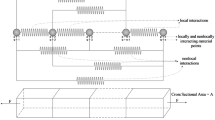
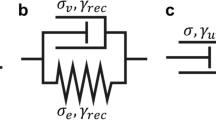
Abstract
In this article tension, compression and torsion tests are presented using thin-walled tubes of polyoxymethylene (POM). These isothermal experiments show non-linear rate dependence, a tension–compression asymmetry and a pronounced relaxation behaviour. On the basis of the experiments carried out, a constitutive model of viscoplasticity with an equilibrium hysteresis in the small-strain regime is developed. Test calculations using finite elements based on the DAE approach show the capabilities of the thermomechanically consistent model. In particular, a very efficient stress algorithm can be derived which has no iteration on the element level. Moreover, it will be shown that time-adaptive finite elements could be of high importance if rate-dependent constitutive models are applied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aya T., Nakayama T.(1997): Influence of environmental temperature on yield stress of polymers. JSME Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. Int. J. Ser. A 40(3): 343–348
Cash J.(1979): Diagonally implicit Runge-Kutta formulae with error estimates. J. Inst. Math. Appl. 24: 293–301
Domininghaus H.(1998): Die Kunststoffe und ihre Eigenschaften, 5th edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Eckert S., Baaser H., Gross D., Scherf O.(2004): A BDF2 integration method with stepsize control for elastoplasticity. Comput. Mech. 34(5): 377–386
El-Sayed H., Barton D., Abdel-Latif L., Kenawy M.(2001): Experimental and numerical investigation of deformation and fracture of semicrystalline polymers under varying strain rate and triaxial states of stress. Plast. Rubber Composites 30(2): 82–87
Ellsiepen P., Hartmann S. (2001): Remarks on the interpretation of current non-linear finite-element-analyses as differential-algebraic equations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 51: 679–707
Hairer E., Wanner G.(1996): Solving Ordinary Differential Equations II, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Hartmann S.(2002): Computation in finite strain viscoelasticity: finite elements based on the interpretation as differential-algebraic equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 191(13–14): 1439–1470
Hartmann S.(2005): A remark on the application of the Newton–Raphson method in non-linear finite element analysis. Comput. Mech. 36(2): 100–116
Hartmann S., Tschöpe T., Schreiber L., Haupt P. (2003): Large deformations of a carbon black-filled rubber Experiment, optical measurement and parameter identification using finite elements. Eur. J. Mech. Ser. A Solids 22: 309–324
Hashemi S., Gilbride M., Hodgkinson J.(1996): Mechanical property relationships in glass-filled polyoxymethylene. J. Mater. Sci. 31: 5017–5025
Haupt P.(2000): Continuum Mechanics and Theory of Materials. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Haupt P., Lion A.(1995): Experimental identification and mathematical modelling of viscoplastic material behavior. J. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 7: 73–96
Haupt P., Sedlan K.(2001): Viscoplasticity of elastomeric materials. experimental facts and constitutive modelling. Arch. Appl. Mech. 71: 89–109
Hoyer W., Schmidt J.(1984): Newton-type decomposition methods for equations arising in network analysis. ZAMM Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 64: 397–405
Kitagawa M., Zhou D., Qiu J.(1995): Stress–strain curves for solid polymers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 35(22): 1725–1732
Kletschkowski T., Schomburg U., Bertram A.(2001): Viskoplastische Materialmodellierung am Beispiel des Dichtungswerkstoffs Polytetrafluorethylen. Tech. Mech. 21: 227–241
Korzen, M.: Beschreibung des inelastischen Materialverhaltens im Rahmen der Kontinuumsmechanik: Vorschlag einer Materialgleichung vom viskoelastisch-plastischen Typ. PhD thesis, TH Darmstadt (1988)
Lion A.(1996): A constitutive model for black filled rubber. experimental investigations and mathematical representations. J. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 8: 153–169
Liu M., Krempl E.(1979): A uniaxial viscoplastic model based on total strain and overstress. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 27: 377–391
Plummer C., Beguelin P., Kausch H.H.(1995): The temperature and strain-rate dependence of mechanical properties in polyoxymethylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 35(16): 1300–1312
Plummer C., Scaramuzzino P., Kausch H.H., Phillippoz J.(2000): High temperature slow crack growth in polyoxymethylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 40(6): 1306–1317
Rabbat N., Sangiovanni-Vincentelli A., Hsieh H.(1979). A multilevel Newton algorithm with macromodeling and latency for the analysis of large-scale nonlinear circuits in the time domain. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 26: 733–740
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartmann, S. A Thermomechanically Consistent Constitutive Model for Polyoxymethylene. Arch Appl Mech 76, 349–366 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-006-0034-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-006-0034-8