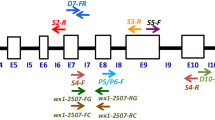
Abstract
The Waxy (Wx) gene product controls the formation of a straight chain polymer of amylose in the starch pathway. Dominance/recessiveness of the Wx allele is associated with amylose content, leading to non-waxy/waxy phenotypes. For a total of 113 foxtail millet accessions, agronomic traits and the molecular differences of the Wx gene were surveyed to evaluate genetic diversities. Molecular types were associated with phenotypes determined by four specific primer sets (non-waxy, Type I; low amylose, Type VI; waxy, Type IV or V). Additionally, the insertion of transposable element in waxy was confirmed by ex1/TSI2R, TSI2F/ex2, ex2int2/TSI7R and TSI7F/ex4r. Seventeen single nucleotide polymorphims (SNPs) were observed from non-coding regions, while three SNPs from coding regions were non-synonymous. Interestingly, the phenotype of No. 88 was still non-waxy, although seven nucleotides (AATTGGT) insertion at 2,993 bp led to 78 amino acids shorter. The rapid decline of r 2 in the sequenced region (exon 1–intron 1–exon 2) suggested a low level of linkage disequilibrium and limited haplotype structure. K s values and estimation of evolutionary events indicate early divergence of S. italica among cereal crops. This study suggested the Wx gene was one of the targets in the selection process during domestication.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brookes AJ (1999) The essence of SNPs. Gene 234:177–186
Cai CM, Van K, Kim MY, Lee S-H (2005) Optimization of SNP genotyping assay with fluorescence polarization detection. Korean J Crop Sci 50:361–367
Cho RJ, Mindrinos M, Richards DR, Sapolsky RJ, Anderson M, Drenkard E, Dewdney J, Reuber TL, Stammers M, Federspiel N, Theologis A, Yang WH, Hubbell E, Au M, Chung EY, Lashkari D, Lemieux B, Dean C, Lipshutz RJ, Ausubel FM, Davis RW, Oefner PJ (1999) Genome-wide mapping with biallelic markers in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 23:203–207
Collines FS, Brookes LD, Charkravati A (1998) A DNA polymorphism discovery resource for research on human genetic variation. Genome Res 8:1229–1231
Coryell VH, Jessen H, Schupp JM, Webb D, Keim P (1999) Allele-specific hybridization markers for soybean. Theor Appl Genet 98:690–696
Domon E, Fujita M, Ishikawa N (2002) The insertion/deletion polymorphisms in the waxy gene of barley genetic resources from East Asia. Theor Appl Genet 104:132–138
Eyre-Walker A, Gaut RL, Hilton H, Feldman DL, Gaut BS (1998) Investigation of the bottleneck leading to the domestication of maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1495:4441–4446
Fisher RA (1935) The logic of inductive interference. J Roy Stat Soc Ser A 98:39–54
Flint-Garcia SA, Thornsberry JM, Buckler ES IV (2003) Structure of linkage disequilibrium in plants. Ann Rev Plant Biol 54:357–374
Fukunaga K, Domon E, Kawase M (1997a) Ribosomal DNA variation in foxtail millet and a survey of variation from Europe and Asia. Theor Appl Genet 95:751–756
Fukunaga K, Kawase M, Sakamoto S (1997b) Variation of caryopsis length and width among landraces of foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv. Jpn J Trop Agric 41:235–240
Fukunaga K, Kawase M, Kato K (2002a) Structural variation in the Waxy gene and differentiation in foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.]: implications for multiple origins of the waxy phenotype. Mol Genet Genomics 268:214–222
Fukunaga K, Wang ZM, Kato K, Kawase M (2002b) Geographical variation of nuclear genome RFLPs and genetic differentiation in foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv. Genet Res Crop Evol 49:95–101
Gaut BS, Long AD (2003) The lowdown on linkage disequilibrium. Plant Cell 165:1502–1506
Gaut BS, Morton BR, McCaig BC, Clegg MT (1996) Substitutions ate comparisons between grasses and palms: synonymous rate differences at the nuclear gene Adh parallel ate differences at the plastid gene rbcL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10274–10279
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Kulwal PL (2005) Linkage disequilibrium and association studies in higher plants: present status and future prospects. Plant Mol Biol 57:461–485
Hirano HY, Sano Y (1991) Molecular characterization of the waxy locus of rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Cell Physiol 32:989–997
Issiki K, Morino K, Nakajima M, Okagaki RJ, Wessler SR, Izawa T, Shimamoto K (1998) A naturally occurring functional allele of the rice waxy locus has a GT to TT mutation at the 5′ splice site of the intron. Plant J 15:133–138
Jusuf M, Pernes J (1985) Genetic variability of foxtail millet (Setaria italica Beauv.): electorophretic study of five isoenzyme systems. Theor Appl Genet 71:385–391
Kawase M (1986) Genetic variation and landrace differentiation of foxtail millet, Setaria italica, in Eurasia. Ph. D. thesis, Kyoto University, Japan
Kawase M, Sakamoto S (1984) Variation, geographical distribution and genetic analysis of esterase isozymes in foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv. Theor Appl Genet 67:529–533
Kawase M, Sakamoto S (1987) Geographical distribution of landrace groups classified by intraspecific hybrid pollen sterility in foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv. Jpn J Breed 37:1–9
Kawase M, Fukunaga K, Kato K (2005) Diverse origins of waxy foxtail millet crops in East and Southeast Asia mediated by multiple transposable elements insertions. Mol Genet Genomics 274:131–140
Kellogg EA (1998) Relationships of cereal crops and other grasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:2005–2010
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rated of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kuppuswamy MN, Hoffman JW, Kasper CK, Spitzer SG, Groce SL, Bajaj SP (1991) Single nucleotide primer extension to detect genetic disease: experimental application to hemophilia B (factor IX) and cystic fibrosis genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:1143–1147
Kwok P-Y, Gu Z (1999) Single nucleotide polymorphism libraries: why and how are we building them? Mol Med Today 5:538–543
Larkin PD, Park WD (2003) Association of waxy gene single nucleotide polymorphisms with starch characteristics in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed 12:335–339
Mason-Gamer RJ, Weil CF, Kellogg EA (1998) Granule-bound starch synthase: structure, function, and phylogenetic utility. Mol Biol Evol 15:1658–1673
Morinaga T, Nagamatu T, Kawahara E (1943) New linkage relations in rice. Jpn J Genet 19:206–208. (in Japanese with English résumé)
Naciri Y, Darmency H, Belliard J, Dessaint F, Pernes J (1992) Breeding strategy in foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L. P. Beauv.), following interspecific hybridization. Euphytica 60:97–103
Nakamura T, Yamamori M, Yamaguchi I (1990) Variation of starch-granule bound protein (Wx protein) in foxtail millet and Japanese barnyard millet. Jpn J Breed 40(Suppl):418–419. (in Japanese)
Nakayama H, Afzal M, Okuno K (1998) Intraspecific differentiation and geographical distribution of Wx alleles for low amylose content in endosperm of foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv. Euphytica 102:289–293
Nei M (1987) Molecular evolutionary genetics. Columbia University Press, New York
Nordborg M (2000) Linkage disequilibrium, gene trees, and selfing: an ancestral recombination graph with partial self-fertilization. Genetics 154:923–929
Nordborg M, Borevitz JO, Bergelson J, Berry CC, Chory J, Hagenblad J, Kreitman M, Maloof JN, Noyes T, Oefner PJ, Stahl EA, Weigel D (2002) The extent of linkage disequilibrium in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 30:190–193
Ochiai Y (1996) Minor millet in Cheju Island, Korea. Millet News Lett 8:8–10. (in Japanese)
Ochiai Y, Kawase M, Sakamoto S (1994) Variation and distribution of foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.) in mountainous areas of northern Pakistan. Breed Sci 37:413–418
Olsen KM, Purugganan MD (2002) Molecular evidence on the origin and evolution of glutinous rice. Genetics 162:941–950
Page RD (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. CABIOS 12:357–358
Rafalski A (2002) Application of single nucleotide polymorphisms in crop genetics. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:94–100
Remington DL, Thornsberry JM, Matsuoka Y, Wilson LM, Whitt SR, Doebley J, Kresovich S, Goodman MM, Buckler ES IV (2001) Structure of linkage disequilibrium and phenotypic associations in the maize genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11479–11484
Rozas J, Rozas R (1999) DnaSP version 3: an integrated program for molecular population genetics and molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics 15:174–175
Rozas J, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Messenguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics 19:2496–2497
Sakamoto S (1982) Waxy endosperm and perisperm of cereals and grain amaranth and their geographical distributions. J Jpn Soc Starch Sci 29:41–55
Sakamoto S (1987) Origin and dispersal of common millet and foxtail millet. Jpn Agric Res Q 21:84–89
SanMiguel P, Gaut BS, Tikhonov A, Nakajima Y, Bennetzen JL (1998) The paleontology of intergene retrotransposons of maize. Nat Genet 20:43–45
SanMiguel P, Ramakrishna W, Bennetzen JL, Busso CS, Dubcovsky J (2002) Transposable elements, genes and recombination in a 215-kb contig from wheat chromosome 5Am. Funct Integr Genomics 2:70–80
Sano Y (1984) Differential regulation of waxy gene expression in rice endosperm. Theor Appl Genet 68:467–473
Schontz D, Rether B (1998) Genetic variability in foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.—RFLP using a heterologous rDNA probe. Plant Breed 117:231–234
Seo Y-W, Hong B-H, Ha Y-W (1998) Identification of granule bound starch synthase (GBSS) isoforms in wheat. Korean J Crop Sci 43:89–94
Shure M, Wessler S, Fedoroff N (1983) Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell 35:225–233
Takeda K, Chang C (1996) Inheritance and geographical distribution of phenol reaction-less varieties of barley. Euphytica 90:217–221
Takei E, Sakamoto S (1989) Further analysis of geographical variation of heading response to daylength in foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.). Jpn J Breed 39:285–298
Tenaillon MI, Sawkins MC, Long AD, Gaut RL, Doebley JF, Gaut BS (2001) Patterns of DNA sequence polymorphism along chromosome 1 of maize (Zea mays ssp. mays L.). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:961–966
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Umeda M, Ohtsubo H, Ohtsubo E (1991) Diversification of the rice Waxy gene by insertion of mobile DNA elements into introns. Jpn J Genet 66:569–586
Van K, Hwang E-Y, Kim MY, Kim Y-H, Cho YI, Cregan PB, Lee S-H (2004) Discovery of single nucleotide polymorphisms in soybean using primers designed from ESTs. Euphytica 139:147–157
Van K, Hwang E-Y, Kim MY, Park HJ, Lee S-H, Cregan PB (2005) Discovery of SNPs in soybean genotypes frequently used as the parents of mapping populations in the United States and Korea. J Hered 96:529–535
Wang ZM, Devos KM, Liu CJ, Wang RQ, Gale MD (1998) Construction of RFLP-based maps of foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv. Theor Appl Genet 96:31–36
Weir BS (1996) Genetic data analysis II. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Yanagisawa T, Kiribuchi-Otobe C, Yoshida H (2001) An alanine to threonine change in the Wx-D1 protein reduces GBSS I activity in waxy mutant wheat. Euphytica 121:209–214
Zhu YL, Song QJ, Hyten DL, Van Tassell CP, Matukumalli LK, Grimm DR, Hyatt SM, Fickus EW, Young ND, Cregan PB (2003) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in soybean. Genetics 163:1123–1134
Acknowledgments
This research was also supported by a grant (code no. CG3121) from the Crop Functional Genomics Center of the twenty-first Century Frontier Research Program funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST), Republic of Korea. Dr. K. Van and K. D. Kim are recipients of a fellowship and a scholarship, respectively, from the BK21 program granted by the Ministry of Education & Human Resources Development (ME & HRD), the Republic of Korea. We also thank the National Instrumentation Center for Environmental Management at Seoul National University in Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Hagemann.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van, K., Onoda, S., Kim, M.Y. et al. Allelic variation of the Waxy gene in foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.] by single nucleotide polymorphisms. Mol Genet Genomics 279, 255–266 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-007-0310-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-007-0310-5