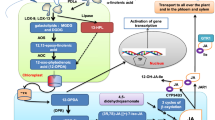
Abstract
Studies of abscisic acid (ABA) and auxin have revealed that these pathways impinge on each other. The Daucus carota (L.) Dc3 promoter: uidA (β-glucuronidase: GUS) chimaeric reporter (ProDc3:GUS) is induced by ABA, osmoticum, and the auxin indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) in vegetative tissues of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Here, we describe the root tissue-specific expression of ProDc3:GUS in the ABA-insensitive-2 (abi2-1), auxin-insensitive-1 (aux1), auxin-resistant-4 (axr4), and rooty (rty1) mutants of Arabidopsis in response to ABA, IAA and synthetic auxins naphthalene acetic acid (NAA), and 2, 4-(dichlorophenoxy) acetic acid. Quantitative analysis of ProDc3:GUS expression showed that the abi2-1 mutant had reduced GUS activity in response to ABA, IAA, or 2, 4-d, but not to NAA. Similarly, chromogenic staining of ProDc3:GUS activity showed that the aux1 and axr4 mutants gave predictable hypomorphic ProDc3:GUS expression phenotypes in roots treated with IAA or 2, 4-d, but not the diffusible auxin NAA. Likewise the rty mutant, which accumulates auxin, showed elevated ProDc3:GUS expression in the absence or presence of hormones relative to wild type. Interestingly, the aux1 and axr4 mutants showed a hypomorphic effect on ABA-inducible ProDc3:GUS expression, demonstrating that ABA and IAA signaling pathways interact in roots. Possible mechanisms of crosstalk between ABA and auxin signaling are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- ABI:
-
ABA-insensitive
- AREBs=ABFs:
-
ABA-Response Element Binding Factors
- ARFs:
-
Auxin-responsive factors
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- IAA:
-
Indole-3-acetic acid
- IBA:
-
Indole-3-butyric acid
- GUS:
-
β-glucuronidase (uidA)
- 2, 4-D:
-
2, 4-(dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid
- DPBFs:
-
Dc3 Promoter Binding Factors
- LEA:
-
Late-Embryogenesis-Abundant
- NAA:
-
Naphthalene acetic acid
- 4-MU:
-
4-methylumbelliferone
- The 1.5 kbp promoter of Dc3 :
-
ProDc3
References
Bartel B, Bartel, DP (2003) MicroRNAs: at the root of plant development? Plant Physiol 132:709–717
Bennett M, Marchant A, Green HG, May ST, Ward SP, Millner PA, Walker AR, Schulz B, Feldmann KA (1996) Arabidopsis AUX1 gene: a permease-like regulator of root gravitropism. Science 273:948–950
Bhalerao RP, Salchert K, Bakó L, Ökrész L, Szabados L, Muranaka T, Machida Y, Schell J, Koncz C (1999) Interaction of PRL1 WD protein with Arabidopsis SNF1-like protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:5322–5327
Boerjan W, Cervera M, Delarue M, Beeckman T, Dewitte W, Bellini C, Caboche M, Onckelen HV, Van Montagu M, Inze D (1995) Superroot, a recessive mutation in Arabidopsis, confers auxin overproduction. Plant Cell 7:1405–1419
Boonsirichai K, Guan C, Chen R, Masson PH (2002) Root gravitropism: an experimental tool to investigate basic cellular and molecular processes underlying mechanosensing and signal transmission in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:421–447
Brady SM, Sarkar SF, Bonetta D, McCourt P (2003) The Abscisic Acid Insensitive 3 (ABI3) gene is modulated by farnesylation and is involved in auxin signaling and lateral root development in Arabidopsis. Plant J 34:67–75
Carrington JC, Ambros V (2003) Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science 301:336–338
Casimiro I, Beeckman T, Graham N, Bhalerao R, Zhang HM, Casero P, Sandberg G, Bennett MJ (2003) Dissecting Arabidopsis lateral root development. Trends Plant Sci 8:165–171
Chak RKF, Thomas TL, Quatrano RS, Rock CD (2000) The genes ABI1 and ABI2 are involved in abscisic acid- and drought-inducible expression of the Daucus carota L. Dc3 promoter in guard cells of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana L. Heynh. Planta 210:875–883
Chinnusamy V, Schumaker K, Zhu JK (2004) Molecular genetic perspectives on cross-talk and specificity in abiotic stress signalling in plants. J Exper Bot 55:225–236
Delbarre A, Muller P, Imhoff V, Guern J (1996) Comparison of mechanisms controlling uptake and accumulation of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid, naphthalene-1-acetic acid, and indole-3-acetic acid in suspension-cultured tobacco cells. Planta 198: 532–541
DeLong A, Mockaitis K, Christensen S (2002) Protein phosphorylation in the delivery of and response to auxin signals. Plant Mol Biol 49:285–303
Dharmasiri N, Estelle M (2004) Auxin signaling and regulated protein degradation. Trends Plant Sci 9:302–308
Ephritikhine G, Fellner M, Vannini C, Lapous D, Barbier-Brygoo H (1999) The sax1 dwarf mutant of Arabidopsis shows altered sensitivity of growth responses to ABA, auxin, gibberellins and ethylene and is partially rescued by exogenous brassinosteroid. Plant J 18:303–314
Finkelstein RR, Gibson SI (2002) ABA and sugar interactions regulating development: “cross-talk” or “voices in a crowd”? Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:26–32
Finkelstein R, Lynch T (2000) ABI5 encodes a basic leucine zipper transcription factor. Plant Cell 12: 599–609
Finkelstein RR, Rock CD (2002) Abscisic acid biosynthesis and response (48 pp.) In: EM Meyerowitz and CR Somerville (eds) Arabidopsis, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, New York See http://www.bioone.org/bioone/?request=get-toc&issn=1543–8120
Friml J, Wisniewska J, Benkova E, Mendgen K, Palme K (2002) Lateral relocation of auxin efflux regulator PIN3 mediates tropism in Arabidopsis. Nature 415:806–809
Friml J, Vieten A, Sauer M, Weijers D, Schwarz H, Hamann T, Offringa R, Jurgens G (2003) Efflux–dependent auxin gradients establish the apical-basal axis of Arabidopsis. Nature 426:147–153
Gopalraj M, Tseng T-S, Olszewski N (1996) The rooty gene of Arabidopsis encodes a protein with highest similarity to aminotransferases. Plant Physiol 111:S-469
Hagen G, Guilfoyle TJ, Gray WM (2004) Auxin signal transduction. In: Davies P (ed) Plant hormones-biosynthesis, signal transduction, action!. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 282–303
Han M-H, Goud S, Song L, Fedoroff N (2004) The Arabidopsis double-stranded RNA-binding protein HYL1 plays a role in microRNA-mediated gene regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1093–1098
Himmelbach A, Iten M, Grill E (1998) Signalling of abscisic acid to regulate plant growth. Phil Trans R Soc Lond 353:1439–1444
Hobbie L, Estelle M (1995) The axr4 auxin-resistant mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana defines a gene important for root gravitropsim and lateral root initiation. Plant J 7:211–220
Kim SY, Ma JZ, Perret P, Li Z, Thomas TL (2002) Arabidopsis ABI5 sub-family members have distinct DNA-binding and transcriptional activities. Plant Physiol 130:688–697
Kim S, Kang J-Y, Cho D-I, Park JH, Kim SY (2004) ABF2, an ABRE-binding bZIP factor is an essential component of glucose signaling and its overexpression affects multiple stress tolerance. Plant J 40:75–87
King JJ, Stimart DP, Fisher RH, Bleecker AB (1995) A mutation altering auxin homeostasis and plant morphology in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 7:2023–2037
Koiwai H, Nakaminami K, Seo M, Mitsuhashi W, Toyomasu T, Koshiba T (2004) Tissue-specific localization of an abscisic acid biosynthetic enzyme, AAO3, in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 134:1697–1707
Leung J, Merlot S, Giraudat J (1997) The Arabidopsis ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE2 (ABI2) and ABI1 genes encode homologous protein phosphatases 2C involved in abscisic acid signal transduction. Plant Cell 9: 759–771
Li Y, Wu YH, Hagen G, Guilfoyle T (1999) Expression of the auxin-inducible GH3 Promoter GUS fusion gene as a useful molecular marker for auxin physiology. Plant Cell Physiol 40:675–682
Liscum E, Reed JW (2002) Genetics of Aux/IAA and ARF action in plant growth and development. Plant Mol Biol 49:387–400
Lu C, Fedoroff N (2000) A mutation in the arabidopsis HYL1 gene encoding a dsRNA binding protein affects responses to abscisic acid, auxin, and cytokinin. Plant Cell 12:2351–2365
Maher E, Martindale S (1980) Mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana with altered responses to auxin and gravity. Biochem Genet 18:1041–1053
Marchant A, Kargul J, May S, Muller P, Delbarre A, Perrot-Rechenmann C, Bennett M (1999) AUX1 regulates root gravitropism in Arabidopsis by facilitating auxin uptake within root apical tissues. EMBO J 18:2066–2073
McCarty DR, Chory J (2000) Conservation and innovation in plant signaling pathways. Cell 103:201–209
McCourt P (1999) Genetic analysis of hormone signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol Plant Mol Biol 50:219–243
Moller SG, Chua NH (1999) Interactions and intersections of plant signaling pathways. J Mol Biol 293:219–234
Monroe-Augustus M, Zolman BK, Bartel B (2003) IBR5, a dual-specificity phosphatase-like protein modulating auxin and abscisic acid responsiveness in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:2979–2991
Nagpal P, Walker LM, Young JC, Sonawala A, Timpte C, Estelle M, Reed JW (2000) AXR2 encodes a member of the Aux/IAA protein family. Plant Physiol 123:563–573
Oono Y, Chen QG, Overvoorde PJ, Kohler C, Theologis A (1998) age Mutants of Arabidopsis exhibit altered auxin-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 10:1649–1662
Ottenschlager I, Wolff P, Wolverton C, Bhalerao RP, Sandberg G, Ishikawa H, Evans M, Palme K (2003) Gravity-regulated differential auxin transport from columella to lateral root cap cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 2987–2991
Park W, Li J, Song R, Messing J, Chen X (2002) Carpel Factory, a Dicer homolog, and HEN1, a novel protein, act in microRNA metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Biol 12:1484–1495
Pickett FB, Wilson AK, Estelle M (1990) The aux1 mutation of Arabidopsis confers both auxin and ethylene resistance. Plant Physiol 94:1462–1466
Poupart J, Waddell C (2000) The rib1 mutant is resistant to indole-3-butyric acid, an endogenous auxin in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 124:1739–1751
Reinhardt D, Pesce ER, Stieger P, Mandel T, Baltensperger K, Bennett M, Traas J, Friml J, Kuhlemeier C (2003) Regulation of phyllotaxis by polar auxin transport. Nature 426:255–260
Rhoades M, Reinhart B, Lim L, Burge C, Bartel B, Bartel D (2002) Prediction of plant microRNA targets. Cell 110:513–520
Rock CD (2000) Pathways to abscisic acid-regulated gene expression. New Phytol 148:357–396
Rodriguez P, Benning G, Grill E (1998) ABI2, a second protein phosphatase 2C involved in ABA signal transduction in Arabidopsis. FEBS Lett 421:185–190
Rogg LE, Lasswell J, Bartel B (2001) A gain-of-function mutation in IAA28 suppresses lateral root development. Plant Cell 13:465–480
Schnall JA, Quatrano RS (1992) Abscisic acid elicits the water-stress response in root hairs of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 100:216–218
Scholl R, Rivero-Lepinckas L, Crist D (1998) Growth of plants and preservation of seeds. In: Martínez-Zapater JM, Salinas J (Eds) Arabidopsis protocols. Humana, Totowa, pp 1–12.
Siddiqui NU, Chung HJ, Thomas TL, Drew MC (1998) Abscisic acid-dependent and–independent expression of the carrot late-embryogenesis-abundant class gene Dc3 in transgenic tobacco seedlings. Plant Physiol 118:1181–1190
Simmons C, Migliaccio F, Masson P, Caspar T, Söll D (1995) A novel root gravitropism mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana exhibiting altered auxin physiology. Physiol Plant 93:790–798
Subramanian S, Rajagopal B, Rock CD (2002) Harlequin (hlq) and short blue root (sbr), two Arabidopsis mutants that ectopically express an ABA- and auxin-inducible transgenic carrot promoter and have pleiotropic effects on morphogenesis. Plant Mol Biol 49:93–105
Sun X (2003) Characterization of an auxin- and abscisic acid-inducible reporter gene: Dc3-GUS in reported auxin mutants, and mutant screening based on auxin-responsive Dc3-GUS expression. M.Phil. Dissertation. Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, 99 pp
Sunkar R, Zhu JK (2004) Novel and stress-regulated microRNAs and other small RNAs from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:2001–2019
Suzuki M, Kao C-Y, Cocciolone S, McCarty DR (2001) Maize VP1 complements Arabidopsis abi3 and confers a novel ABA/auxin interaction in roots. Plant J 28: 409–418
Takahashi N, Goto N, Okada K, Takahashi H (2002) Hydrotropism in abscisic acid, wavy, and gravitropic mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 216:203–211
Thomas T, Chung HJ, Nunberg AN (1997) ABA signalling in plant development and growth. In: Aducci P (ed) Signal transduction in plants. Birkhauser, Basel, pp 23–43
Timpte C, Lincoln C, Pickett FB, Turner J, Estelle M (1995) The AXR1 and AUX1 genes of Arabidopsis function in separate auxin-response pathways. Plant J 8:561–569
Tiwari SB, Hagen G, Guilfoyle T (2003) The roles of auxin response factor domains in auxin-responsive transcription. Plant Cell 15:533–543
Trewavas A (1992) What remains of the Cholodny-Went theory? Plant Cell Environ 15:759–794
Uno Y, Furihata T, Abe H, Yoshida R, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2000) Arabidopsis bZIP transcription factors involved in an abscisic acid-dependent signal transduction pathway under drought and high-salinity conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11632–11637
Vazquez F, Vaucheret H, Rajagopalan R, Lepers C, Gasciolli V, Mallory AC, Hilbert JL, Bartel DP, Crete P (2004) Endogenous trans-acting siRNAs regulate the accumulation of Arabidopsis mRNAs. Mol Cell 16:69–79
Walton DC (1980) Biochemistry and physiology of abscisic acid. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 31:453–489
Wilson A, Pickett F, Turner J, Estelle M (1990) A dominant mutation in Arabidopsis confers resistance to auxin, ethylene and abscisic acid. Mol Gen Genet 222:377–383
Yamamoto M, Yamamoto K (1999) Effects of natural and synthetic auxins on the gravitropic growth habit of roots in two auxin-resistant mutants of Arabidopsis, axr1 and axr4: evidence for defects in the auxin influx mechanism of axr4. J Plant Res 112:31–396
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Terry Thomas, Texas A&M University, for the gift of ProDc3:GUS transgenic Arabidopsis, the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments, and Kevin Lee, HKUST, for encouragement. This work was funded by Hong Kong Government CERG HKUST 6134/99M and a 2003 Research Enhancement Fund grant from the Texas Tech University Institute for University Research to C.D.R.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rock, C.D., Sun, X. Crosstalk between ABA and auxin signaling pathways in roots of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh.. Planta 222, 98–106 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-1521-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-1521-9