Abstract
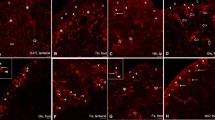
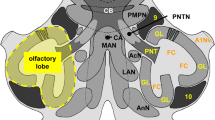
While the central ganglia of gastropod molluscs have been studied extensively, relatively little is known about the organization and functions of the peripheral nervous system in these animals. In the present study, we used immunohistochemical procedures to examine the innervation of the rhinophores, oral tentacles and region around the mouth of the aeolid nudibranch, Phestilla sibogae. Serotonin-like immunoreactivity was found in an extensive network of efferent projections apparently originating from central neurons, but was not detected within any peripheral cell bodies. In contrast, large numbers of peripheral, and presumably sensory, somata exhibited reactivity to an antibody raised against tyrosine hydroxylase (the enzyme catalyzing the initial step in the conversion of tyrosine into the catecholamines). Additional tyrosine hydroxylase-like immunoreactivity was detected in afferent fibers of the peripheral cells and in several cells within the rhinophoral ganglia. The presence of serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine in the rhinophores, tentacles and central ganglia was confirmed using high-performance liquid chromatography. Finally, FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity was detected in cells and tangles of fibers found within the rhinophore, possibly revealing glomerulus-like structures along olfactory pathways. FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity was also found in somata of the rhinophoral ganglia, in a small number of cells located in the body wall lateral to the tentacles and in what appeared to be varicose terminals of efferent projections to the periphery. Together, these results indicate several new features of the gastropod peripheral nervous system and suggest future experiments that will elucidate the function of the novel cells and innervation patterns described here.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audesirk TE (1975) Chemoreception in Aplysia californica. I. Behavioral localization of distance chemoreceptors used in food finding. Behav Biol 15:45–55
Audesirk TE (1977) Chemoreception in Aplysia californica III. Evidence for pheromones influencing reproductive behavior. Behav Biol 20:235–243
Bicker G, Davis WJ, Matera EM, Kovac MP, Stormo-Gipson DJ (1982a) Chemoreception and mechanoreception in the gastropod mollusc Pleurobranchaea californica. I. Extracellular analysis of afferent pathways. J Comp Physiol 149:221–234
Bicker G, Davis WJ, Matera EM, Kovac MP, Stormo-Gipson DJ (1982b) Chemoreception and mechanoreception in the gastropod mollusc Pleurobranchaea californica. II. Neuroanatomical and intracellular analysis of afferent pathways. J Comp Physiol 149:235–250
Boudko DY, Hadfield MG (1995) Pharmacological analysis of chemoreception in the nudibranch Phestilla sibogae. Am Zool 35:27A
Boudko DY, Hadfield MG, Croll RP (1998) Transmitters in anterior sensory organs of the gastropod mollusc Phestilla sibogae. Soc Neurosci Abstr 24:1841
Boudko DY, Switzer-Dunlap M, Hadfield MG (1999) Cellular and subcellular structure of anterior sensory pathways in Phestilla sibogae (Gastropoda, Nudibranchia). J Comp Neurol 403:39–52
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Buckett KJ, Peters M, Benjamin PR (1990) Excitation and inhibition of the heart of the snail, Lymnaea, by non-FMRFamidergic motoneurons. J Neurophysiol 63:1436–1447
Bulloch TH, Horridge GA (1965) Structure and function in the nervous systems of invertebrates. WH Freeman, San Francisco
Cawthorpe D, Lukowiak K (1990) Dopamine and FMRFamide act directly on isolated gill muscle fibers in culture. Neurosci Lett 113:345–348
Chase R (1979a) An electrophysiological search for pheromones of Aplysia californica. Can J Zool 57:781–784
Chase R (1979b) Photic sensitivity of the rhinophore in Aplysia. Can J Zool 57:698–701
Chase R (2002) Behavior and its neural control in gastropod molluscs. Oxford University Press, New York
Chase R, Tolloczko B (1986) Synaptic glomeruli in the olfactory system of a snail, Achatina fulica. Cell Tissue Res 246:567–571
Cooper JR, Bloom FE, Roth RH (1996) The biochemical basis of neuropharmacology. Oxford University Press, New York
Croll RP (1983) Gastropod chemoreception. Biol Rev 58:293–319
Croll RP (1987) Distribution of monoamines in the central nervous system of the nudibranch gastropod Hermissenda crassicornis. Brain Res 405:337–347
Croll RP (1988) Distribution of monoamines within the central nervous system of the pulmonate snail Achatina fulica. Brain Res 460:29–49
Croll RP (2001) Catecholamine-containing cells in the central nervous system and periphery of Aplysia californica. J Comp Neurol 441:91–105
Croll RP, Chiasson BJ (1989) Post-embryonic development of serotonin-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. J Comp Neurol 280:122–142
Croll RP, Lo RYS (1986) Distribution of serotonin-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the periwinkle, Littorina littorea (Gastropoda, Prosobranchia, Mesogastropoda). Biol Bull 171:426–440
Croll RP, Too CKL, Pani AK, Nason J (1995) Distribution of serotonin in body tissues of the sea scallop Plactopecten magellanicus. Invert Reprod Dev 28:125–135
Croll RP, Jackson DL, Voronezhskaya EE (1997) Catecholamine-containing cells in larval and post-larval bivalve molluscs. Biol Bull 193:116–124
Croll RP, Voronezhskaya EE, Hiripi L, Elekes K (1999) Development of catecholaminergic neurons in the pond snail, Lymnaea stagnalis II: postembryonic development of central and peripheral cells. J Comp Neurol 404:297–309
Croll RP, Boudko DY, Hadfield MG (2001) Histochemical survey of transmitters in the central ganglia of the gastropod mollusc, Phestilla sibogae. Cell Tissue Res 305:417–432
Davis WJ, Matera EM (1982) Chemoreception in gastropod molluscs: electron microscopy of putative receptor cells. J Neurobiol 13:79–84
Dickinson AJG, Nason J, Croll RP (1999) Histochemical localization of FMRFamide, serotonin and catecholamine in embryonic Crepidula fornicata (Prosobranchia: Gastropoda). Zoomorphology 119:49–62
Dickinson AJG, Croll RP, Voronezhskaya EE (2000) Development of embryonic cells containing serotonin, catecholamines and FMRFamide-related peptides in Aplysia californica. Biol Bull 199:305–315
Emery DJ (1992) Fine structure of olfactory epithelia of gastropod molluscs. Microsc Res Tech 22:307–324
Emery DG, Audesirk TE (1978) Sensory cells in Aplysia. J Neurobiol 9:173–179
Evans CG, Vilim FS, Harish O, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR, Cropper EC (1999) Modulation of radula opener muscles in Aplysia. J Neurophysiol 82:1339–1351
Field LH, Macmillan DL (1973) An electrophysiological and behavioral study of sensory responses in Tritonia (Gastropoda, Nudibranchia). Mar Behav Physiol 2:171–185
Giloh H, Sedat JW (1982) Fluorescence microscopy: reduced photobleaching of rhodamine and fluorescein protein conjugates by n-propyl gallate. Science 217:1252–1255
Greenberg MJ, Price DA (1992) Relationships among the FMRFamide-like peptides. Prog Brain Res 92:25–37
Hadfield MG (1978) Metamorphosis in marine molluscan larvae: an analysis of stimulus and response. In: Chia F, Rice ME (eds) Settlement and metamorphosis of marine invertebrate larvae. Elsevier, New York, pp 165–175
Hadfield MG, Pennington JT (1990) Nature of the metamorphic signal and its internal transduction in larvae of the nudibranch, Phestilla sibogae. Bull Mar Sci 46:455–464
Jahan-Parwar B (1972) Behavioral and electrophysiological studies on chemoreception in Aplysia. Am Zool 12:27–37
Kabotyanskii EA, Sakharov DA (1990) Catecholaminergic neurons in the pteropod mollusc, Clione limacina. J Evol Biochem Physiol 25:198–207
Kandel ER (1979) Behavioral biology of Aplysia. WH Freeman, San Francisco
Katz PS, Fickbohm DJ, Lynn-Bullock C (2001) Evidence that the swim CPG of Tritonia arose from a non-rhythmic neuromodulatory arousal system: implications for the evolution of specialized behavior. Am Zool 41:962–975
Kempf SC, Chun GV, Hadfield MG (1992) An immunocytochemical search for potential neurotransmitters in larvae of Phestilla sibogae (Gastropoda, Opisthobranchia). Comp Biochem Physiol 101C:299–305
Kits KS, Boer HH, Joosse J (1991) Molluscan neurobiology. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Korsching S (2002) Olfactory maps and odor images. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12:387–392
Kovac MP, Davis WJ (1980) Neural mechanism underlying behavioral choice in Pleurobranchaea. J Neurophysiol 43:469–487
Kupfermann I (1974) Feeding behavior in Aplysia: a simple system for the study of motivation. Behav Biol 10:1–26
Lee RM, Liegeois RJ (1974) Motor and sensory mechanisms of feeding in Pleurobranchaea. J Neurobiol 5:545–564
Lei H, Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (2002) Local inhibition modulates odor-evoked synchronization of glomerulus-specific output neurons. Nat Neurosci 5:557–565
Levy M, Blumberg S, Susswein AJ (1997) The rhinophores sense pheromones regulating multiple behaviors in Aplysia fasciata. Neurosci Lett 225:113–116
Longley RD, Longley AJ (1986) Serotonin-like immunoreactivity in gastropod Aplysia californica. J Neurobiol 17:339–358
Matera EM, Davis WJ (1982) Paddle cilia (discocilia) in chemosensitive structures of the gastropod mollusk Pleurobranchaea californica. Cell Tissue Res 222:25–40
McCaman MW (1984) Neurochemistry of invertebrates. In: Lajtha A (ed) Handbook of neurochemistry, vol 7. Plenum, New York, pp 613–700
McCaman MW, Weinreich D, McCaman RE (1973) The determination of picomole level of 5-hydroxytyptamine and dopamine in Aplysia, Tritonia and leech nervous tissues. Brain Res 53:129–137
Miller SE, Hadfield MG (1990) Developmental arrest during larval life and life-span extension in a marine mollusc. Science 248:356–358
Moroz LL, Sudlow LC, Jing J, Gillette R (1997) Serotonin-immunoreactivity in peripheral tissues of the opisthobranch molluscs Pleurobranchaea californica and Tritonia diomedea. J Comp Neurol 382:176–188
Murphy BF, Hadfield MG (1997) Chemoreception in the nudibranch gastropod Phestilla sibogae. Comp Biochem Physiol 118A:727–735
Murray JA, Willows AOD (1996) Function of identified nerves in orientation to water flow in Tritonia diomedea. J Comp Physiol 176A:201–209
Nezlin L, Voronezhskaya E (1997) GABA-immunoreactive neurones and interactions of GABA with serotonin and FMRFamide in a peripheral sensory ganglion of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Brain Res 772:217–225
Pani AK, Croll RP (1995) Distribution of catecholamines, indoleamines, and their precursors and metabolites in the scallop, Placopecten magellanicus (Bivalvia, Pectinidae). Cell Mol Neurobiol 15:371–386
Pani AK, Croll RP (1998) Pharmacological analysis of monoamine synthesis and catabolism in the scallop, Placopecten magellanicus. Gen Pharmacol 31:67–73
Pires A, Coon SL, Hadfield MG (1997) Catecholamines and dihydroxyphenylalanine in metamorphosing larvae of the nudibranch Phestilla sibogae Bergh (Gastropoda: Opisthobranchia). J Comp Physiol 181A:187–194
Pires A, Croll RP, Hadfield MG (2000) Catecholamines modulate metamorphosis in the opisthobranch gastropod, Phestilla sibogae. Biol Bull 198:319–331
Ram JL, Shukla UA, Ajimal GS (1981) Serotonin has both excitatory and inhibitory modulatory effects on feeding muscles in Aplysia. J Neurobiol 12:613–621
Ram JL, Moore D, Putchakayala S, Paredes AA, Ma D, Croll RP (1999) Serotonergic responses of the siphons and adjacent mantle tissue of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha. Comp Biochem Physiol 124C:211–220
Salimova NB, Sakharov DA, Milosevic I, Rakic L (1987) Catecholamine-containing neurons in the peripheral nervous system of Aplysia. Acta Biol Hung 38:203–212
Shepherd GM (1972) Synaptic organization of the mammalian olfactory bulb. Physiol Rev 52:864–917
Skelton M, Alevizos A, Koester J (1992) Control of the cardiovascular system of Aplysia by identified neurons. Experientia 48:809–817
Smith SA, Nason J, Croll RP (1998) Distribution of catecholamines in the sea scallop, Placopecten magellanicus. Can J Zool 76:1254–1262
Sudlow LC, Jing J, Moroz LL, Gillette R (1998) Serotonin immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the marine molluscs Pleurobranchaea californica and Tritonia diomedea. J Comp Neurol 395:466–480
Susswein AJ, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1976) The stimulus control of biting in Aplysia. J Comp Physiol 108:75–96
Suzuki H, Kimura T, Sekiguchi T, Mizukami A (1997) FMRFamide-like-immunoreactive primary sensory neurons in the olfactory system of the terrestrial mollusc, Limax marginatus. Cell Tissue Res 289:339–345
Teyke T, Weiss KR, Kupfermann I (1990) Appetitive feeding behavior of Aplysia: behavior and neural analysis of head turning. J Neurosci 10:3922–3934
Todd CD, Hadfield MG, Snedden WA (1997) Juvenile mating and sperm storage in the tropical coralivorous nudibranch Phestilla sibogae. Invert Biol 116:322–330
Twarog BM (1954) Responses of a molluscan smooth muscle to acetylcholine and 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Cell Comp Physiol 44 141–164
Voronezhskaya EE, Hiripi L, Elekes K, Croll RP (1999) Development of catecholaminergic neurons in the pond snail, Lymnaea stagnalis I: embryonic development of dopaminergic neurons and dopamine-dependent behaviors. J Comp Neurol 404:297–309
Walker RJ (1986) Transmitters and modulators. In: Willows AOD (ed) Neurobiology and behavior. The Mollusca, vol 9, part 2. Academic, Orlando, pp 279–485
Weiss KR, Cohen JL, Kupfermann I (1978) Modulatory control of buccal musculature by a serotonergic neuron (metacerebral cell) in Aplysia. J Neurophysiol 41:181–203
Willows AOD (1985a) Neural control of behavioral responses in the nudibranch mollusc Phestilla sibogae. J Neurobiol 16:157–170
Willows AOD (1985b) Neurobiology and behavior, vol 8, part I. The Mollusca. Academic, New York
Willows AOD (1986) Neurobiology and behavior, vol 8, part II. The Mollusca. Academic, New York
Acknowledgements
We thank Annette Kolb-Klussman for critically reading an earlier version of this report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by Natural Sciences and Research Council of Canada Grant #OPG38863 to R.P.C. and Office of Naval Research Grant #N00014-94-1-0524 to M.G.H.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Croll, R.P., Boudko, D.Y., Pires, A. et al. Transmitter contents of cells and fibers in the cephalic sensory organs of the gastropod mollusc Phestilla sibogae . Cell Tissue Res 314, 437–448 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0778-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0778-1