Abstract
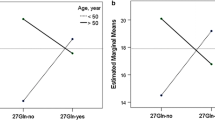
β2-Adrenergic receptor (β2AR) gene polymorphisms have been reported to be associated with various asthma-related traits in different racial/ethnic populations. However, it is unknown whether β 2 AR genetic variants are associated with asthma in African Americans. In this study, we have examined whether there is association between β 2 AR genetic variants and asthma in African Americans. We have recruited 264 African American asthmatic subjects and 176 matched healthy controls participating in the Study of African Americans, Asthma, Genes and Environments (SAGE). We genotyped seven known and recently identified β 2 AR SNP variants, then tested genotype and haplotype association of asthma-related traits with the β 2 AR SNPs in our African American cohort with adjustment of confounding effect due to admixture background and environmental risk factors. We found a significant association of the SNP −47 (Arg-19Cys) polymorphism with ΔFEF25–75, a measure of bronchodilator drug responsiveness, in African American asthmatics after correction for multiple testing (P=0.001). We did not observe association of the SNP +46 (Arg16Gly) variant with asthma disease diagnosis and asthma-related phenotypes. In contrast to previous results between the Arg16Gly variant and traits related to bronchodilator responsiveness, our results indicate that the Arg-19Cys polymorphism in β upstream peptide may play an important role in bronchodilator drug responsiveness in African American subjects. Our findings highlight the importance of investigating genetic risk factors for asthma in different populations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecasis GR, Cardon LR, Cookson WO (2000) A general test of association for quantitative traits in nuclear families. Am J Hum Genet 66:279–292
Alberts WM, Ferris MC, Brooks SM, Goldman AL (1994) The FEF25-5% and the clinical diagnosis of asthma. Ann Allergy 73:221–225
American Thoracic Society (1995) Standardization of spirometry (1994 update). Am J Respir Crit Care Med 152:1107–1136
Benjamini Y, Yekutieli D (2001) The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann Statist 29:1165–1188
Burchard EG, Ziv E, Coyle N, Gomez SL, Tang H, Karter AJ, Mountain JL, Perez-Stable EJ, Sheppard D, Risch N (2003) The importance of race and ethnic background in biomedical research and clinical practice. N Engl J Med 348:1170–1175
Burchard EG, Avila PC, Nazario S, Casal J, Torres A, Rodriguez-Santana JR, Toscano M, Sylvia JS, Alioto M, Salazar M, Gomez I, Fagan JK, Salas J, Lilly C, Matallana H, Ziv E, Castro R, Selman M, Chapela R, Sheppard D, Weiss ST, Ford JG, Boushey HA, Rodriguez-Cintron W, Drazen JM, Silverman EK (2004) Lower bronchodilator responsiveness in Puerto Rican than in Mexican subjects with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 169:386–392
Burroughs VJ, Maxey RW, Levy RA (2002) Racial and ethnic differences in response to medicines: towards individualized pharmaceutical treatment. J Natl Med Assoc 94:1–26
Chen X, Kwok PY (1999) Homogeneous genotyping assays for single nucleotide polymorphisms with fluorescence resonance energy transfer detection. Genet Anal 14:157–163
Choudhry S, Ung N, Avila PC, Ziv E, Nazario S, Casal J, Torres A, Gorman JD, Salari K, Rodriguez-Santana JR, Toscano M, Sylvia JS, Alioto M, Castro RA, Salazar M, Gomez I, Fagan JK, Salas J, Clark S, Lilly C, Matallana H, Selman M, Chapela R, Sheppard D, Weiss ST, Ford JG, Boushey HA, Drazen JM, Rodriguez-Cintron W, Silverman EK, Burchard EG (2005) Pharmacogenetic differences in response to albuterol between Puerto Ricans and Mexicans with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 171:563–570
Clayton D, Jones H (1999) Transmission/disequilibrium tests for extended marker haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet 65:1161–1169
Contopoulos-Ioannidis DG, Manoli EN, Ioannidis JP (2005) Meta-analysis of the association of beta2-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms with asthma phenotypes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 115:963–972
Covolo L, Gelatti U, Metra M, Nodari S, Picciche A, Pezzali N, Zani C, Alberti A, Donato F, Nardi G, Dei Cas L (2004) Role of beta1- and beta2-adrenoceptor polymorphisms in heart failure: a case-control study. Eur Heart J 25:1534–1541
Devlin B, Risch N (1995) A comparison of linkage disequilibrium measures for fine-scale mapping. Genomics 29:311–322
Drysdale CM, McGraw DW, Stack CB, Stephens JC, Judson RS, Nandabalan K, Arnold K, Ruano G, Liggett SB (2000) Complex promoter and coding region beta 2-adrenergic receptor haplotypes alter receptor expression and predict in vivo responsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10483–10488
Enright PL, Johnson LR, Connett JE, Voelker H, Buist AS (1991) Spirometry in the lung health study. 1. Methods and quality control. Am Rev Respir Dis 143:1215–1223
Enright PL, Lebowitz MD, Cockroft DW (1994) Physiologic measures: pulmonary function tests. Asthma outcome (discussion S19–S20). Am J Respir Crit Care Med 149:S9–S18
Evans DA, McLeod HL, Pritchard S, Tariq M, Mobarek A (2001) Interethnic variability in human drug responses. Drug Metab Dispos 29:606–610
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2003) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164:1567–1587
Ferris BG (1978) Epidemiology standardization project (American Thoracic Society). Am Rev Respir Dis 118:1–120
Fuhlbrigge AL, Kitch BT, Paltiel AD, Kuntz KM, Neumann PJ, Dockery DW, Weiss ST (2001) FEV(1) is associated with risk of asthma attacks in a pediatric population. J Allergy Clin Immunol 107:61–67
Ge D, Huang J, He J, Li B, Duan X, Chen R, Gu D (2005) beta2-Adrenergic receptor gene variations associated with stage-2 hypertension in northern Han Chinese. Ann Hum Genet 69:36–44
de Groote P, Helbecque N, Lamblin N, Hermant X, Mc Fadden E, Foucher-Hossein C, Amouyel P, Dallongeville J, Bauters C (2005) Association between beta-1 and beta-2 adrenergic receptor gene polymorphisms and the response to beta-blockade in patients with stable congestive heart failure. Pharmacogenet Genomics 15:137–142
Hankinson JL, Odencrantz JR, Fedan KB (1999) Spirometric reference values from a sample of the general U.S. population. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159:179–187
Hill WG (1974) Estimation of linkage disequilibrium in randomly mating populations. Heredity 33:229–239
Hoggart CJ, Parra EJ, Shriver MD, Bonilla C, Kittles RA, Clayton DG, McKeigue PM (2003) Control of confounding of genetic associations in stratified populations. Am J Hum Genet 72:1492–1504
Holloway JW, Dunbar PR, Riley GA, Sawyer GM, Fitzharris PF, Pearce N, Le Gros GS, Beasley R (2000) Association of beta2-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms with severe asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 30:1097–1103
Holloway JW, Yang IA (2005) Beta2-Adrenergic receptor polymorphism and asthma: true or false? J Allergy Clin Immunol 115:960–962
Insel PA (1996) Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. Adrenergic receptors—evolving concepts and clinical implications. N Engl J Med 334:580–585
Israel E, Drazen JM, Liggett SB, Boushey HA, Cherniack RM, Chinchilli VM, Cooper DM, Fahy JV, Fish JE, Ford JG, Kraft M, Kunselman S, Lazarus SC, Lemanske RF, Martin RJ, McLean DE, Peters SP, Silverman EK, Sorkness CA, Szefler SJ, Weiss ST, Yandava CN (2000) The effect of polymorphisms of the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor on the response to regular use of albuterol in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 162:75–80
Jasper JR, Insel PA (1992) Evolving concepts of partial agonism. The beta-adrenergic receptor as a paradigm. Biochem Pharmacol 43:119–30
Jolliffe IT (2002) Principal component analysis, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp xxix, 487 p
Kitch BT, Paltiel AD, Kuntz KM, Dockery DW, Schouten JP, Weiss ST, Fuhlbrigge AL (2004) A single measure of FEV1 is associated with risk of asthma attacks in long-term follow-up. Chest 126:1875–1882
Klein RB, Fritz GK, Yeung A, McQuaid EL, Mansell A (1995) Spirometric patterns in childhood asthma: peak flow compared with other indices. Pediatr Pulmonol 20:372–379
Kobilka BK, Dixon RA, Frielle T, Dohlman HG, Bolanowski MA, Sigal IS, Yang-Feng TL, Francke U, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ (1987) cDNA for the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor: a protein with multiple membrane-spanning domains and encoded by a gene whose chromosomal location is shared with that of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:46–50
Lebecque P, Kiakulanda P, Coates AL (1993) Spirometry in the asthmatic child: is FEF25-75 a more sensitive test than FEV1/FVC? Pediatr Pulmonol 16:19–22
Leineweber K, Brodde OE (2004) Beta2-adrenoceptor polymorphisms: relation between in vitro and in vivo phenotypes. Life Sci 74:2803–2814
Lind DL, Choudhry S, Ung N, Ziv E, Avila PC, Salari K, Ha C, Lovins EG, Coyle NE, Nazario S, Casal J, Torres A, Rodriguez-Santana JR, Matallana H, Lilly CM, Salas J, Selman M, Boushey HA, Weiss ST, Chapela R, Ford JG, Rodriguez-Cintron W, Silverman EK, Sheppard D, Kwok PY, Gonzalez Burchard E (2003) ADAM33 is not associated with asthma in Puerto Rican or Mexican populations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168:1312–1316
Litonjua AA, Silverman EK, Tantisira KG, Sparrow D, Sylvia JS, Weiss ST (2004) Beta 2-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms and haplotypes are associated with airways hyperresponsiveness among nonsmoking men. Chest 126:66–74
Mannino DM, Homa DM, Akinbami LJ, Moorman JE, Gwynn C, Redd SC (2002) Surveillance for asthma—United States, 1980–1999. MMWR Surveill Summ 51:1–13
Martinez FD, Graves PE, Baldini M, Solomon S, Erickson R (1997) Association between genetic polymorphisms of the beta2-adrenoceptor and response to albuterol in children with and without a history of wheezing. J Clin Invest 100:3184–3188
McGraw DW, Forbes SL, Kramer LA, Liggett SB (1998) Polymorphisms of the 5′ leader cistron of the human beta2-adrenergic receptor regulate receptor expression. J Clin Invest 102:1927–1932
Paull K, Covar R, Jain N, Gelfand EW, Spahn JD (2005) Do NHLBI lung function criteria apply to children? A cross-sectional evaluation of childhood asthma at National Jewish Medical and Research Center, 1999–2002. Pediatr Pulmonol 39:311–317
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Silverman EK, Kwiatkowski DJ, Sylvia JS, Lazarus R, Drazen JM, Lange C, Laird NM, Weiss ST (2003) Family-based association analysis of beta2-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms in the childhood asthma management program. J Allergy Clin Immunol 112:870–876
Stephens M, Donnelly P (2003) A comparison of bayesian methods for haplotype reconstruction from population genotype data. Am J Hum Genet 73:1162–1169
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P (2001) A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 68:978–989
Tsai HJ, Choudhry S, Naqvi M, Rodriguez-Cintron W, Burchard EG, Ziv E (2005) Comparison of three methods to estimate genetic ancestry and control for stratification in geetic association studies among admixed populations. Hum Genet Oct:1–10
United States, Dept. of Health and Human Services (2000) Healthy people 2010: understanding and improving health. U.S. Dept. of Health and Human Services : for sale by the U.S. G.P.O., Supt. of Docs., Washington, DC
Ziv E, Burchard EG (2003) Human population structure and genetic association studies. Pharmacogenomics 4:431–441
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health (K23 HL04464, HL07185, GM61390, American Lung Association of California, RWJ Amos Medical Faculty Development Award, NCMHD Health Disparities Scholar, Extramural Clinical Research Loan Repayment Program for Individuals from Disadvantaged Backgrounds, 2001–2003, to EGB), American Lung Association of California (Research Training Fellowship to HJT), U01-HL 65899, UCSF-Children’s Hospital of Oakland Pediatric Clinical Research Center (M01 RR01271), Oakland, CA, Sandler Center for Basic Research in Asthma and the Sandler Family Supporting Foundation. We would like to acknowledge the families and the patients for their participation. We would also like to thank the numerous health care providers for their support and participation in the SAGE Study. Finally, we would like to thank the Sandler Family Foundation, the main sponsor of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hui-Ju Tsai and Nishat Shaikh have contributed equally to this manuscript
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, HJ., Shaikh, N., Kho, J.Y. et al. β2-Adrenergic receptor polymorphisms: pharmacogenetic response to bronchodilator among African American asthmatics. Hum Genet 119, 547–557 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0169-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0169-2