Abstract
Purpose
Downregulation of miRNA expression has been identified as a novel feature of renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Recently, miR-129-2 is well known to be frequently reduced by DNA methylation and has anti-tumor effects in various tumors but so far not in RCC. The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical significance and the role of it in RCC.
Methods
The expression levels of miR-129-3p and miR-129-5p, two mature products of miR-129-2, were determined by real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR in 69 cases of paired different kidney tumors and normal tissues and clear cell RCC (ccRCC) cell lines. The roles of them in RCC cells were assessed by functional analyses. Protein expression was detected by Western blot.
Results
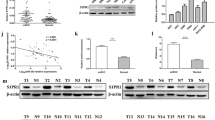
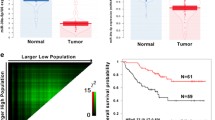
miR-129-3p, but not miR-129-5p, was widely attenuated in human ccRCC, and chromophobe RCC. miR-129-3p could yield 73.5 % accuracy in discriminating ccRCCs from normal tissues. The relative miR-129-3p expression significantly differed between malignant and benign kidney tumors. Importantly, low miR-129-3p levels were associated with short disease-free and overall survival. Ectopic expression of miR-129-3p robustly impaired RCC cell migratory and invasive properties, but had no impact on cell viability and cell cycle distribution. Finally, miR-129-3p decreased multiple metastasis-related genes in RCC cells, including SOX4, phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase and MMP-2/9 expression.
Conclusions
miR-129-3p may act as a promising diagnostic biomarker for discriminating ccRCC from benign tumors and normal tissues and an independent prognostic biomarker in ccRCC. miR-129-3p may exert its anti-metastatic function through modulating multiple targets.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Anwar SL, Albat C, Krech T, Hasemeier B, Schipper E, Schweitzer N, Vogel A, Kreipe H, Lehmann U (2013) Concordant hypermethylation of intergenic microRNA genes in human hepatocellular carcinoma as new diagnostic and prognostic marker. Int J Cancer 133(3):660–670. doi:10.1002/ijc.28068
Bandres E, Agirre X, Bitarte N, Ramirez N, Zarate R, Roman-Gomez J, Prosper F, Garcia-Foncillas J (2009) Epigenetic regulation of microRNA expression in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 125(11):2737–2743. doi:10.1002/ijc.24638
Berkers J, Govaere O, Wolter P, Beuselinck B, Schoffski P, van Kempen LC, Albersen M, Van den Oord J, Roskams T, Swinnen J, Joniau S, Van Poppel H, Lerut E (2013) A possible role for microRNA-141 down-regulation in sunitinib resistant metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma through induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and hypoxia resistance. J Urol 189(5):1930–1938. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2012.11.133
Cao J, Shen Y, Zhu L, Xu Y, Zhou Y, Wu Z, Li Y, Yan X, Zhu X (2012) miR-129-3p controls cilia assembly by regulating CP110 and actin dynamics. Nat Cell Biol 14(7):697–706. doi:10.1038/ncb2512
Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA (2011) A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 331(6024):1559–1564. doi:10.1126/science.1203543
Chen X, Hu H, Guan X, Xiong G, Wang Y, Wang K, Li J, Xu X, Yang K, Bai Y (2012) CpG island methylation status of miRNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 130(7):1607–1613. doi:10.1002/ijc.26171
Chen X, Zhang L, Zhang T, Hao M, Zhang X, Zhang J, Xie Q, Wang Y, Guo M, Zhuang H, Lu F (2013) Methylation-mediated repression of microRNA 129-2 enhances oncogenic SOX4 expression in HCC. Liver Int 33(3):476–486. doi:10.1111/liv.12097
Chen X, Wang X, Ruan A, Han W, Zhao Y, Lu X, Xiao P, Shi H, Wang R, Chen L, Chen S, Du Q, Yang H, Zhang X (2014) miR-141 is a key regulator of renal cell carcinoma proliferation and metastasis by controlling EphA2 expression. Clin Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3224
Cho NH, Shim HS, Rha SY, Kang SH, Hong SH, Choi YD, Hong SJ, Cho SH (2003) Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 correlates with poor prognostic variables in renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol 44(5):560–566
Choueiri TK (2013) Clinical treatment decisions for advanced renal cell cancer. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 11(5 Suppl):694–697
Cohen HT, McGovern FJ (2005) Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 353(23):2477–2490. doi:10.1056/NEJMra043172
Djuranovic S, Nahvi A, Green R (2011) A parsimonious model for gene regulation by miRNAs. Science 331(6017):550–553. doi:10.1126/science.1191138
Dyrskjot L, Ostenfeld MS, Bramsen JB, Silahtaroglu AN, Lamy P, Ramanathan R, Fristrup N, Jensen JL, Andersen CL, Zieger K, Kauppinen S, Ulhoi BP, Kjems J, Borre M, Orntoft TF (2009) Genomic profiling of microRNAs in bladder cancer: miR-129 is associated with poor outcome and promotes cell death in vitro. Cancer Res 69(11):4851–4860. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4043
Edge SB, Compton CC (2010) The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol 17(6):1471–1474. doi:10.1245/s10434-010-0985-4
Esteller M (2008) Epigenetics in cancer. N Engl J Med 358(11):1148–1159. doi:10.1056/NEJMra072067
Gebauer K, Peters I, Dubrowinskaja N, Hennenlotter J, Abbas M, Scherer R, Tezval H, Merseburger AS, Stenzl A, Kuczyk MA, Serth J (2013) Hsa-mir-124-3 CpG island methylation is associated with advanced tumours and disease recurrence of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 108(1):131–138. doi:10.1038/bjc.2012.537
Hildebrandt MA, Gu J, Lin J, Ye Y, Tan W, Tamboli P, Wood CG, Wu X (2010) Hsa-miR-9 methylation status is associated with cancer development and metastatic recurrence in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 29(42):5724–5728. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.305
Huang YW, Liu JC, Deatherage DE, Luo J, Mutch DG, Goodfellow PJ, Miller DS, Huang TH (2009) Epigenetic repression of microRNA-129-2 leads to overexpression of SOX4 oncogene in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res 69(23):9038–9046. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1499
Juan D, Alexe G, Antes T, Liu H, Madabhushi A, Delisi C, Ganesan S, Bhanot G, Liou LS (2010) Identification of a microRNA panel for clear-cell kidney cancer. Urology 75(4):835–841. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2009.10.033
Jung M, Mollenkopf HJ, Grimm C, Wagner I, Albrecht M, Waller T, Pilarsky C, Johannsen M, Stephan C, Lehrach H, Nietfeld W, Rudel T, Jung K, Kristiansen G (2009) MicroRNA profiling of clear cell renal cell cancer identifies a robust signature to define renal malignancy. J Cell Mol Med 13(9B):3918–3928. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00705.x
Kaelin WG Jr (2008) The von Hippel–Lindau tumour suppressor protein: O2 sensing and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 8(11):865–873. doi:10.1038/nrc2502
Kallakury BV, Karikehalli S, Haholu A, Sheehan CE, Azumi N, Ross JS (2001) Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases 1 and 2 correlate with poor prognostic variables in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 7(10):3113–3119
Kang M, Li Y, Liu W, Wang R, Tang A, Hao H, Liu Z, Ou H (2013) miR-129-2 suppresses proliferation and migration of esophageal carcinoma cells through downregulation of SOX4 expression. Int J Mol Med 32(1):51–58. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2013.1384
Li M, Tian L, Wang L, Yao H, Zhang J, Lu J, Sun Y, Gao X, Xiao H, Liu M (2013) Down-regulation of miR-129-5p inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting APC. PLoS One 8(10):e77829. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077829
Liu Y, Hei Y, Shu Q, Dong J, Gao Y, Fu H, Zheng X, Yang G (2012) VCP/p97, down-regulated by microRNA-129-5p, could regulate the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One 7(4):e35800. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035800
Lu CY, Lin KY, Tien MT, Wu CT, Uen YH, Tseng TL (2013) Frequent DNA methylation of MiR-129-2 and its potential clinical implication in hepatocellular carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 52(7):636–643. doi:10.1002/gcc.22059
Mikhaylova O, Stratton Y, Hall D, Kellner E, Ehmer B, Drew AF, Gallo CA, Plas DR, Biesiada J, Meller J, Czyzyk-Krzeska MF (2012) VHL-regulated MiR-204 suppresses tumor growth through inhibition of LC3B-mediated autophagy in renal clear cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell 21(4):532–546. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.019
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik C, Kim ST, Chen I, Bycott PW, Baum CM, Figlin RA (2007) Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356(2):115–124. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa065044
Nakada C, Matsuura K, Tsukamoto Y, Tanigawa M, Yoshimoto T, Narimatsu T, Nguyen LT, Hijiya N, Uchida T, Sato F, Mimata H, Seto M, Moriyama M (2008) Genome-wide microRNA expression profiling in renal cell carcinoma: significant down-regulation of miR-141 and miR-200c. J Pathol 216(4):418–427. doi:10.1002/path.2437
Nakada C, Tsukamoto Y, Matsuura K, Nguyen TL, Hijiya N, Uchida T, Sato F, Mimata H, Seto M, Moriyama M (2011) Overexpression of miR-210, a downstream target of HIF1alpha, causes centrosome amplification in renal carcinoma cells. J Pathol 224(2):280–288. doi:10.1002/path.2860
Protzel C, Maruschke M, Hakenberg OW (2012) Epidemiology, aetiology, and pathogenesis of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol Suppl 11(3):52–59. doi:10.1016/j.eursup.2012.05.002
Rini BI, Atkins MB (2009) Resistance to targeted therapy in renal-cell carcinoma. Lancet Oncol 10(10):992–1000. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70240-2
Seike M, Goto A, Okano T, Bowman ED, Schetter AJ, Horikawa I, Mathe EA, Jen J, Yang P, Sugimura H, Gemma A, Kudoh S, Croce CM, Harris CC (2009) MiR-21 is an EGFR-regulated anti-apoptotic factor in lung cancer in never-smokers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(29):12085–12090. doi:10.1073/pnas.0905234106
Shen R, Pan S, Qi S, Lin X, Cheng S (2010) Epigenetic repression of microRNA-129-2 leads to overexpression of SOX4 in gastric cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394(4):1047–1052. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.121
Tsai KW, Wu CW, Hu LY, Li SC, Liao YL, Lai CH, Kao HW, Fang WL, Huang KH, Chan WC, Lin WC (2011) Epigenetic regulation of miR-34b and miR-129 expression in gastric cancer. Int J Cancer 129(11):2600–2610. doi:10.1002/ijc.25919
Vogt M, Munding J, Gruner M, Liffers ST, Verdoodt B, Hauk J, Steinstraesser L, Tannapfel A, Hermeking H (2011) Frequent concomitant inactivation of miR-34a and miR-34b/c by CpG methylation in colorectal, pancreatic, mammary, ovarian, urothelial, and renal cell carcinomas and soft tissue sarcomas. Virchows Arch 458(3):313–322. doi:10.1007/s00428-010-1030-5
Wang X, Chen X, Wang R, Xiao P, Xu Z, Chen L, Hang W, Ruan A, Yang H, Zhang X (2013) microRNA-200c modulates the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human renal cell carcinoma metastasis. Oncol Rep 30(2):643–650. doi:10.3892/or.2013.2530
Weng L, Wu X, Gao H, Mu B, Li X, Wang JH, Guo C, Jin JM, Chen Z, Covarrubias M, Yuan YC, Weiss LM, Wu H (2010) MicroRNA profiling of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by whole-genome small RNA deep sequencing of paired frozen and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue specimens. J Pathol 222(1):41–51. doi:10.1002/path.2736
Wu J, Qian J, Li C, Kwok L, Cheng F, Liu P, Perdomo C, Kotton D, Vaziri C, Anderlind C, Spira A, Cardoso WV, Lu J (2010) miR-129 regulates cell proliferation by downregulating Cdk6 expression. Cell Cycle 9(9):1809–1818
Yi Z, Fu Y, Zhao S, Zhang X, Ma C (2010) Differential expression of miRNA patterns in renal cell carcinoma and nontumorous tissues. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136(6):855–862. doi:10.1007/s00432-009-0726-x
Young AC, Craven RA, Cohen D, Taylor C, Booth C, Harnden P, Cairns DA, Astuti D, Gregory W, Maher ER, Knowles MA, Joyce A, Selby PJ, Banks RE (2009) Analysis of VHL gene alterations and their relationship to clinical parameters in sporadic conventional renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 15(24):7582–7592. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2131
Zhang X, Jin TG, Yang H, DeWolf WC, Khosravi-Far R, Olumi AF (2004) Persistent c-FLIP(L) expression is necessary and sufficient to maintain resistance to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 64(19):7086–7091. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1498
Zhao X, Guan JL (2011) Focal adhesion kinase and its signaling pathways in cell migration and angiogenesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63(8):610–615. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2010.11.001
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant Nos. 30872924, 81072095 & 81372760), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University from Department of Education of China (NCET-08-0223), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (2012AA021101) to Xiaoping Zhang and the NSFC (Grant Nos. 31070142 & 81272560) to Hongmei Yang.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2014_1690_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplemental Information Fig. S1 No significant correlation between miR-129-3p and tumor size, stage or grade was observed in ccRCC (PDF 128 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Ruan, A., Wang, X. et al. miR-129-3p, as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for renal cell carcinoma, attenuates cell migration and invasion via downregulating multiple metastasis-related genes. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140, 1295–1304 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1690-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1690-7