phatsara C, Tholen E, Schellander K, Tesfaye D (2009) Identification and characterization of miRNAs expressed in the bovine ovary. BMC Genomics 10:443
Hossain MM, Sohel MM, Schellander K, Tesfaye D (2012) Chracterization and importance of microRNAs in mammalian gonadal functions. Cell Tissue Res 349:679–690
Huang J, Ju Z, Li Q, Hou Q, Wang C, Li J, Li R, Wang L, Sun T, Hang S, Gao Y, Hou M, Zhong J (2011) Solexa sequencing of novel and differentially expressed microRNAs in testicular and ovarian tissues in Holstein cattle. Int J Biol Sci 7:1016–1026
Imbar T, Eisenberg I (2014) Regulatory role of microRNAs in ovarian function. Fertil Steril 101:1524–1530
Iwamune M, Nakamura K, Kitahara Y, Minegishi T (2014) MicroRNA-376a regulates 78-kilodalton glucose-regulated protein expression in rat granulosa cells. PLoS One 9:e108997
Jiang L, Huang J, Li L, Chen Y, Chen X, Zhao X, Yang D (2015) MicroRNA-93 promotes ovarian granulosa cells proliferation through targeting CDKN1A in polycystic ovarian syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:E729–E738
Kitahara Y, Nakamura K, Kogure K, Minegishi T (2013) Role of microRNA-136-3p on the expression of luteinizing hormone-human chorionic gonadotropin receptor mRNA in rat ovaries. Biol Reprod 89:114
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 294:853–858
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP (2001) An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294:858–862
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75:843–854
Lei L, Jin S, Gonzalez G, Behringer RR, Woodruff TK (2010) The regulatory role of Dicer in folliculogenesis in mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol 315:63–73
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Li M, Liu W, Wang T, Guan J, Luo Z, Chen H, Wang X, Chen L, Ma J, Mu Z, Jiang AA, Zhu L, Lang Q, Zhou X, Wang J, Zeng W, Li N, Li K, Gao X, Li X (2011) Repertoire of porcine microRNAs in adult ovary and testis by deep sequencing. Int J Biol Sci 7:1045–1055
Li Y, Fang Y, Liu Y, Yang X (2015) MicroRNAs in ovarian function and disorders. J Ovarian Res 8:51–58
Liang M, Yao G, Yin M, Lu M, Tian H, Liu L, Lian J, Huang X, Sun F (2013) Transcriptional cooperation between p53 and NF-kB p65 regulates microRNA-224 transcription in mouse ovarian granulosa cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 370:119–129
Liang Y, Ridzon D, Wong L, Chen C (2007) Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in normal human tissues. BMC Genomics 8:166
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS, Johnson JM (2005) Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 433:769–773
Ling YH, Ren CH, Guo XF, Xu LN, Huang YF, Luo JC, Zhang YH, Zhang XR, Zhang ZJ (2014) Identification and characterization of microRNAs in the ovaries of multiple and uniparous goats (Capra hircus) during follicular phase. BMC Genomics 15:339
Liu J, Du X, Zhou J, Pan Z, Liu H, Li Q (2014a) MicroRNA-26b functions as a proapoptotic factor in porcine follicular granulosa cells by targeting Sma- and Mad- related protein 4. Biol Reprod 91:146
Liu J, Yao W, Yao Y, Du X, Zhou J, Ma B, Liu H, Li Q, Pan Z (2014b) MiR-92a inhibits porcine ovarian granulosa cell apoptosis by targeting Smad7 gene. FEBS Lett 588:4497–4503
Luense LJ, Carletti MZ, Christenson LK (2009) Role of dicer in female fertility. Trends Endocrinol Metab 20:265–272
Lytle JR, Yario TA, Steitz JA (2007) Target mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the 5′UTR as in the 3′UTR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:9667–9672
Ma T, Jiang H, Gao Y, Zhao Y, Dai L, Xiong Q, Xu Y, Zhao Z, Zhang J (2011) Microarray analysis of differentially expressed microRNAs in non-regressed and regressed bovine corpus luteum tissue; microRNA-378 may suppress luteal cell apoptosis by targeting the interferon gamma receptor 1 gene. J Appl Genet 52:481–486
Maalouf SW, Liu W-S, Albert I, Pate JL (2014) Regulating life or death: potential role of microRNA in rescue of the corpus luteum. Mol Cell Endocrinol 398:78–88
Matzuk MM, Burns KH, Viveiros MM, Eppig JJ (2002) Intercellular communication in the mammalian ovary: oocytes carry the conversation. Science 296:2178–2180
McBride D, Carré W, Sontakke SD, Hogg CO, Law A, Donadeu FX, Clinton M (2012) Identification of miRNAs associated with the follicular-luteal transition in the ruminant ovary. Reproduction 144:221–233
McGinnis LK, Luense LJ, Christenson LK (2015) MicroRNA in ovarian biology and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 5.pii:a022962
Miles JR, McDaneld TG, Wiedmann RT, Cushman RA, Echternkamp SE, Vallet JL, Smith TP (2012) MicroRNA expression profile in bovine cumulus-oocyte complexes: possible role of let-7 and miR-106a in the development of bovine oocytes. Anim Reprod Sci 130:16–26
Mishima T, Takizawa T, Luo SS, Ishibashi O, Kawahigashi Y, Mizuguchi Y, Ishikawa T, Mori M, Kanda T, Goto T, Takizawa T (2008) MicroRNA (miRNA) cloning analysis reveals sex differences in miRNA expression profiles between adult mouse testis and ovary. Reproduction 136:811–822
Murchison EP, Stein P, Xuan Z, Pan H, Zhang MQ, Schultz RM, Hannon GJ (2007) Critical roles for dicer in the female germline. Genes Dev 21:682–693
Nagaraja AK, Andrewu-Vieyra C, Frnaco HL, Ma L, Chen R, Han DY, Zhu H, Agno JE, Gunaratne PH, DeMayo FJ, Matzuk MM (2008) Deletion of dicer in somatic cells of the female reproductive tract causes sterility. Mol Endocrinol 22:2336–2352
Nothnick WB (2012) The role of micro-RNAs in the female reproductive tract. Reproduction 143:559–576
Okamura K, Phillips MD, Tyler DM, Duan H, Chou YT, Lai EC (2008) The regulatory activity of microRNA* species has substantial influence on microRNA and 3′UTR evolution. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15:354–363
Orom UA, Nielsen FC, Lund AH (2008) MicroRNA-10a binds the 5′UTR of ribosomal protein mRNAs and enhances their translation. Cell 30:460–471
Otsuka M, Jing Q, Georgel P, New L, Chen J, Mois J, Kang YJ, Jiang Z, Du X, Cook R, Das SC, Pattnaik AK, Beutler B, Han J (2007) Hypersusceptibility to vesicular stomatitis virus infection in Dicer-1-deficient mice is due to impaired miR24 and miR93 expression. Immunity 27:123–134
Otsuka M, Zheng M, Hayashi M, Lee J-D, Yoshino O, Lin S, Han J (2008) Impaired microrNA processing causes corpus luteum insufficiency and infertility in mice. J Clin Invest 118:1944–1954
Pan B, Toms D, Shen W, Li J (2015) MicroRNA-378 regulates oocyte maturation via the suppression of aromatase in porcine cumulus cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 308:E525–E534
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, Maller B, Hayward DC, Ball EE, Degnan B, Muller P, Spring J, Srinivasan A, Frishman M, Finnerty J, Corbo J, Levine M, Leahy P, Davidson E, Ruvkun G (2000) Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 408:86–89
Pate JL, Landis Keyes P (2001) Immune cells in the corpus luteum: friends of foes? Reproduction 122:665–676
Petrich BG (2009) Talin-dependent integrin signaling in vivo. Thromb Haemost 101:1020–1024
Petroff MG, Petroff BK, Pate JL (1999) Expression of cytokine messenger ribonucleic acids in the bovine corpus luteum. Endocrinology 140:1018–1021
Place RF, Li LC, Pookot D, Noonan EJ, Dahiya R (2008) MicroRNA-373 induces expression of genes with complementary promoter sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:1608–1613
Poole DH, Pate JL (2012) Luteal microenvironment directs resident T lymphocyte function in cows. Biol Reprod 86:29
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR, Ruvkun G (2000) The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 403:901–906
Ro S, Song R, Park C, Zheng H, Sanders KM, Yan W (2007) Cloning and expression profiling of small RNAs expressed in the mouse ovary. RNA 13:2366–2380
Salilew-Wondim D, Ahmad I, Gebremedhn S, Sahadevan S, Hossain MM, Rings F, Hoelker M, Tholen E, Neuhoff C, Looft C, Schellander K, Tesfaye D (2014) The expression pattern of microRNAs in granulosa cells of subordinate and dominant follicles during the early luteal phase of the bovine estrous cycle. PLoS One 9:e106795
Sang Q, Yao Z, Wang H, Feng R, Wang H, Zhao X, Xing Q, Jin L, He L, Wu L, Wang L (2013) Identification of microRNAs in human follicular fluid: characterization of microRNAs that govern steroidogenesis in vitro and are associated with polycystic ovary syndrome in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:3068–3079
Santonocito M, Vento M, Guglielmino MR, Battaglia R, Wahlgren J, Ragusa M, Barbagallo D, Borzi P, Rizzari S, Maugeri M, Scollo P, Tatone C, Valadi H, Purello M, Di Pietro C (2014) Molecular characterization of exosomes and their microRNA cargo in human follicular fluid: bioinformatics analysis reveals that exosomal microRNAs control pathways involved in follicular maturation. Fertil Steril 102:1751–1761
Schauer SN, Sontakke SD, Watson ED, Esteves CL, Donadeu FX (2013) Involvement of miRNAs in equine follicle development. Reproduction 146:273–282
Sen A, Prizant H, Light A, Biswas A, Hayes E, Lee HJ, Barad D, Gleicher N, Hammes SR (2014) Androgens regulate ovarian follicular development by increasing follicle stimulating hormone receptor and microRNA-125b expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:3008–3013
Shen G, Lin Y, Yang X, Zhang J, Xu Z, Jia H (2014) MicroRNA-26b inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting USP9X. BMC Cancer 14:393
Sirotkin AV, Ovcharenko D, Grossmann R, Laukova M, Mlyncek M (2009) Identification of microRNAs controlling human ovarian cell steroidogenesis via a genome-scale screen. J Cell Physiol 219:415–420
Sirotkin AV, Laukova M, Ovcharenko D, Brenaut P, Mlyncek M (2010) Identification of microRNAs controlling human ovarian cell proliferation and apoptosis. J Cell Physiol 223:49–56
Sirotkin AV, Alexa R, Kisova G, Harrath AH, Alwasel S, Ovcharenko D, Mlyncek M (2014) MicroRNAs control transcription factor NF-kB (p65) expression in human ovarian cells. Funct Integr Genomics 15:271–275
Sohel MM, Hoelker M, Noferesti SS, Salilew-Wondim D, Tholen E, Looft C, Rings F, Uddin MJ, Spencer TE, Schellander K, Tesfaye D (2013) Exosomal and non-exosomal transport of extra-cellular microRNAs in follicular fluid: implications for bovine oocyte developmental competence. PLoS One 8:e78505
Sontakke SD, Mohammed BT, McNeilly AS, Donadeu FX (2014) Characterization of microRNAs differentially expressed during bovine follicle development. Reproduction 148:271–283
Sood P, Krek A, Zavolan M, Macino G, Rajewsky N (2006) Cell-type-specific signatures of microRNAs on target mRNA expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:2746–2751
Spencer TE, Bazer FW (2004) Conceptus signals for establishment and maintenance of pregnancy. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2:49
Stein P, Rozhkov NV, Li F, Cardenas FL, Davydenk O, Le V, Gregory BD, Hannon GJ, Schultz RM (2015) Essential role for endogenous siRNAs during meiosis in mouse oocytes. PLoS Genet 11:e1005013
Tesfaye D, Worku D, Rings F, Phatsara C, Tholen E, Schellander K, Hoelker M (2009) Identification and expression profiling of microRNAs during bovine oocyte maturation using heterologous approach. Mol Reprod Dev 76:665–677
Toloubeydokhti T, Bukulmez O, Chegini N (2008) Potential regulatory functions of microRNAs in the ovary. Semin Reprod Med 26:469–478
Toms D, Xu S, Pan B, Wu D, Li J (2015) Progesterone receptor expression in granulosa cells is suppressed by microRNA-378-3p. Mol Cell Endocrinol 399:95–102
Tripurani SK, Xiao C, Salem M, Yao J (2010) Cloning and analysis of fetal ovary microRNAs in cattle. Anim Reprod Sci 120:16–22
Troppmann B, Kossack N, Nordhoff V, Schuring AN, Gromoll J (2014) MicroRNA miR-513a-3p acts as co-regulator of luteinizing hormone/chorionic gonadotropin receptor gene expression in human granulosa cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 390:65–72
Tu F, Pan ZX, Yao Y, Liu HL, Liu SR, Xie Z, Li QF (2014) MiR-34a targets the inhibin beta B gene, promoting granulosa cell apoptosis in the porcine ovary. Genet Mol Res 13:2504–2512
Vidigal JA, Ventura A (2015) The biological functions of miRNAs: lessons from in vivo studies. Trends Cell Biol 25:137–147
Walusimbi SS, Pate JL (2013) Physiology and endocrinology symposium: role of immune cells in the corpus luteum. J Anim Sci 91:1650–1659
Wang B, Wang H, Yang Z (2012) MiR-122 inhibts cell proliferation and tumorigenesis of breast cancer by targeting IGF1R. PLoS One 7:e47053
Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G (1993) Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 75:855–862
Wu S, Sun H, Zhang Q, Jiang Y, Fang T, Cui I, Yan G, Hu Y (2015) MicroRNA-132 promotes estradiol synthesis in ovarian granulosa cells via translational repression of Nurr1. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 13:94
Xu B, Hua J, Zhang Y, Jiang X, Zhang H, Ma T, Zheng W, Sun R, Shen W, Sha J, Cooke HJ, Shi Q (2011) Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) regulates primordial follicle assembly by promoting apoptosis of oocytes in fetal and neonatal mouse ovaries. PLoS One 6:e16046
Xu B, Zhang U-W, Tong X-H, Liu Y-S (2015) Characterization of miNRA profile in human cumulus granulosa cells: identification of microRNAs that regulate Notch signaling and are associated with PCOS. Mol Cell Endocrinol 404:26–36
Xu S, Linher-Melville K, Yang BB, Wu D, Li J (2011) Micro-RNA378 (miR-378) regulates ovarian estradiol production by targeting aromatase. Endocrinology 152:3941–3951
Yang JS, Lai EC (2011) Alternative miRNA biogenesis pathways and the interpretation of core miRNA pathway mutants. Mol Cell 43:892–903
Yang S, Wang S, Luo A, Ding T, Lai Z, Shen W, Ma X, Cao C, Shi L, Jiang J, Rong F, Ma L, Tian Y, Du X, Lu Y, Li Y, Wang S (2013) Expression patterns and regulatory functions of microRNAs during the initiation of primordial follicle development in the neonatal mouse ovary. Biol Reprod 89:126
Yang WJ, Yang DD, Na S, Sandusky GE, Zhang Q, Zhao G (2005) Dicer is required for embryonic angiogenesis during mouse development. J Biol Chem 280:9330–9335
Yang X, Zhou Y, Peng S, Wu L, Lin HY, Wang S, Wang H (2012) Differentially expressed plasma microRNAs in premature ovarian failure patients and the potential regulatory function of miR-23a in granulosa cell apoptosis. Reproduction 144:235–244
Yao G, Yin M, Lian J, Tian H, Liu L, Li X, Sun F (2010) MicroRNA-224 is involved in transforming growth factor-beta-mediated mouse granulosa cell proliferation and granulosa cell function by targeting Smad4. Mol Endocrinol 24:540–551
Yin M, Lu M, Yao G, Tian H, Lian J, Liu L, Liang M, Wang Y, Sun F (2012) Transactivation of microRNA-383 by steroidogenic factor-1 promotes estradiol release from mouse ovarian granulosa cells by targeting RBMS1. Mol Endocrinol 26:1129–1143
Yin M, Wang X, Yao G, Lu M, Liang M, Sun Y, Sun F (2014) Transactivation of microRNA-320 by microrNA-383 regulates granulosa cell functions by targeting E2F1 and SF-1 proteins. J Biol Chem 289:18239–18257
Yuan S, Ortogero N, Wu Q, Zheng H, Yan W (2014) Murine follicular development requires oocyte dicer but not drosha. Biol Reprod 91:39
Zhang H, Jiang X, Zhang Y, Xu B, Hua J, Ma T, Zheng W, Sun R, Shen W, Cooke HJ, Hao Q, Qiao J, Shi Q (2014) microRNA 376a regulates follicle assembly by targeting Pcna in fetal and neonatal mouse ovaries. Reproduction 148:43–54
Zhang J, Ji X, Zhou D, Li Y, Lin J, Liu J, Luo H, Cui S (2013) MiR-143 is critical for the formation of primordial follicles in mice. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 18:588–597
Zhang Q, Sun H, Jiang Y, Ding L, Wu S, Fang T, Yan G, Hu Y (2013) MicroRNA-181a suppresses mouse granulosa cell proliferation by targeting activin receptor IIA. PLoS One 8:e59667
Zhao H, Rajkovic A (2008) MicroRNAs and mammalian ovarian development. Semin Reprod Med 26:461–468
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maalouf, S.W., Liu, W.S. & Pate, J.L. MicroRNA in ovarian function. Cell Tissue Res 363, 7–18 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2307-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2307-4