Abstract
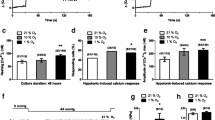
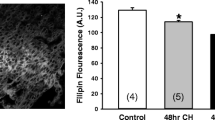
5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a potent pulmonary vasoconstrictor and mitogenic agent whose concentration increases in pulmonary hypertensive patients. Chronic hypoxia induces selective pulmonary arterial hypertension; therefore, we investigated chronic hypoxia effect on the calcium and contractile responses to 5-HT focusing on voltage-independent calcium influx in rat intrapulmonary arteries. Chronic hypoxia, induced by introducing rats in a hypobaric chamber for 3 weeks, potentiated the contraction to 5-HT and this effect was insensitive to nitrendipine. Calcium signal to 5-HT was characterized by a transient followed by a sustained phase in both normoxia and chronic hypoxia. The sustained phase was dependent on extracellular calcium and inhibited by lanthanum. RHC 80267, a specific inhibitor of diacylglycerol lipase, reduced the 5-HT-induced calcium influx in chronic hypoxia but not in normoxia. Furthermore, unlike gadolinium, RHC 80267 inhibited more the contraction to 5-HT in chronic hypoxia. Despite the apparent role of voltage-independent calcium channels in chronic hypoxia, Western blot and flow cytometry analyses demonstrated no variations in TRPC6 expression. This study shows for the first time that the 5-HT-induced calcium and contractile signals in chronic hypoxia are more dependent on a voltage-independent, RHC 80267-sensitive calcium influx and the hyperreactivity to 5-HT may thus be explained by this influx.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert AP, Large WA (2006) Signal transduction pathways and gating mechanisms of native TRP-like cation channels in vascular myocytes. J Physiol 570:45–51
Archer SL, Huang JM, Reeve HL, Hampl V, Tolarova S, Michelakis E, Weir EK (1996) Differential distribution of electrophysiologically distinct myocytes in conduit and resistance arteries determines their response to nitric oxide and hypoxia. Circ Res 78:431–442
Bonnet S, Belus A, Hyvelin JM, Roux E, Marthan R, Savineau JP (2001) Effect of chronic hypoxia on agonist-induced tone and calcium signaling in rat pulmonary artery. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 281:L193–L201
Figueroa XF, Isakson BE, Duling BR (2004) Connexins: gaps in our knowledge of vascular function. Physiology (Bethesda) 19:277–284
Guibert C, Marthan R, Savineau JP (2004) 5-HT induces an arachidonic acid-sensitive calcium influx in rat small intrapulmonary artery. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 286:L1228–L1236
Guibert C, Savineau JP, Crevel H, Marthan R, Rousseau E (2005) Effect of short-term organoid culture on the pharmaco-mechanical properties of rat extra- and intrapulmonary arteries. Br J Pharmacol 146:692–701
Humbert M, Sitbon O, Simonneau G (2004) Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med 351:1425–1436
Inoue R, Okada T, Onoue H, Hara Y, Shimizu S, Naitoh S, Ito Y, Mori Y (2001) The transient receptor potential protein homologue TRP6 is the essential component of vascular alpha(1)-adrenoceptor-activated Ca(2+)-permeable cation channel. Circ Res 88:325–332
Jernigan NL, Broughton BR, Walker BR, Resta TC (2006) Impaired NO-dependent inhibition of store- and receptor-operated calcium entry in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle after chronic hypoxia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 290:L517–L525
Keegan A, Morecroft I, Smillie D, Hicks MN, MacLean MR (2001) Contribution of the 5-HT(1B) receptor to hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension: converging evidence using 5-HT(1B)-receptor knockout mice and the 5-HT(1B/1D)-receptor antagonist GR127935. Circ Res 89:1231–1239
Kereveur A, Callebert J, Humbert M, Herve P, Simonneau G, Launay JM, Drouet L (2000) High plasma serotonin levels in primary pulmonary hypertension. Effect of long-term epoprostenol (prostacyclin) therapy. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:2233–2239
Konrad RJ, Major CD, Wolf BA (1994) Diacylglycerol hydrolysis to arachidonic acid is necessary for insulin secretion from isolated pancreatic islets: sequential actions of diacylglycerol and monoacylglycerol lipases. Biochemistry 33:13284–13294
Lin MJ, Leung GP, Zhang WM, Yang XR, Yip KP, Tse CM, Sham JS (2004) Chronic hypoxia-induced upregulation of store-operated and receptor-operated Ca2+ channels in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells: a novel mechanism of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res 95:496–505
MacLean MR, Sweeney G, Baird M, McCulloch KM, Houslay M, Morecroft I (1996) 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptors mediating vasoconstriction in pulmonary arteries from control and pulmonary hypertensive rats. Br J Pharmacol 119:917–930
Mandegar M, Fung YC, Huang W, Remillard CV, Rubin LJ, Yuan JX (2004) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pulmonary vascular remodeling: role in the development of pulmonary hypertension. Microvasc Res 68:75–103
Marcos E, Fadel E, Sanchez O, Humbert M, Dartevelle P, Simonneau G, Hamon M, Adnot S, Eddahibi S (2004) Serotonin-induced smooth muscle hyperplasia in various forms of human pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res 94:1263–1270
Pedersen SF, Owsianik G, Nilius B (2005) TRP channels: an overview. Cell Calcium 38:233–252
Robertson TP, Hague D, Aaronson PI, Ward JP (2000) Voltage-independent calcium entry in hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction of intrapulmonary arteries of the rat. J Physiol 525(Pt 3):669–680
Shimoda LA, Sham JS, Shimoda TH, Sylvester JT (2000) L-type Ca(2+) channels, resting [Ca(2+)](i), and ET-1-induced responses in chronically hypoxic pulmonary myocytes. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 279:L884–L894
Shuttleworth TJ, Thompson JL, Mignen O (2004) ARC channels: a novel pathway for receptor-activated calcium entry. Physiology (Bethesda) 19:355–361
Weigand L, Sylvester JT, Shimoda LA (2006) Mechanisms of endothelin-1-induced contraction in pulmonary arteries from chronically hypoxic rats. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 290:L284–L290
Yu Y, Fantozzi I, Remillard CV, Landsberg JW, Kunichika N, Platoshyn O, Tigno DD, Thistlethwaite PA, Rubin LJ, Yuan JX (2004) Enhanced expression of transient receptor potential channels in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13861–13866
Yuan XJ, Bright RT, Aldinger AM, Rubin LJ (1997) Nitric oxide inhibits serotonin-induced calcium release in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol 272:L44–L50
Acknowledgements
We thank Huguette Crevel for her technical assistance and Thomas Trian for his help in performing FACS analysis. This work was supported by the Conseil Régional d’Aquitaine (200220301301A) and the Fondation de France (2006005603) and Lise Rodat was funded by the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM- M. Josso).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodat, L., Savineau, JP., Marthan, R. et al. Effect of chronic hypoxia on voltage-independent calcium influx activated by 5-HT in rat intrapulmonary arteries. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 454, 41–51 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-006-0178-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-006-0178-y