Abstract
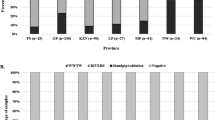
The prevalence and geographical distribution of the intestinal protozoa Blastocystis in humans across China is unknown, and the relative importance of different subtypes has yet to be investigated. We assessed the community prevalence and relative frequencies of different Blastocystis subtypes in four epidemiological settings in China, i.e., Shanghai municipality, Yongjia county (Zhejiang province), Eryuan county, and Menghai county (both Yunnan province). Blastocystis infection was detected with the culture method, and the subtype was identified with polymerase chain reaction using a set of subtype-specific primers. The prevalence at the four study settings was 1.9, 5.9, 18.4, and 32.6%, respectively. People aged greater than or equal to 60 years had a higher prevalence in the former two settings, Shanghai and Yongjia, whereas the highest infection rate was found among individuals aged 10–17 years in the latter two settings, Eryuan and Menghai. A higher prevalence was found in men in the former two settings but in women in the latter two settings. Five different Blastocystis subtypes were identified from the 192 isolates. Subtype 3 was the predominant type, followed by subtype 1. In conclusion, the epidemiology of Blastocystis varies across China.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banister J, Zhang XB (2005) China, economic development and mortality decline. World Dev 33:21–41
Bohm-Gloning B, Knobloch J, Walderich B (1997) Five subgroups of Blastocystis hominis from symptomatic and asymptomatic patients revealed by restriction site analysis of PCR-amplified 16S-like rDNA. Trop Med Int Health 2:771–778
Brumpt E (1912) Blastocystis hominis n.sp. et formes voisines. Bull Soc Pathol Exot 5:725–730
Clark CG (1997) Extensive genetic diversity in Blastocystis hominis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 87:79–83
El-Shazly AM, Abdel-Magied AA, El-Beshbishi SN, El-Nahas HA, Fouad MA, Monib MS (2005) Blastocystis hominis among symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals in Talkha Center, Dakahlia Governorate, Egypt. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 35:653–666
Ertug S, Karakas S, Okyay P, Ergin F, Oncu S (2006) The effect of Blastocystis hominis on the growth status of children. Med Sci Monit 13:CR40–CR43
Ho LC, Singh M, Suresh K, Ng GC, Yap EH (1994) A study of the karyotypic patterns of Blastocystis hominis by pulsed-field gradient electrophoresis. Parasitol Res 80:620–622
Hunter PR, Hughes S, Woodhouse S, Syed Q, Verlander NQ, Chalmers RM, Morgan K, Nichols G, Beeching N, Osborn K (2004) Sporadic cryptosporidiosis case–control study with genotyping. Emerg Infect Dis 10:1241–1249
Init I, Mak JW, Lokman Hakim S, Yong HS (1999) Strain differences in Blastocystis isolates as detected by a single set of polymerase chain reaction primers. Parasitol Res 85:131–134
Jin QX, Yu KM, Tang LF, Tian CL, Lu ZC (2005) Investigation of infectious status of Blastocystis hominis in 1354 outpatients. China Trop Med 5:1469–1471 (in Chinese)
Karanis P, Kourenti C, Smith H (2007) Waterborne transmission of protozoan parasites: a worldwide review of outbreaks and lessons learnt. J Water Health 5:1–38
Lai KP (1992) Intestinal protozoan infections in Malaysia. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 23:578–586
Li LH, Zhou XN, Du ZW, Wang XZ, Wang LB, Jiang JY, Yoshikawa H, Steinmann P, Utzinger J, Wu Z, Chen JX, Chen SH, Zhang L (2007) Molecular epidemiology of human Blastocystis in a village in Yunnan province, China. Parasitol Int 56:281–286
Liu CH, Han JJ, Liu CY, Wang ZY (1997) Survey on human parasites infection in Sichuan province. Sichuan J Zool 16:105–108 (in Chinese)
Muller M, Sanchez RM, Suswillo RR (1989) Evaluation of a sanitation programme using eggs of Ascaris lumbricoides in household yard soils as indicators. J Trop Med Hyg 92:10–16
Noël C, Dufernez F, Gerbod D, Edgcomb VP, Delgado-Viscogliosi P, Ho LC, Singh M, Wintjens R, Sogin ML, Capron M, Pierce R, Zenner L, Viscogliosi E (2005) Molecular phylogenies of Blastocystis isolates from different hosts: implications for genetic diversity, identification of species, and zoonosis. J Clin Microbiol 43:348–355
Schulz S, Kroeger A (1992) Soil contamination with Ascaris lumbricoides eggs as an indicator of environmental hygiene in urban areas of north-east Brazil. J Trop Med Hyg 95:95–103
Scicluna SM, Tawari B, Clark CG (2006) DNA barcoding of Blastocystis. Protist 157:77–85
Steinmann P, Zhou XN, Li YL, Li HJ, Chen SR, Yang Z, Fan W, Jia TW, Li LH, Vounatsou P, Utzinger J (2007a) Helminth infections and risk factor analysis among residents in Eryuan county, Yunnan province, China. Acta Trop 104 (in press)
Steinmann P, Zhou XN, Du ZW, Jiang JY, Wang LB, Wang XZ, Li LH, Marti H, Utzinger J (2007b) Occurrence of Strongyloides stercoralis in Yunnan province, China and comparison of diagnostic methods. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 1:e75, doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000075
Stensvold CR, Brillowska-Dabrowska A, Nielsen HV, Arendrup MC (2006) Detection of Blastocystis hominis in unpreserved stool specimens by using polymerase chain reaction. J Parasitol 92:1081–1087
Stensvold CR, Suresh GK, Tan KSW, Thompson RCA, Traub RJ, Viscogliosi E, Yoshikawa H, Clark CG (2007) Terminology for Blastocystis subtypes—a consensus. Trends Parasitol 23:93–96
Stenzel DJ, Boreham PFL (1996) Blastocystis hominis revisited. Clin Microbiol Rev 9:563–584
Su YP, He LJ, Shang LY, Li C (1995) Research status of Blastocystis hominis in China. Henan J Prev Med 6:361–363 (in Chinese)
Suresh K, Smith H (2004) Comparison of methods for detecting Blastocystis hominis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 23:509–511
Tan KSW, Singh M, Yap EH (2002) Recent advances in Blastocystis hominis research: hot spots in terra incognita. Int J Parasitol 32:789–804
Termmathurapoj S, Leelayoova S, Aimpun P, Thathaisong U, Nimmanon T, Taamasri P, Mungthin M (2004) The usefulness of short-term in vitro cultivation for the detection and molecular study of Blastocystis hominis in stool specimens. Parasitol Res 93:445–447
Upcroft JA, Dunn LA, Dommett LS, Healey A, Upcroft P, Boreham PF (1989) Chromosomes of Blastocystis hominis. Int J Parasitol 19:879–883
Wang J, Li CP (2002) Epidemiology investigation of Blastocystis hominis in Huainan areas. J Fourth Military Med Univers 23:1480–1482 (in Chinese)
Wang YK, Yu H, Yang JL, Yang HM (1994) A survey of human intestinal protozoa in Yunnan. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis 12:89–92 (in Chinese)
Woolhouse MEJ (1998) Patterns in parasite epidemiology: the peak shift. Parasitol Today 14:428–434
Xu LQ, Yu SH, Xu SH (2000) Distribution and pathogenic impact of human parasites in China. People's Medical, Beijing China (in Chinese)
Yan YM, Su SL, Lai RY, Liao H, Ye JH, Li XB, Luo XT, Chen GF (2006) Genetic variability of Blastocystis hominis isolates in China. Parasitol Res 99:597–601
Yoshikawa H, Nagano I, Wu Z, Yap EH, Singh M, Takahashi Y (1998) Genomic polymorphism among Blastocystis hominis strains and development of subtype-specific diagnostic primers. Mol Cell Probes 12:153–159
Yoshikawa H, Abe N, Iwasawa M, Kitano S, Nagano I, Wu Z, Takahashi Y (2000) Genomic analysis of Blastocystis hominis strains isolated from two long-term health care facilities. J Clin Microbiol 38:1324–1330
Yoshikawa H, Abe N, Wu Z (2003) Genomic polymorphism among Blastocystis isolates and development of PCR-based identification of zoonotic isolates. J Eukaryot Microbiol 50(Suppl):710–711
Yoshikawa H, Morimoto K, Wu Z, Singh M, Hashimoto T (2004a) Problems in speciation in the genus Blastocystis. Trends Parasitol 20:251–255
Yoshikawa H, Wu Z, Kimata I, Iseki M, Ali IK, Hossain MB, Zaman V, Haque R, Takahashi Y (2004b) Polymerase chain reaction-based subtype classification among human Blastocystis hominis populations isolated from different countries. Parasitol Res 92:22–29
Zierdt CH (1991) Blastocystis hominis—past and future. Clin Microbiol Rev 4:61–79
Acknowledgments
We thank all participants and the staff of the Yunnan Institute for Parasitic Diseases Control and Prevention, Center for Disease Control and Prevention of Menghai county and Simao prefecture, the Yunnan Institute for Schistosomiasis Control and Prevention, Eryuan branch, the Center for Disease Control and Prevention of Shanghai, and the People’s Hospital of Yongjia county for their commitment during the cross-sectional surveys. This investigation received financial support from the Ministry of Science and Technology, China (grant no. 2005DKA21104), which supports the Key Laboratory of Parasite and Vector Biology of the Ministry of Health in China, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Sciences to H. Y. (B17406007), and the Swiss National Science Foundation (project no. PPOOB-102883). P. Steinmann acknowledges support from the Freiwillige Akademische Gesellschaft, Basel, the SDC-sponsored program “Jeunes Chercheurs,” and is grateful to the Janggen Pöhn Foundation for a personal stipend for the last year of his Ph.D. The execution of the research described in this article complied with all applicable laws of the People’s Republic of China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L.H., Zhang, X.P., Lv, S. et al. Cross-sectional surveys and subtype classification of human Blastocystis isolates from four epidemiological settings in China. Parasitol Res 102, 83–90 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0727-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0727-0