Abstract
Background and aims
Colonoscopic complications are not frequent. Cases with colon perforations without the presence of pneumoperitoneum are very rare, and those with the development of tension pneumothorax are even rarer. The aim of this article was to present a unique case of the colon perforation during colonoscopic polypectomy.
Case report
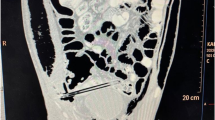
We report a unique case of the colon perforation made between the two layers of the sigmoid mesocolon during colonoscopic polypectomy. The colon perforation had not been recognized during colonoscopic polypectomy, but the patient stayed at the hospital to be observed for the possible remitted bleeding after polypectomy. The colon perforation was followed by the development of the left-sided tension pneumothorax with massive mediastinum tending to move to the right, pneumoretroperitoneum, subcutaneous emphysema of the head, neck, and body, but without pneumoperitoneum. Tube drainage of the left pleural cavity was performed with release a great amount of air under pressure and then an urgent laparotomy when there was no free gas in the peritoneal cavity. After mobilizing the sigmoid colon, pneumoretroperitoneum and sigmoid colon perforation of 1.5 mm in diameter between two mesosigmoid layers were discovered. Partial sigmoidectomy was performed. A pathohistological examination verified a deepithelized area of 12 mm and a perforation of 1.5-mm diameter. The patient was dismissed as recovered 7 days after.
Conclusion
The patient was well prepared for colonoscopy, without other general diseases, and operated on quickly after the perforation (within 2 h from the perforation), without any significant retroperitoneum contamination. These are the factors for a favorable outcome of the treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zeno BR, Sahn SA (2006) Colonoscopy-associated pneumothorax: a case of tension pneumothorax and review of the literature. Am J Med Sci 332(3):153–155
Ball CG, Kirkpatrick AW, Mackenzie S, Bagshaw SM, Peets AD, Temple WJ, Boiteau P (2006) Tension pneumothorax secondary to colonic perforation during diagnostic colonoscopy: report of a case. Surg Today 36(5):478–480
Cordoba Lopez A, Bueno Alvarez-Arenas MI, Alzugaray Fraga RJ, Veiga Gonzalez MD, Corcho Sanchez G (1997) Tension pneumothorax as a complication of colonoscopy. Gastroenterol Hepatol 20(10):494–496
Baumann UA, Mettler M (1999) Diagnosis and hazards of unexpected diaphragmatic hernias during colonoscopy: report of two cases. Endoscopy 31(3):274–276
Hearnshaw SA, Oppong K, Jaques B, Thompson NP (2004) Tension pneumothorax as a complication of colonoscopy. Endoscopy 36(2):190
Lovisetto F, Zonta S, Rota E, Mazzilli M, Faillace G, Bianca A, Fantini A, Longoni M (2007) Left pneumothorax secondary to colonoscopic perforation of the sigmoid colon: a case report. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 17(1):62–64
Saitz R. Serious complications of colonoscopy are not rare. Journal Watch General Medicine January 16, 2007. Available from: URL: http://general-medicine.jwatch.org/cgi/content/full/2007/116/1?q=etoc
Levin TR, Zhao W, Conell C, Seeff LC, Manninen DL, Shapiro JA, Schulman J (2006) Complications of colonoscopy in an integrated health care delivery system. Ann Intern Med 145(12):880–886
Anderson ML, Pasha TM, Leighton JA (2000) Endoscopic perforation of the colon: lessons from a 10-year study. Am J Gastroenterol 95(12):3418–3422
Damore LJ 2nd, Rantis PC, Vernava AM 3rd, Longo WE (1996) Colonoscopic perforations. Etiology, diagnosis, and management. Dis Colon Rectum 39(11):1308–1314
Heldwein W, Dollhopf M, Rosch T, Meining A, Schmidtsdorff G, Hasford J, Hermanek P, Burlefinger R, Birkner B, Schmitt W (2005) The Munich Polypectomy Study (MUPS): prospective analysis of complications and risk factors in 4000 colonic snare polypectomies. Endoscopy 37(11):1116–1122
Tulchinsky H, Madhala-Givon O, Wasserberg N, Lelcuk S, Niv Y (2006) Incidence and management of colonoscopic perforations: 8 years’ experience. World J Gastroenterol 12(26):4211–4213
Webb WA, McDaniel L, Jones L (1985) Experience with 1000 colonoscopic polypectomies. Ann Surg 201(5):626–32
Cobb WS, Heniford BT, Sigmon LB, Hasan R, Simms C, Kercher KW, Matthews BD (2004) Colonoscopic perforations: incidence, management, and outcomes. Am Surg 70(9):750–758
Araghizadeh FY, Timmcke AE, Opelka FG, Hicks TC, Beck DE (2001) Colonoscopic perforations. Dis Colon Rectum 44(5):713–716
Ettersperger L, Zeitoun P, Thiefin G (1995) Colonic perforations complicating colonoscopy. Apropos of 15 consecutive cases observed over 16 years. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 19(12):1018–1022
Gatto NM, Frucht H, Sundararajan V, Jacobson JS, Grann VR, Neugut AI (2003) Risk of perforation after colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy: a population-based study. J Natl Cancer Inst 95(3):230–236
Viiala CH, Zimmerman M, Cullen DJ, Hoffman NE (2003) Complication rates of colonoscopy in an Australian teaching hospital environment. Intern Med J 33(8):355–359
Orsoni P, Berdah S, Verrier C, Caamano A, Sastre B, Boutboul R, Grimaud JC, Picaud R (1997) Colonic perforation due to colonoscopy: a retrospective study of 48 cases. Endoscopy 29(3):160–164
Iqbal CW, Chun YS, Farley DR (2005) Colonoscopic perforations: a retrospective review. J Gastrointest Surg 9(9):1229–1236
Garbay JR, Suc B, Rotman N, Fourtanier G, Escat J (1996) Multicentre study of surgical complications of colonoscopy. Br J Surg 83(1):42–44
Freitag M, Albert W, Petersen S, Ludwig K (2000) Iatrogenic colon perforation from the viewpoint of the surgeon. Experiences with 11 patients. Chirurg 71(5):568–571
Ludvik P, Kricka M (2005) Laparoscopy-assisted colonoscopic polypectomias. Rozhl Chir 84(4):191–192
Ho HC, Burchell S, Morris P, Yu M (1996) Colon perforation, bilateral pneumothoraces, pneumopericardium, pneumomediastinum, and subcutaneous emphysema complicating endoscopic polypectomy: anatomic and management considerations. Am Surg 62(9):770–774
Clements RH, Jordan LM, Webb WA (2000) Critical decisions in the management of endoscopic perforations of the colon. Am Surg 66(1):91–93
Christie JP, Marrazzo J, (1992) “Mini-perforation” of the colon—not all postpolypectomy perforations require laparotomy. Dis Colon Rectum 34(2):132–135
Pretre R, Robert J, Mirescu D, Witzig JA, Rohner A (1993) Pathophysiology, recognition and management of pneumoretroperitoneum. Br J Surg 80(9):1138–1140
Goerg KJ, Duber C (1996) Retroperitoneal, mediastinal and subcutaneous emphysema with pneumothorax after colonoscopy. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 121(21):693–696
Ota H, Fujita S, Nakamura T, Tanaka S, Tono T, Murata Y, Tanaka N, Okajima S (2003) Pneumoretroperitoneum, pneumomediastinum, pneumopericardium, and subcutaneous emphysema complicating sigmoidoscopy: report of a case. Surg Today 33(4):305–308
Cirt N, de Lajarte-Thirouard AS, Olivie D, Pagenault M, Bretagne JF (2006) Subcutaneous emphysema, pneumomediastinum, pneumoperitoneum and retropneumoperitoneum following a colonoscopy with mucosectomy. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 30(5):779–782
Webb T (1998) Pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum during colonoscopy. Anaesth Intensive Care 26(3):302–304
Tam WC, Pollard I, Johnson RD (1996) Case report: pneumomediastinum and pneumothorax complicating colonoscopy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(8):789–792
Schmidt G, Borsch G, Wegener M (1986) Subcutaneous emphysema and pneumothorax complicating diagnostic colonoscopy. Dis Colon Rectum 29(2):136–138
Fu KI, Sano Y, Kato S, Fujii T, Sugito M, Ono M, Saito N, Kawashima K, Yoshida S, Fujimori T (2005) Pneumoscrotum: a rare manifestation of perforation associated with therapeutic colonoscopy. World J Gastroenterol 11(32):5061–5063
Lai W, Dowell J (2004) Images in clinical medicine. Diffuse subcutaneous air due to a perforated colonic diverticulum. N Engl J Med 350(13):e12
Farley DR, Bannon MP, Zietlow SP, Pemberton JH, Ilstrup DM, Larson DR (1997) Management of colonoscopic perforations. Mayo Clin Proc 72(8):729–733
Hall C, Dorricott NJ, Donovan IA, Neoptolemos JP (1991) Colon perforation during colonoscopy: surgical versus conservative management. Br J Surg 78(5):542–544
Lo AY, Beaton HL (1994) Selective management of colonoscopic perforations. J Am Coll Surg 179(3):333–337
Kavin H, Sinicrope F, Esker AH (1992) Management of perforation of the colon at colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol 87(2):161–167
Allam M, Piskun G, Fogler R (1997) Laparoscopic-assisted repair of extensive rectosigmoid injury after colonoscopy. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 7(2):127–130
Wullstein C, Koppen M, Gross E (1999) Laparoscopic treatment of colonic perforations related to colonoscopy. Surg Endosc 13(5):484–487
Ker TS, Wasserberg N, Beart RW Jr (2004) Colonoscopic perforation and bleeding of the colon can be treated safely without surgery. Am Surg 70(10):922–924
Jentschura D, Raute M, Winter J, Henkel T, Kraus M, Manegold BC (1994) Complications in endoscopy of the lower gastrointestinal tract. Therapy and prognosis. Surg Endosc 8(6):672–676
Kirkpatrick AW, Koo J, Zalev AH, Burnstein MJ, Warren RE (1999) Endoscopic perforation of the rectum presenting initially as a change in voice. Can J Surg 42:305–306
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ignjatović, M., Jović, J. Tension pneumothorax, pneumoretroperitoneum, and subcutaneous emphysema after colonoscopic polypectomy: a case report and review of the literature. Langenbecks Arch Surg 394, 185–189 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-008-0309-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-008-0309-3