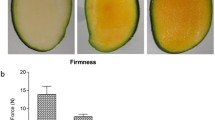
Abstract
A thorough understanding of molecular mechanisms underlying ripening is the prerequisite for genetic manipulation of fruits for better shelf-life and nutritional quality. Mutation in LeMADS-RIN, a MADS-box gene, leads to non-ripening phenotype of rin fruits in tomato. Characterization of ripening-inhibitor (rin) mutant has elucidated important role of ethylene in the regulation of climacteric fruit ripening. A complete understanding of this mutation will unravel novel genetic regulatory mechanisms involved in fruit ripening. In this study, fruit transcriptomes of two genotypes, including a cultivated Indian cultivar Solanum lycopersicum cv. Pusa Ruby and a homozygous line harboring the rin mutation (LA1795) were compared to get better insight into RIN-regulated ethylene-dependent and ethylene-independent events during ripening. Cluster analysis of ripening-related genes indicated a major shift in their expression profiles in rin mutant fruit. A total of 112 genes, exhibiting expression patterns similar to that of LeMADS-RIN in wild-type fruits, showed down regulation of expression in the rin mutant. In silico analysis of putative promoters of these genes for the presence of CArG box along with ERE and ethylene inducibility of these genes revealed that genes lacking CArG box in their regulatory regions could be indirectly regulated by LeMADS-RIN. New regulators of ethylene-dependent aspect of ripening were also identified. In this study, we have made an attempt to distinguish between ethylene-dependent and ethylene-independent aspects of ripening, which will be useful for developing strategies to improve fruit-related agronomic traits in tomato and other crops.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alba R, Payton P, Fei Z, McQuinn R, Debbie P, Martin GB, Tanksley SD, Giovannoni JJ (2005) Transcriptome and selected metabolite analyses reveal multiple points of ethylene control during tomato fruit development. Plant Cell 17:2954–2965
Anjanasree KN, Srivastava A, Handa A, Bansal KC (2005) Identification of differentially expressed ripening-related cDNA clones from tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) using tomato EST array. Curr Sci 88:792–796
Arora R, Agarwal P, Ray S, Singh AK, Singh VP, Tyagi AK, Kapoor S (2007) MADS-box gene family in rice: genome-wide identification, organization and expression profiling during reproductive development and stress. BMC Genomics 8:242
Barry C, Giovannoni JJ (2007) Ethylene and fruit ripening. J Plant Growth Regul 26:143–159
Barry CS, Blume B, Bouzayen M, Cooper W, Hamilton AJ, Grierson D (1996) Differential expression of the 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase gene family of tomato. Plant J 9:525–535
Barry CS, Llop-Tous MI, Grierson D (2000) The regulation of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase gene expression during the transition from system-1 to system-2 ethylene synthesis in tomato. Plant Physiol 123:979–986
Busi MV, Bustamante C, D’Angelo C, Hidalgo-Cuevas M, Boggio SB, Valle EM, Zabaleta E (2003) MADS-box genes expressed during tomato seed and fruit development. Plant Mol Biol 52:801–815
Carrari F, Fernie AR (2006) Metabolic regulation underlying tomato fruit development. J Exp Bot 57:1883–1897
Causier B, Kieffer M, Davies B (2002) MADS-Box genes reach maturity. Science 296:275–276
Chen G, Hu Z, Grierson D (2008) Differential regulation of tomato ethylene responsive factor LeERF3b, a putative repressor, and the activator Pti4 in ripening mutants and in response to environmental stresses. J Plant Physiol 165:662–670
Chung MY, Vrebalov J, Alba R, Lee J, McQuinn R, Chung JD, Klein P, Giovannoni J (2010) A tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) APETALA2/ERF gene, SlAP2a, is a negative regulator of fruit ripening. Plant J 64:936–947
Coen ES, Meyerowitz EM (1991) The war of the whorls: genetic interactions controlling flower development. Nature 353:31–37
de Jong M, Mariani C, Vriezen WH (2009a) The role of auxin and gibberellin in tomato fruit set. J Exp Bot 60:1523–1532
de Jong M, Wolters-Arts M, Feron R, Mariani C, Vriezen WH (2009b) The Solanum lycopersicum auxin response factor 7 (SlARF7) regulates auxin signaling during tomato fruit set and development. Plant J 57:160–170
Dellapenna D, Kates DS, Bennett AB (1987) Polygalacturonase gene expression in Rutgers, rin, nor, and Nr tomato fruits. Plant Physiol 85:502–507
Dellapenna D, Lincoln JE, Fischer RL, Bennett AB (1989) Transcriptional analysis of Polygalacturonase and other ripening-associated genes in Rutgers, rin, nor, and Nr tomato fruit. Plant Physiol 90:1372–1377
Dellapenna D, Lashbrook CC, Toenjes K, Giovannoni JJ, Fischer RL, Bennett AB (1990) Polygalacturonase isozymes and pectin depolymerization in transgenic rin tomato fruit. Plant Physiol 94:1882–1886
Eriksson EM, Bovy A, Manning K, Harrison L, Andrews J, De Silva J, Tucker GA, Seymour GB (2004) Effect of the Colorless non-ripening mutation on cell wall biochemistry and gene expression during tomato fruit development and ripening. Plant Physiol 136:4184–4197
Fei Z, Tang X, Alba R, Giovannoni J (2006) Tomato Expression Database (TED): a suite of data presentation and analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D766–D770
Fraser PD, Truesdale MR, Bird CR, Schuch W, Bramley PM (1994) Carotenoid biosynthesis during tomato fruit development (evidence for tissue-specific gene expression). Plant Physiol 105:405–413
Fujisawa M, Nakano T, Ito Y (2011) Identification of potential target genes for the tomato fruit-ripening regulator RIN by chromatin immunoprecipitation. BMC Plant Biol 11:26
Giovannoni J (2001) Molecular biology of fruit maturation and ripening. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:725–749
Giovannoni JJ (2004) Genetic regulation of fruit development and ripening. Plant Cell 16(Suppl):S170–S180
Giuliano G, Bartley GE, Scolnik PA (1993) Regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis during tomato development. Plant Cell 5:379–387
Griffiths A, Barry C, Alpuche-Solis A, Grierson D (1999) Ethylene and developmental signals regulate expression of lipoxygenase genes during tomato fruit ripening. J Exp Bot 50:793–798
Guillon F, Philippe S, Bouchet B, Devaux MF, Frasse P, Jones B, Bouzayen M, Lahaye M (2008) Down-regulation of an auxin response factor in the tomato induces modification of fine pectin structure and tissue architecture. J Exp Bot 59:273–288
Guo X, Chen J, Brackett RE, Beuchat LR (2001) Survival of salmonellae on and in tomato plants from the time of inoculation at flowering and early stages of fruit development through fruit ripening. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4760–4764
Gupta V, Mathur S, Solanke AU, Sharma MK, Kumar R, Vyas S, Khurana P, Khurana JP, Tyagi AK, Sharma AK (2009) Genome analysis and genetic enhancement of tomato. Crit Rev Biotechnol 29:152–181
Herner RC, Sink KC (1973) Ethylene production and respiratory behavior of the rin tomato mutant. Plant Physiol 52:38–42
Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T (1999) Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database: 1999. Nucleic Acids Res 27:297–300
Hileman LC, Sundstrom JF, Litt A, Chen M, Shumba T, Irish VF (2006) Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of the MADS-box gene family in tomato. Mol Biol Evol 23:2245–2258
Itkin M, Seybold H, Breitel D, Rogachev I, Meir S, Aharoni A (2009) The TOMATO AGAMOUS-LIKE 1 is a component of the fruit ripening regulatory network. Plant J 60:1081–1095
Ito Y, Kitagawa M, Ihashi N, Yabe K, Kimbara J, Yasuda J, Ito H, Inakuma T, Hiroi S, Kasumi T (2008) DNA-binding specificity, transcriptional activation potential, and the rin mutation effect for the tomato fruit-ripening regulator RIN. Plant J 55:212–223
Janssen BJ, Thodey K, Schaffer RJ, Alba R, Balakrishnan L, Bishop R, Bowen JH, Crowhurst RN, Gleave AP, Ledger S, McArtney S, Pichler FB, Snowden KC, Ward S (2008) Global gene expression analysis of apple fruit development from the floral bud to ripe fruit. BMC Plant Biol 8:16
Jones B, Frasse P, Olmos E, Zegzouti H, Li ZG, Latche A, Pech JC, Bouzayen M (2002) Down-regulation of DR12, an auxin-response-factor homolog, in the tomato results in a pleiotropic phenotype including dark green and blotchy ripening fruit. Plant J 32:603–613
Karlova R, Rosin FM, Busscher-Lange J, Parapunova V, Do PT, Fernie AR, Fraser PD, Baxter C, Angenent GC, de Maagd RA (2010) Transcriptome and metabolite profiling show that APETALA2a is a major regulator of tomato fruit ripening. Plant Cell 23:923–941
Katz YS, Galili G, Amir R (2006) Regulatory role of cystathionine-gamma-synthase and de novo synthesis of methionine in ethylene production during tomato fruit ripening. Plant Mol Biol 61:255–268
Klee HJ (2002) Control of ethylene-mediated processes in tomato at the level of receptors. J Exp Bot 53:2057–2063
Knapp J, Moureau P, Schuch W, Grierson D (1989) Organization and expression of polygalacturonase and other ripening related genes in Ailsa Craig ‘Neverripe’ and ‘ripening inhibitor’ tomato mutants. Plant Mol Biol Rep 12:105–116
Kok EJ, Franssen-van Hal NL, Winnubst LN, Kramer EH, Dijksma WT, Kuiper HA, Keijer J (2007) Assessment of representational difference analysis (RDA) to construct informative cDNA microarrays for gene expression analysis of species with limited transcriptome information, using red and green tomatoes as a model. J Plant Physiol 164:337–349
Kolotilin I, Koltai H, Tadmor Y, Bar-Or C, Reuveni M, Meir A, Nahon S, Shlomo H, Chen L, Levin I (2007) Transcriptional profiling of high pigment −2dg tomato mutant links early fruit plastid biogenesis with its overproduction of phytonutrients. Plant Physiol 145:389–401
Kumar R, Tyagi AK, Sharma AK (2010) Genome-wide analysis of auxin response factor (ARF) gene family from tomato and analysis of their role in flower and fruit development. Mol Genet Genomics 285:245–260
Lanahan MB, Yen HC, Giovannoni JJ, Klee HJ (1994) The never ripe mutation blocks ethylene perception in tomato. Plant Cell 6:521–530
Lashbrook CC, Gonzalez-Bosch C, Bennett AB (1994) Two divergent endo-beta-1, 4-glucanase genes exhibit overlapping expression in ripening fruit and abscising flowers. Plant Cell 6:1485–1493
Lelievre JM, Tichit L, Dao P, Fillion L, Nam YW, Pech JC, Latche A (1997) Effects of chilling on the expression of ethylene biosynthetic genes in Passe-Crassane pear (Pyrus communis L.) fruits. Plant Mol Biol 33:847–855
Lemaire-Chamley M, Petit J, Garcia V, Just D, Baldet P, Germain V, Fagard M, Mouassite M, Cheniclet C, Rothan C (2005) Changes in transcriptional profiles are associated with early fruit tissue specialization in tomato. Plant Physiol 139:750–769
Lenka SK, Lohia B, Kumar A, Chinnusamy V, Bansal KC (2009) Genome-wide targeted prediction of ABA responsive genes in rice based on over-represented cis-motif in co-expressed genes. Plant Mol Biol 69:261–271
Leseberg CH, Eissler CL, Wang X, Johns MA, Duvall MR, Mao L (2008) Interaction study of MADS-domain proteins in tomato. J Exp Bot 59:2253–2265
Li Y, Zhu B, Xu W, Zhu H, Chen A, Xie Y, Shao Y, Luo Y (2007) LeERF1 positively modulated ethylene triple response on etiolated seedling, plant development and fruit ripening and softening in tomato. Plant Cell Rep 26:1999–2008
Li L, Zhu B, Fu D, Luo Y (2011a) RIN transcription factor plays an important role in ethylene biosynthesis of tomato fruit ripening. J Sci Food Agric 91:2308–2314
Li L, Zhu B, Yang P, Fu D, Zhu Y, Luo Y (2011b) The regulation mode of RIN transcription factor involved in ethylene biosynthesis in tomato fruit. J Sci Food Agric 91:1822–1828
Lin Z, Hong Y, Yin M, Li C, Zhang K, Grierson D (2008) A tomato HD-Zip homeobox protein, LeHB-1, plays an important role in floral organogenesis and ripening. Plant J 55:301–310
Lincoln JE, Fischer RL (1988) Regulation of gene expression by ethylene in wild-type and rin tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) fruit. Plant Physiol 88:370–374
Lincoln JE, Cordes S, Read E, Fischer RL (1987) Regulation of gene expression by ethylene during Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato) fruit development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2793–2797
Lincoln JE, Campbell AD, Oetiker J, Rottmann WH, Oeller PW, Shen NF, Theologis A (1993) Le-ACS4, a fruit ripening and wound-induced 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase gene of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). Expression in Escherichia coli, structural characterization, expression characteristics, and phylogenetic analysis. J Biol Chem 268:19422–19430
Lois LM, Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Gallego F, Campos N, Boronat A (2000) Carotenoid biosynthesis during tomato fruit development: regulatory role of 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase. Plant J 22:503–513
Manning K, Tor M, Poole M, Hong Y, Thompson AJ, King GJ, Giovannoni JJ, Seymour GB (2006) A naturally occurring epigenetic mutation in a gene encoding an SBP-box transcription factor inhibits tomato fruit ripening. Nat Genet 38:948–952
Martel C, Vrebalov J, Giovannoni JJ (2011) The tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) MADS-box transcription factor RIN interacts with promoters involved in numerous ripening processes in a CNR dependent manner. Plant Physiol. doi:10.1104/pp.111.181107
Martin MN, Saftner RA (1995) Purification and Characterization of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid N-malonyltransferase from tomato fruit. Plant Physiol 108:1241–1249
Meli VS, Ghosh S, Prabha TN, Chakraborty N, Chakraborty S, Datta A (2010) Enhancement of fruit shelf life by suppressing N-glycan processing enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:2413–2418
Mintz-Oron S, Mandel T, Rogachev I, Feldberg L, Lotan O, Yativ M, Wang Z, Jetter R, Venger I, Adato A, Aharoni A (2008) Gene expression and metabolism in tomato fruit surface tissues. Plant Physiol 147:823–851
Mounet F, Moing A, Garcia V, Petit J, Maucourt M, Deborde C, Bernillon S, Le Gall G, Colquhoun I, Defernez M, Giraudel JL, Rolin D, Rothan C, Lemaire-Chamley M (2009) Gene and metabolite regulatory network analysis of early developing fruit tissues highlights new candidate genes for the control of tomato fruit composition and development. Plant Physiol 149:1505–1528
Nakatsuka A, Murachi S, Okunishi H, Shiomi S, Nakano R, Kubo Y, Inaba A (1998) Differential expression and internal feedback regulation of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase, and ethylene receptor genes in tomato fruit during development and ripening. Plant Physiol 118:1295–1305
Osorio S, Alba R, Damasceno CM, Lopez-Casado G, Lohse M, Zanor MI, Tohge T, Usadel B, Rose JK, Fei Z, Giovannoni JJ, Fernie AR (2011) Systems biology of tomato fruit development: combined transcript, protein, and metabolite analysis of tomato transcription factor (nor, rin) and ethylene receptor (Nr) mutants reveals novel regulatory interactions. Plant Physiol 157:405–425
Ozaki S, Ogata Y, Suda K, Kurabayashi A, Suzuki T, Yamamoto N, Iijima Y, Tsugane T, Fujii T, Konishi C, Inai S, Bunsupa S, Yamazaki M, Shibata D, Aoki K (2010) Coexpression analysis of tomato genes and experimental verification of coordinated expression of genes found in a functionally enriched coexpression module. DNA Res 17:105–116
Pelaz S, Ditta GS, Baumann E, Wisman E, Yanofsky MF (2000) B and C floral organ identity functions require SEPALLATA MADS-box genes. Nature 405:200–203
Picton S, Gray JE, Payton S, Barton SL, Lowe A, Grierson D (1993) A histidine decarboxylase-like mRNA is involved in tomato fruit ripening. Plant Mol Biol 23:627–631
Pilati S, Perazzolli M, Malossini A, Cestaro A, Dematte L, Fontana P, Dal Ri A, Viola R, Velasco R, Moser C (2007) Genome-wide transcriptional analysis of grapevine berry ripening reveals a set of genes similarly modulated during three seasons and the occurrence of an oxidative burst at veraison. BMC Genomics 8:428
Pirrello J, Jaimes-Miranda F, Sanchez-Ballesta MT, Tournier B, Khalil-Ahmad Q, Regad F, Latche A, Pech JC, Bouzayen M (2006) Sl-ERF2, a tomato ethylene response factor involved in ethylene response and seed germination. Plant Cell Physiol 47:1195–1205
Reymond P, Weber H, Damond M, Farmer EE (2000) Differential gene expression in response to mechanical wounding and insect feeding in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:707–720
Rohrmann J, Tohge T, Alba R, Osorio S, Caldana C, McQuinn R, Arvidsson S, van der Merwe MJ, Riano-Pachon DM, Mueller-Roeber B, Fei Z, Nesi AN, Giovannoni JJ, Fernie AR (2011) Combined transcription factor profiling, microarray analysis and metabolite profiling reveals the transcriptional control of metabolic shifts occurring during tomato fruit development. Plant J. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04750.x
Rose JK, Lee HH, Bennett AB (1997) Expression of a divergent expansin gene is fruit-specific and ripening-regulated. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:5955–5960
Rose JK, Cosgrove DJ, Albersheim P, Darvill AG, Bennett AB (2000) Detection of expansin proteins and activity during tomato fruit ontogeny. Plant Physiol 123:1583–1592
Seymour GB, Manning K, Eriksson EM, Popovich AH, King GJ (2002) Genetic identification and genomic organization of factors affecting fruit texture. J Exp Bot 53:2065–2071
Sharma MK, Kumar R, Solanke AU, Sharma R, Tyagi AK, Sharma AK (2010) Identification, phylogeny, and transcript profiling of ERF family genes during development and abiotic stress treatments in tomato. Mol Genet Genomics 284:455–475
Srivastava A, Gupta AK, Datsenka T, Mattoo AK, Handa AK (2010) Maturity and ripening-stage specific modulation of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit transcriptome. GM Crops 1:237–249
Tanksley SD, Ganal MW, Prince JP, de Vicente MC, Bonierbale MW, Broun P, Fulton TM, Giovannoni JJ, Grandillo S, Martin GB, Messeguer R, Miller JC, Paterson AH, Pineda O, Roder MS, Wing RA, Young ND (1992) High density molecular linkage maps of the tomato and potato genomes. Genetics 132:1141–1160
Theissen G, Becker A, Di Rosa A, Kanno A, Kim JT, Munster T, Winter KU, Saedler H (2000) A short history of MADS-box genes in plants. Plant Mol Biol 42:115–149
Tigchelaar E, McGlasson W, Buescher R (1978) Genetic regulation of tomato fruit ripening. Hort Sci 13:508–513
Tournier B, Sanchez-Ballesta MT, Jones B, Pesquet E, Regad F, Latche A, Pech JC, Bouzayen M (2003) New members of the tomato ERF family show specific expression pattern and diverse DNA-binding capacity to the GCC box element. FEBS Lett 550:149–154
Trainotti L, Tadiello A, Casadoro G (2007) The involvement of auxin in the ripening of climacteric fruits comes of age: the hormone plays a role of its own and has an intense interplay with ethylene in ripening peaches. J Exp Bot 58:3299–3308
Vrebalov J, Ruezinsky D, Padmanabhan V, White R, Medrano D, Drake R, Schuch W, Giovannoni J (2002) A MADS-box gene necessary for fruit ripening at the tomato ripening-inhibitor (rin) locus. Science 296:343–346
Vrebalov J, Pan IL, Arroyo AJ, McQuinn R, Chung M, Poole M, Rose J, Seymour G, Grandillo S, Giovannoni J, Irish VF (2009) Fleshy fruit expansion and ripening are regulated by the tomato SHATTERPROOF gene TAGL1. Plant Cell 21:3041–3062
Wang H, Jones B, Li Z, Frasse P, Delalande C, Regad F, Chaabouni S, Latche A, Pech JC, Bouzayen M (2005) The tomato Aux/IAA transcription factor IAA9 is involved in fruit development and leaf morphogenesis. Plant Cell 17:2676–2692
Yokotani N, Tamura S, Nakano R, Inaba A, McGlasson WB, Kubo Y (2004) Comparison of ethylene- and wound-induced responses in fruit of wild-type, rin and nor tomatoes. Postharvest Biol Technol 32:247–252
Zegzouti H, Jones B, Marty C, Lelievre JM, Latche A, Pech JC, Bouzayen M (1997) ER5, a tomato cDNA encoding an ethylene-responsive LEA-like protein: characterization and expression in response to drought, ABA and wounding. Plant Mol Biol 35:847–854
Zegzouti H, Jones B, Frasse P, Marty C, Maitre B, Latch A, Pech JC, Bouzayen M (1999) Ethylene-regulated gene expression in tomato fruit: characterization of novel ethylene-responsive and ripening-related genes isolated by differential display. Plant J 18:589–600
Zhang Z, Zhang H, Quan R, Wang XC, Huang R (2009) Transcriptional regulation of the ethylene response factor LeERF2 in the expression of ethylene biosynthesis genes controls ethylene production in tomato and tobacco. Plant Physiol 150:365–377
Zheng Y, Ren N, Wang H, Stromberg AJ, Perry SE (2009) Global identification of targets of Arabidopsis MADS domain protein AGAMOUS-Like15. Plant Cell 21:2563–2577
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by grants received from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India. RK acknowledges CSIR for the fellowship granted during his tenure as a research fellow. Authors also acknowledge use of the draft tomato genome sequence, which was generated by the International Tomato Genome Sequencing Consortium (http://solgenomics.net/tomato/).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R., Sharma, M.K., Kapoor, S. et al. Transcriptome analysis of rin mutant fruit and in silico analysis of promoters of differentially regulated genes provides insight into LeMADS-RIN-regulated ethylene-dependent as well as ethylene-independent aspects of ripening in tomato. Mol Genet Genomics 287, 189–203 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-011-0671-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-011-0671-7