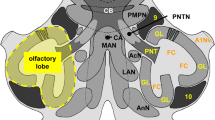
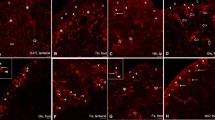
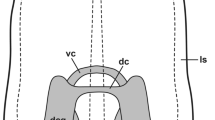
Abstract
The structure and function of the central nervous systems of opisthobranch gastropods have been studied extensively. However, the organisation and function of the peripheral nervous system are poorly understood. The cephalic sensory organs (CSOs) are known to be chemosensory structures in the head region of opisthobranchs. In the present study, we used immunohistochemical methods and confocal laserscanning microscopy to comparatively examine the CSOs of different opisthobranchs, namely Acteon tornatilis, Aplysia punctata, Archidoris pseudoargus and Haminoea hydatis. We wanted to characterise sensory epithelia in order to infer the function of sensory structures and the organs they constitute. Immunoreactivity against the three antigens tyrosine hydroxylase, FMRFamide and serotonin was very similar in the CSOs of all investigated species. Tyrosine hydroxylase-like immunoreactivity was detected primarily in subepidermal sensory cell bodies, which were much more abundant in the anteriorly situated CSOs. This observation indicates that these cells and the respective organs may be involved in contact chemoreception and mechanoreception. The dominant features of FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity, especially in the posterior CSOs, were tightly knotted fibres which reveal glomerulus-like structures. This suggests an olfactory role for these organs. Serotonin-like immunoreactivity was detected in an extensive network of efferent fibres, but was not found within any peripheral cell bodies. Serotonin-like immunoreactivity was found in the same glomerulus-like structures as FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity, indicating a function of serotonin in the efferent control of olfactory inputs. Besides this functional implication, this study could also add some knowledge on the doubtful homology of the CSOs in opisthobranch gastropods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audesirk TE (1975) Chemoreception in Aplysia californica. I. Behavioral localization of distance chemoreceptors used in food-finding. Behav Biol 15:45–55. doi:10.1016/S0091-6773(75)92066-0
Bicker G, Davis WJ, Matera EM (1982) Chemoreception and mechanoreception in the gastropod mollusc Pleurobranchaea californica. II. Neuroanatomical and intracellular analysis of afferent pathways. J Comp Physiol 149:235–250. doi:10.1007/BF00619217
Boudko DY, Switzer-Dunlap M, Hadfield MG (1999) Cellular and subcellular structure of anterior sensory pathways in Phestilla sibogae (Gastropoda, Nudibranchia). J Comp Neurol 403:39–52. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19990105)403:1≤39::AID-CNE4≥3.0.CO;2-B
Cardot J, Fellman D (1983) Immunofluorescent evidence of an FMRFamide-like peptide in the peripheral nervous system of the gastropod mollusc Helix aspersa. Neurosci Lett 43:167–172. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(83)90182-9
Chase R (1979) Photic sensitivity of the rhinophore in Aplysia. Can J Zool 57:698–701
Chase R (2002) Behavior and its neural control in gastropod molluscs. Oxford University Press, New York
Chase R, Tolloczko B (1986) Synaptic glomeruli in the olfactory system of a snail, Achatina fulica. Cell Tissue Res 246:567–573. doi:10.1007/BF00215198
Chiasson BJ, Baker MW, Croll RP (1994) Morphological changes and functional recovery following axotomy of a serotonergic cerebrobuccal neurone in the land snail Achatina fulica. J Exp Biol 192:147–167
Cooke IRC, Gelperin A (1988) Distribution of FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity in the nervous system of the slug Limax maximus. Cell Tissue Res 253:69–76
Cottrell GA (1989) The biology of the FMRFamide-series of peptides in molluscs with special reference to Helix. Comp Biochem Physiol 93A(1):41–45. doi:10.1016/0300-9629(89)90189-8
Croll RP (1983) Gastropod chemoreception. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 58:293–319. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.1983.tb00391.x
Croll RP (1987) Distribution of monoamines in the central nervous system of the nudibranch gastropod, Hermissenda crassicornis. Brain Res 405:337–347. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(87)90303-9
Croll RP (2001) Catecholamine-containing cells in the central nervous system and periphery of Aplysia californica. J Comp Neurol 441:91–105. doi:10.1002/cne.1399
Croll RP, Boudko DY, Hadfield MG (2001) Histochemical survey of transmitters in the central ganglia of the gastropod mollusc Phestilla sibogae. Cell Tissue Res 305:417–432. doi:10.1007/s004410100394
Croll RP, Boudko DY, Pires A, Hadfield MG (2003) Transmitter contents of cells and fibres in the cephalic sensory organs of the gastropod mollusc Phestilla sibogae. Cell Tissue Res 314:437–448. doi:10.1007/s00441-003-0778-1
Croll RP, Staubauch S, Klussmann-Kolb A (2004) FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous systems and periphery of Aplysia californica. World Congress of Malacology, Perth, Australia
Davis WJ, Matera EM (1982) Chemoreception in gastropod molluscs: electron microscopy of putative receptor cells. J Neurobiol 13(1):79–84. doi:10.1002/neu.480130109
Dayrat B, Tillier S (2002) Evolutionary relationships of euthyneuran gastropods (Mollusca): a cladistic re-evaluation of morphological characters. Zool J Linn Soc 135:403–470. doi:10.1046/j.1096-3642.2002.00018.x
Dayrat B, Tillier A, Lecointre G, Tillier S (2001) New clades of euthyneuran gastropods (Mollusca) from 28S rRNA sequences. Mol Phyl Evol 19(2):225–235. doi:10.1006/mpev.2001.0926
Edlinger K (1980) Zur Phylogenie der chemischen Sinnesorgane einiger Cephalaspidea (Mollusca-Opisthobranchia). Z Zool Syst Evol 18:241–256
Elekes K (1992) Neurotransmitters in the gastropod CNS: comparative immunocytochemistry. Acta Biol Hung 43(1–4):213–220
Elekes K, Nässel DR (1990) Distribution of FMRFamide-like immunoreactive neurons in the central nervous system of the snail Helix pomatia. Cell Tissue Res 262:177–190. doi:10.1007/BF00327760
Elekes K, Kemenes G, Hiripi L, Geffard M, Benjamin PR (1991) Dopamine-immunoreactive neurones in the central nervous system of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. J Comp Neurol 307:214–224. doi:10.1002/cne.903070205
Emery DG (1992) Fine structure of olfactory epithelia of gastropod molluscs. Microsc Res Tech 22:307–324. doi:10.1002/jemt.1070220402
Emery DG, Audesirk TE (1978) Sensory cells in Aplysia. J Neurobiol 9:173–179. doi:10.1002/neu.480090207
Göbbeler K, Klussmann-Kolb A (2007) A comparative ultrastructural investigation of the cephalic sensory organs in Opisthobranchia (Mollusca, Gastropoda). Tissue Cell 39(6):399–414. doi:10.1016/j.tice.2007.07.002
Gosliner TM (1994) Gastropoda: Opisthobranchia. Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates Volume 5. Mollusca I:253–355
Hernadi L, Elekes K (1999) Topographic organization of serotonergic and dopaminergic neurons in the cerebral ganglia and their peripheral projection patterns in the head areas of the snail Helix pomatia. J Comp Neurol 411:274–287. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19990823)411:2≤274::AID-CNE8≥3.0.CO;2-9
Hernadi L, Elekes K, S-Rozsa K (1989) Distribution of serotonin-containing neurons in the central nervous system of the snail Helix pomatia. Cell Tissue Res 257:313–323. doi:10.1007/BF00261835
Hernadi L, Juhos S, Elekes K (1993) Distribution of tyrosine-hydroxylase-immunoreactive and dopamine-immunoreactive neurons in the central nervous system of the snail Helix pomatia. Cell Tissue Res 274:503–513. doi:10.1007/BF00314547
Hochberg R (2007) Serotonin-like immunoreactivity in the central and peripheral nervous systems of the interstitial acochlidean Asperspina sp. Biol Bull 213:43–54
Huber G (1993) On the cerebral nervous system of marine Heterobranchia (Gastropoda). J Molluscan Stud 59:381–420. doi:10.1093/mollus/59.4.381
Jacklet JW (1980) Light sensitivity of the rhinophores and eyes of Aplysia. J Comp Physiol 136(3):257–262. doi:10.1007/BF00657541
Jahan-Parwar B (1972) Behavioral and electrophysiological studies on chemoreception in Aplysia. Am Zool 12:525–537
Kemenes G, Elekes K, Hiripi L, Benjamin PR (1989) A comparison of four techniques for mapping the distribution of serotonin and serotonin-containing neurons in fixed and living ganglia of the snail, Lymnaea. J Neurocytol 18(2):193–208. doi:10.1007/BF01206662
Klussmann-Kolb A, Dinapoli A, Kuhn K, Streit B, Albrecht C (2008) From sea to land and beyond—new insights into the evolution of the euthyneuran Gastropoda (Mollusca). BMC Evol Biol 8:57. doi:10.1186/1471–2148-8-57
Longley RD, Longley AJ (1986) Serotonin immunoreactivity of neurons in the gastropod Aplysia californica. J Neurobiol 17(4):339–358. doi:10.1002/neu.480170408
Merton H (1920) Untersuchungen über die Hautsinnesorgane der Mollusken. I. Opisthobranchia. Abhandl Senckenb Naturf Ges 36(4):449–473
Moroz LL (2006) Localization of putative nitrergic neurons in peripheral chemosensory areas and the central nervous sytem of Aplysia californica. J Comp Neurol 495:10–20. doi:10.1002/cne.20842
Moroz LL, Sudlow LC, Jing J, Gillette R (1997) Serotonin-immunoreactivity in peripheral tissues of the opisthobranch molluscs Pleurobranchaea californica and Tritonia diomedea. J Comp Neurol 382:176–188. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19970602)382:2≤176::AID-CNE3≥3.0.CO;2-0
Newcomb JM, Fickbohm DJ, Katz PS (2006) Comparative mapping of serotonin-immunoreactive neurons in the central nervous system of nudibranch molluscs. J Comp Neurol 499:485–505. doi:10.1002/cne.21111
Ono JK, McCaman RE (1984) Immunocytochemical localization and direct assays of serotonin-containing neurons in Aplysia. Neuroscience 11(3):549–560. doi:10.1016/0306-4522(84)90044-7
Ponder WF, Lindberg D (1997) Towards a phylogeny of gastropod molluscs: an analysis using morphological characters. Zool J Linn Soc 119:83–265
Price DA, Greenberg MJ (1977) Purification and characterization of a cardioexcitatory neuropeptide from the central ganglia of a bivalve mollusc. Prep Biochem 7:261–281. doi:10.1080/00327487708061643
Price DA, Davies NW, Doble KE, Greenberg MJ (1987) The variety and distribution of the FMRFamide-related peptides in molluscs. Zoolog Sci 4:395–410
Salimova NB, Sakharov DA, Milosevic I, Rakic L (1987) Catecholamine-containing neurons in the peripheral nervous system of Aplysia. Acta Biol Hung 38(2):203–212
Salvini-Plawen L, Steiner G (1996) Synapomorphies and plesiomorphies in higher classification of Mollusca. In: Taylor J (ed) Origin and evolutionary radiation of the Mollusca. Oxford University Press, The Malacological Society of London, pp 29–51
Shirahata T, Watanabe S, Kirino Y (2004) Distribution of serotonin-like immunoreactive neurons in the slug Limax valentianus. Cell Tissue Res 315:285–290. doi:10.1007/s00441-003-0820-3
S.-Rozsa K (1984) The pharmacology of molluscan neurons. Prog Neurobiol 23:79–150. doi:10.1016/0301-0082(84)90013-3
Storch V, Welsch U (1969) Über den Bau und Funktion der Nudibranchier-Rhinophoren. Z Zellforsch 97:528–536. doi:10.1007/BF00332801
Sudlow LC, Jing J, Moroz LL, Gillette R (1998) Serotonin-immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the marine molluscs Pleurobranchaea californica and Tritonia diomedea. J Comp Neurol 395:466–480. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19980615)395:4≤466::AID-CNE4≥3.0.CO;2-#
Suzuki H, Kimura T, Sekiguchi T, Mizukami A (1997) FMRFamide-like-immunoreactive primary sensory neurons in the olfactory system of the terrestrial mollusc, Limax marginatus. Cell Tissue Res 289:339–345. doi:10.1007/s004410050881
Vonnemann V, Schrödl M, Klussmann-Kolb A, Wägele H (2005) Reconstruction of the phylogeny of the Opisthobranchia (Mollusca: Gastropoda) by means of 18S and 28S rRNA gene sequences. J Molluscan Stud 71:113–125. doi:10.1093/mollus/eyi014
Wertz A, Rössler W, Obermayer M, Bickmeyer U (2006) Functional neuroanatomy of the rhinophore of Aplysia punctata. Front Zool 3:6. doi:10.1186/1742-9994-3-6
Wertz A, Rössler W, Obermayer M, Bickmeyer U (2007) Functional neuroanatomy of the rhinophore of Archidoris pseudoargus. Helgol Mar Res 61:135–142. doi:10.1007/s10152-007-0061-z
Wollesen T, Wanninger A, Klussmann-Kolb A (2007) Neurogenesis of cephalic sensory organs of Aplysia californica. Cell Tissue Res 330:361–379. doi:10.1007/s00441-007-0460-0
Wolter H (1967) Beiträge zur Biologie, Histologie und Sinnesphysiologie (insbesondere der Chemorezeption) einiger Nudibranchier (Mollusca, Opisthobranchia) der Nordsee. Z Morphol Oekol Tiere 60:275–337. doi:10.1007/BF00424637
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Roger P. Croll for his helpful comments on an earlier version of this report. We would also like to thank the German Science Foundation (DFG) for supporting this project (KL 1303/3-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faller, S., Staubach, S. & Klussmann-Kolb, A. Comparative immunohistochemistry of the cephalic sensory organs in Opisthobranchia (Mollusca, Gastropoda). Zoomorphology 127, 227–239 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-008-0066-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-008-0066-4