Abstract
Main conclusion
Soybean chalcone isomerase (CHI) family contains twelve members with unique evolutionary background, expression patterns and is compartmentalized to specific subcellular locations.
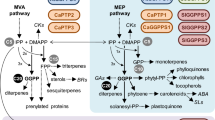
The phenylpropanoid pathway produces a diverse array of plant natural products. A key branch-point enzyme, chalcone isomerase, catalyzes the reaction producing flavanones, the backbone for many downstream metabolites such as flavonoids and isoflavonoids. We have identified twelve soybean GmCHIs that fall into four subfamilies. The study of this family in soybean in the context of various CHIs and CHI-like proteins, across divisions in the plant kingdom and beyond, shows an evolutionary journey from fatty acid-binding proteins (FAPs) to sterically restricted folds that gave rise to the chalcone-to-flavanone isomerase. There are four GmCHIs with this functionality, three of which belong to a legume-specific clade known as ‘type II’ CHIs. Tissue-specific expression of eight core members of the soybean CHI family showed differential temporal and spatial expression, pointing to the potential function of GmCHI1A in seed isoflavonoid production. Promoter analysis of the GmCHIs described the minutiae of sub-organ expression patterns. Subcellular localization of the family was conducted to investigate the possibility of pathway-specific compartmentalization. Subfamilies 1, 2 and 4 localized to the nucleus and cytoplasm, with nuclear localization of CHIs raising questions about alternate function. GmCHI3 isoforms localized to the chloroplast, which, in conjunction with their position on the phylogenetic tree and expression patterns, closely associates them with the FAPs. This study provides the first comprehensive look at soybean CHIs, a family of unique evolutionary background and biochemical function, with the catalytically active members producing the backbone substrate in an important plant metabolic pathway.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Aoki T, Akashi T, Ayabe S (2000) Flavonoids of leguminous plants: structure, biological activity, and biosynthesis. J Plant Res 113:475–488
Bassard JE, Mutterer J, Duval F, Werck-Reichhart D (2012a) A novel method for monitoring the localization of cytochromes P450 and other endoplasmic reticulum membrane associated proteins: a tool for investigating the formation of metabolons. FEBS J 279:1576–1583
Bassard JE, Richert L, Geerinck J, Renault H, Duval F, Ullmann P, Schmitt M, Meyer E, Mutterer J, Boerjan W, De Jaeger G, Mely Y, Goossens A, Werck-Reichhart D (2012b) Protein-protein and protein-membrane associations in the lignin pathway. Plant Cell 24:4465–4482
Bednar RA, Hadcock JR (1988) Purification and characterization of chalcone isomerase from soybeans. J Biol Chem 263:9582–9588
Bosco D, Meda P, Iynedjian PB (2000) Glucokinase and glucokinase regulatory protein: mutual dependence for nuclear localization. Biochem J 348(Pt 1):215–222
Chen AM, Rogan WJ (2004) Isoflavones in soy infant formula: a review of evidence for endocrine and other activity infants. Annu Rev Nutr 24:33–54
Chen H, Seguin P, Archambault A, Constan L, Jabaji S (2009) Gene expression and isoflavone concentrations in soybean sprouts treated with chitosan. Crop Sci 49(1):224–236
Chen H, Seguin P, Jabaji S, Liu W (2011) Spatial distribution of isoflavones and isoflavone-related gene expression in high- and low-isoflavone soybean cultivars. Can J Plant Sci 91:697–705
Cui H, Zhang ST, Yang HJ, Ji H, Wang XJ (2011) Gene expression profile analysis of tobacco leaf trichomes. BMC Plant Biol 11:76
Dhaubhadel S, McGarvey BD, Williams R, Gijzen M (2003) Isoflavonoid biosynthesis and accumulation in developing soybean seeds. Plant Mol Biol 53:733–743
Dhaubhadel S, Gijzen M, Moy P, Farhangkhoee M (2007) Transcriptome analysis reveals a critical role of CHS7 and CHS8 genes for isoflavonoid synthesis in soybean seeds. Plant Physiol 143:326–338
Dhaubhadel S, Farhangkhoee M, Chapman R (2008) Identification and characterisation of isoflavonoid specific glycosyltransferase and malonyltransferase from soybean seeds. J Exp Bot 59:981–994
Dixon RA (2004) Phytooestrogen. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:225–261
Dixon RA, Ferreria D (2002) Genistein. Phytochemistry 60:205–211
Emanuelsson O, Nielsen H, Brunak S, von Heijne G (2000) Predicting subcellular localization of proteins based on their N-terminal amino acid sequence. J Mol Biol 300:1005–1016
Ferguson JA, Mathesius U (2003) Signalling interactions during nodule development. J Plant Growth Regul 22:47–72
Folman Y, Pope GS (1969) Effect of norethisterone acetate, dimethylstilboestrol, genistein and coumestrol on uptake of [3H]oestradiol by uterus, vagina and skeletal muscle of immature mice. J Endocrinol 44:213–218
Fraser LG, Seal AG, Montefiori M, McGhie TK, Tsang GK, Datson PM, Hilario E, Marsh HE, Dunn JK, Hellens RP, Davies KM, McNeilage MA, De Silva HN, Allan AC (2013) An R2R3 MYB transcription factor determines red petal colour in an Actinidia (kiwifruit) hybrid population. BMC Genom 14:28
Gensheimer M, Mushegian A (2004) Chalcone isomerase family and fold: no longer unique to plants. Protein Sci 13:540–544
Jez JM, Noel JP (2002) Reaction mechanism of chalcone isomerase. J Biol Chem 277:1361–1369
Jez JM, Bowman ME, Noel JP (2000) Structure and mechanism of the evolutionarily unique plant enzyme chalcone isomerase. Nat Struc Mol Biol 7:786–791
Jones S, Gonzalez D, Vodkin L (2010) Flux of transcript patterns during soybean seed development. BMC Genom 11:136
Kang JH, McRoberts J, Shi F, Moreno JE, Jones AD, Howe GA (2014) The flavonoid biosynthetic enzyme chalcone isomerase modulates terpenoid production in glandular trichomes of tomato. Plant Physiol 164:1161–1174
Kudou S, Fleury Y, Welt D, Magnolato D, Uchida T, Kitamura K (1991) Malonyl isoflavone glycosides in soybean seeds (Glycine max Merill). Agric Biol Chem 55:2227–2233
Libault M, Thibivilliers S, Bilgin DD, Radwan O, Benitez M, Clough SJ, Stacey G (2008) Identification of four soybean reference genes for gene expression normalization. Plant Gen 1:44–54
Liu CJ, Blount JW, Steele CL, Dixon RA (2002) Bottlenecks for metabolic engineering of isoflavone glycoconjugates in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14578–14583
Livingstone JM, Seguin P, Strömvik MV (2010) An in silico study of the genes for the isoflavonoid pathway enzymes in soybean reveals novel expressed homologues. Can J Plant Sci 90:453–469
Lozovaya VV, Lygin AV, Zernova OV, Li S, Hartman GL, Widholm JM (2004) Isoflavonoid accumulation in soybean hairy roots upon treatment with Fusarium solani. Plant Physiol Biochem 42:671–679
McWilliam H, Li W, Uludag M, Squizzato S, Park YM, Buso N, Cowley AP, Lopez R (2013) Analysis tool web services from the EMBL-EBI. Nucleic Acids Res 41:W597–W600
Morita Y, Takagi K, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Ishiguro K, Tanaka Y, Nitasaka E, Nakayama M, Saito N, Kagami T, Hoshino A, Iida S (2014) A chalcone isomerase-like protein enhances flavonoid production and flower pigmentation. Plant J 78:294–304
Nelson DE, Repetti PP, Adams TR, Creelman RA, Wu J, Warner DC, Anstrom DC, Bensen RJ, Castiglioni PP, Donnarummo MG, Hinchey BS, Kumimoto RW, Maszle DR, Canales RD, Krolikowski KA, Dotson SB, Gutterson N, Ratcliffe OJ, Heard JE (2007) Plant nuclear factor Y (NF-Y) B subunits confer drought tolerance and lead to improved corn yields on water-limited acres. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:16450–16455
Ngaki MN, Louie GV, Philippe RN, Manning G, Pojer F, Bowman ME, Li L, Larsen E, Wurtele ES, Noel JP (2012) Evolution of the chalcone-isomerase fold from fatty-acid binding to stereospecific catalysis. Nature 485:530–533
Phillip DA (1992) Flavonoids:plant signals to soil microbes. In: Stafford HA, Ibrahim RK (eds) Recent advances in phytochemistry:phenolic metabolism in plants. Plenum Press, New York, pp 201–223
Phillips DA, Kapulnik Y (1995) Plant isoflavonoids, pathogens and symbionts. Trends Microbiol 3:58–64
Ralston L, Yu O (2006) Metabolons involving plant cytochrome P450s. Phytochem Rev 5:459–472
Ralston L, Subramanian S, Matsuno M, Yu O (2005) Partial reconstruction of flavonoid and isoflavonoid biosynthesis in yeast using soybean type I and type II chalcone isomerases. Plant Physiol 137:1375–1388
Rasmussen S, Jones C (2013) Potential for producing increased levels of isoflavones in transgenic plants. CAB Reviews: Perspectives in Agriculture, Veterinary Science, Nutrition and Natural Resources 8
Ruuska SA, Girke T, Benning C, Ohlrogge JB (2002) Contrapuntal networks of gene expression during Arabidopsis seed filling. Plant Cell 14:1191–1206
Saslowsky DE, Warek U, Winkel BS (2005) Nuclear localization of flavonoid enzymes in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 280:23735–23740
Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J, Ma J, Mitros T, Nelson W, Hyten DL, Song Q, Thelen JJ, Cheng J, Xu D, Hellsten U, May GD, Yu Y, Sakurai T, Umezawa T, Bhattacharyya MK, Sandhu D, Valliyodan B, Lindquist E, Peto M, Grant D, Shu S, Goodstein D, Barry K, Futrell-Griggs M, Abernathy B, Du J, Tian Z, Zhu L, Gill N, Joshi T, Libault M, Sethuraman A, Zhang XC, Shinozaki K, Nguyen HT, Wing RA, Cregan P, Specht J, Grimwood J, Rokhsar D, Stacey G, Shoemaker RC, Jackson SA (2010) Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 463:178–183
Shih C, Chen Y, Wang M, Chu IK, Lo C (2008) Accumulation of isoflavone genistin in transgenic tomato plants overexpressing a soybean isoflavone synthase gene. J Agric Food Chem 56:5655–5661
Shirley BW, Kubasek WL, Storz G, Bruggemann E, Koornneef M, Ausubel FM, Goodman HM (1995) Analysis of Arabidopsis mutants deficient in flavonoid biosynthesis. Plant J 8:659–671
Sparkes IA, Runions J, Kearns A, Hawes C (2006) Rapid, transient expression of fluorescent fusion proteins in tobacco plants and generation of stably transformed plants. Nat Protoc 1:2019–2025
Sreevidya VS, Rao CS, Sullia SB, Ladha JK, Reddy PM (2006) Metabolic engineering of rice with soybean isoflavone synthase for promoting nodulation gene expression in rhizobia. J Exp Bot 57:1957–1969
Stafford HA (1997) Roles of flavonoids in symbiotic and defense functions in legume roots. Bot Rev 63:27–39
Stangeland B, Salehian Z (2002) An improved clearing method for GUS assay in Arabidopsis endosperm and seeds. Plant Mol Biol Rep 20:107–114
Stothard P (2000) The sequence manipulation suite: JavaScript programs for analyzing and formatting protein and DNA sequences. Biotechniques 28:1102–1104
Subramanian S, Graham MA, Yu O, Graham TL (2005) RNA interference of soybean isoflavone synthase genes leads to silencing in tissues distal to the transformation site and to enhanced susceptibility to Phytophthora sojae. Plant Physiol 137:1345–1353
Subramanian S, Stacey G, Yu O (2006) Endogenous isoflavones are essential for the establishment of symbiosis between soybean and Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Plant J 48:261–273
Tamura K, Hara-Nishimura I (2013) The molecular architecture of the plant nuclear pore complex. J Exp Bot 64:823–832
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Valkama E, Salminen JP, Koricheva J, Pihlaja K (2004) Changes in leaf trichomes and epicuticular flavonoids during leaf development in three birch taxa. Ann Bot 94:233–242
Wang CS, Vodkin LO (1994) Extraction of RNA from tissues containing high levels of procyanidins that bind RNA. Plant Mol Biol 12:132–145
Weis K (2003) Regulating access to the genome: nucleocytoplasmic transport throughout the cell cycle. Cell 112:441–451
Winkel BSJ (2004) Metabolic channeling in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:85–107
Winkel-Shirley B (2001) It takes a garden. How work on diverse plant species has contributed to an understanding of flavonoid metabolism. Plant Physiol 127:1399–1404
Yu XH, Chen MH, Liu CJ (2008) Nucleocytoplasmic-localized acyltransferases catalyze the malonylation of 7-O-glycosidic (iso)flavones in Medicago truncatula. Plant J 55:382–396
Zhang X, Henriques R, Lin SS, Niu QW, Chua NH (2006) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana using the floral dip method. Nat Protoc 1:641–646
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Rima Menassa (Agriculture Canada, London) for eGFP pure protein, Ling Chen, Patrick Chapman and Alex Molnar (Agriculture Canada, London) for technical assistance. This research was supported by Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada’s Abase and Genomics Research and Development Initiative grants to SD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
425_2014_2200_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. S1 Co-localization of GmCHI-YFP and organelle markers fused with CFP. (a) GmCHI1A and NLS-CFP, (b) GmCHI1B1 and NLS-CFP, (c) GmCHI1B2 and NLS-CFP, (d) GmCHI2 and NLS-CFP, (e) GmCHI3A1 and PLS-CFP, (f) GmCHI3A2 and PLS-CFP, (g) GmCHI4A and NLS-CFP, and (h) GmCHI4B and NLS-CFP. YFP, yellow fluorescent protein; CFP, cyan fluorescent protein; NLS, nuclear localization signal; PLS, plastid localization signal. Scale bar indicates 40 µm (TIFF 7100 kb)
425_2014_2200_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. S2 Subcellular localization of GmCHIs in soybean hairy roots. Constructs containing translational fusion of GmCHI-YFP were transformed into A. rhizogenes strain K599, and used in the hairy root transformation of soybean cotyledons. Confocal microscopy was used to detect expression after the emergence of hairy roots. (a) GmCHI1A, (b) GmCHI1B1, (c) GmCHI1B2, (d) GmCHI2, (e) GmCHI3A1, (f) GmCHI3A2, (g) GmCHI4A, and (h) GmCHI4B. Scale bar indicates 40 µm (TIFF 5569 kb)
425_2014_2200_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. S3 Western blot analysis of GmCHI-YFP proteins. Constructs containing translational fusions of GmCHI-YFP were transiently expressed in N. benthamiana leaves. Total soluble proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred into PVDF membrane by electroblotting. Fusion proteins were detected by sequential incubation of the blot with anti-GFP antibody and anti-rabbit IgG conjugated with horseradish peroxidase, followed by chemiluminescent reaction. eGFP fused with hydrophobin (~ 37 kDa) used as a control. All GmCHI-YFP (~ 50 kDa) appear as a single band indicating no cleavage of YFP tag. Supplementary Table 1 Sequences of oligonucleotides used in the study (TIFF 998 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dastmalchi, M., Dhaubhadel, S. Soybean chalcone isomerase: evolution of the fold, and the differential expression and localization of the gene family. Planta 241, 507–523 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-014-2200-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-014-2200-5