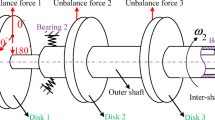
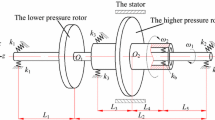
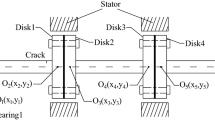
Abstract
In this paper, the nonlinear dynamical behaviors of a complicated dual-rotor aero-engine with rub-impact are investigated. A novel framework is proposed, in which the sophisticated geometrical structure is considered by finite solid element method and efficient model order reduction is applied to the model. The validity and efficiency of the reduced-order model are verified through critical speed and eigen problems. Its stable and unstable solutions are calculated by means of the assembly technique and the multiple harmonic balance method combined with the alternating frequency/time domain technique (MHB–AFT). The accurate frequency amplitudes are obtained accordingly for each harmonic component. The stabilities of the solutions are checked by the Floquet theory. Through the numerical computations, some complex nonlinear phenomena, such as combined frequency vibration, hysteresis, and resonant peak shifting, are discovered when the rub-impact occurs. The results also show that the control parameters of mass eccentricity, rub-impact stiffness, and rotational speed ratio make significant but different influences on the dynamical characteristics of the system. Therefore, a key innovation of this paper is the marriage of a hybrid modeling method—accurate modeling technique combined with model order reduction and solution method—highly efficient semi-analytic method of MHB–AFT. The proposed framework is benefit for parametric study and provides a better understanding of the nonlinear dynamical behaviors of the real complicated dual-rotor aero-engine with rub-impact.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, Y.S., Zhang, H.B.: Review and prospect on the research of dynamics of complete aero-engine systems. Hangkong Xuebao/acta Aeronautica Et Astronautica Sinica 32(8), 1371–1391 (2011)
Goldman, P., Muszynska, A.: Rotor to stator, rub-related, thermal/mechanical effects in rotating machinery. Chaos Soliton Fractals 5(9), 1579–1601 (1995)
Chu, F., Zhang, Z.: Bifurcation and chaos in a rub-impact Jeffcott rotor system. J. Sound Vib. 210(1), 1–18 (1998)
Zhang, L., Ma, Z., Song, B.: Dynamic characteristics of a rub-impact rotor-bearing system for hydraulic generating set under unbalanced magnetic pull. Arch. Appl. Mech. 83(6), 817–830 (2013)
Zhang, L., Ma, Z., Wu, Q.: Vibration analysis of coupled bending-torsional rotor-bearing system for hydraulic generating set with rub-impact under electromagnetic excitation. Arch. Appl. Mech. 86(9), 1665–1679 (2016)
Diken, H.: Nonlinear vibration analysis and sub-harmonic whirl frequencies of the Jeffcott rotor model. J. Sound Vib. 243(1), 117–125 (2001)
Jiang, J., Ulbrich, H.: Stability analysis of sliding whirl in a nonlinear Jeffcott rotor with cross-coupling stiffness coefficients. Nonlinear Dyn. 24(3), 269–283 (2001)
Shen, X.Y., Jia, J., Zhao, M.: Nonlinear analysis of a rub-impact rotor-bearing system with initial permanent rotor bow. Arch. Appl. Mech. 78(3), 225–240 (2008)
Shang, Z., Jiang, J., Hong, L.: The global responses characteristics of a rotor/stator rubbing system with dry friction effects. J. Sound Vib. 330(10), 2150–2160 (2011)
Zhang, H.B., Chen, Y.S.: Bifurcation analysis on full annular rub of a nonlinear rotor system. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 54(8), 1977–1985 (2011)
Chen, G.: A new rotor-ball bearing-stator coupling dynamics model for whole aero-engine vibration. J. Vib. Acoust. 131(6), 1980–1998 (2009)
Rouch, R.W.S.E.: Modeling rotating shafts using axisymmetric solid finite elements with matrix reduction. J Vib. Acoust. 115(4), 484–489 (1993)
Kozhenkov, A.A., Deitch, R.S., Kozhenkov, A.A.: Three-dimensional finite element simulation of nonlinear dynamic rotor systems of a turbocharger. J Vib. Acoust. 130(3), 263–269 (2008)
Ma, W.M., Wang, J.J., Wang, Z.: Frequency and stability analysis method of asymmetric anisotropic rotor-bearing system based on three-dimensional solid finite element Method. J. Eng. Gas Turb. Power-T ASME 137(10), 102502:1–9 (2015)
Khot, S.M., Yelve, N.P.: Modeling and response analysis of dynamic systems by using ANSYS (c) and MATLAB (c). J. Vib. Control. 17(6), 953–958 (2011)
Holl, H.J.: A modal-based substructure method applied to nonlinear rotordynamic systems. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2009, 1–8 (2009)
Batailly, A., Legrand, M., Cartraud, P.: Assessment of reduced models for the detection of modal interaction through rotor stator contacts. J. Sound Vib. 329(26), 5546–5562 (2010)
Legrand, M., Batailly, A., Magnain, B.: Full three-dimensional investigation of structural contact interactions in turbo machines. J. Sound Vib. 331(11), 2578–2601 (2012)
Iwatsubo, T., Shimbo, K., Kawamura, S.: Nonlinear vibration analysis of a rotor system using component mode synthesis method. Arch. Appl. Mech. 72(11), 843–855 (2003)
Li, D.F., Gunter, E.J.: Component mode synthesis of large rotor systems. J. Eng. Gas Turb. Power-T ASME 104(3), 552–560 (1981)
Yang, X.G., Luo, G.H., Yuan, P.: Application and verification of the modal synthesis method in dual-rotor system modeling. Mech. Sci. Technol. Aerosp. Eng. 33(10), 1450–1454 (2014)
Kim, Y.B., Choi, S.K.: A multiple harmonic balance method for the internal resonant vibration of a nonlinear Jeffcott rotor. J Sound Vib. 208(5), 745–761 (1997)
Guskov, M., Sinou, J.J., Thouverez, F.: Multi-dimensional harmonic balance applied to rotor dynamics. Mech. Res. Commun. 35(8), 537–545 (2008)
Zucca, S., Firrone, C.M.: Nonlinear dynamics of mechanical systems with friction contacts: coupled static and dynamic multi-harmonic balance method and multiple solutions. J. Sound Vib. 333(3), 916–926 (2014)
Pušenjak, R.R., Oblak, M.M.: Incremental harmonic balance method with multiple time variables for dynamical systems with cubic nonlinearities. Int. J. Numer. Method Eng. 59(2), 255–292 (2004)
Akgün, D., Cankaya, I.: Frequency response investigations of multi-input multi-output nonlinear systems using automated symbolic harmonic balance method. Nonlinear Dyn. 61(4), 803–818 (2010)
Hou, L., Chen, Y., Fu, Y.: Application of the HB-AFT method to the primary resonance analysis of a dual-rotor system. Nonlinear Dyn. 88(4), 1–21 (2017)
Liu, L., Cao, D.Q., Sun, S.P.: Dynamic characteristics of a disk-drum-shaft rotor system with rub-impact. Nonlinear Dyn. 80(1–2), 1017–1038 (2015)
Bampton, M.C.C., Jr, R.R.C.: Coupling of substructures for dynamic analyses. AIAA J. 4(7), 1313–1319 (2015)
Niordson, F.I.: Dynamics of Rotors. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Das, A.S., Dutt, J.K.: Reduced model of a rotor-shaft system using modified SEREP. Mech. Res. Commun. 35(6), 398–407 (2008)
Sun, C.Z., Chen, Y.S., Hou, L.: Steady-state response characteristics of a dual-rotor system induced by rub-impact. Nonlinear Dyn. 86, 91–105 (2016)
Lam, W.F., Morley, C.T.: Arc-length method for passing limit points in structural calculation. J. Struct Eng-ASCE 118(1), 169–185 (1992)
Seydel, R.: Practical Bifurcation and Stability Analysis. Springer, New York (2010)
Huang, X.D., Zeng, Z.G., Ma, Y.N.: The Theory and Methods for Nonlinear Numerical Analysis. Wuhan University Press, Wuhan (2004)
Chen, Y.S.: Nonlinear Vibrations. Higher Education Press, Beijing (2002)
Hsu, C.S.: Impulsive parametric excitation: theory. J. Appl. Mech. 39(2), 551–558 (1972)
Hsu, C.S., Cheng, W.H.: Applications of the theory of impulsive parametric excitation and new treatments of general parametric excitation problems. J. Appl. Mech. 40(1), 78–86 (1973)
Wang, S.J., Liao, M.F., Jiang, Y.F.: Experimental study on local rub-impact fault of counter-rotating dual-rotor. J. Propuls. Technol. 34(1), 31–36 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial supports from the National Key Basic Research Program (973 Program) of China (Grant No. 2015CB057400), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11602070), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2016M590277).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, C., Chen, Y. & Hou, L. Nonlinear dynamical behaviors of a complicated dual-rotor aero-engine with rub-impact. Arch Appl Mech 88, 1305–1324 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-018-1373-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-018-1373-y