Abstract
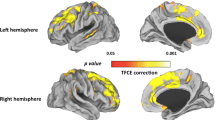
Previous studies using voxel-based morphometry (VBM) provided emerging evidence of structural changes of the thalamus in idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE). However, the location of atrophy within the thalamus in IGE has been somewhat inconsistent across the studies. We, therefore, examined the location of thalamic atrophy and its relationship with clinical factors in IGE, using multiple analytic methods. Fifty IGE patients and 50 controls were scanned on a 3T MRI. Structural evaluation consisted of automated thalamic volumetry, VBM, and thalamic shape analysis. Group comparison between patients and controls was made to assess thalamic atrophy. Within-group correlations between thalamic atrophy and clinical variables were further performed in patients. Both thalamic volumes were reduced in IGE patients, and were negatively correlated with disease duration. The VBM showed a significant regional grey matter volume reduction in bilateral anterior-medial thalami in patients compared to controls. Voxel values extracted from the anterior-medial thalamic cluster were negatively correlated with disease duration. Vertex-based shape analysis revealed regional atrophy on the anterior-medial and posterior-dorsal aspects of thalamus bilaterally in patients compared to controls. Correlation analysis showed that anterior-medial and posterior-dorsal aspects of bilateral thalami were negatively correlated with disease duration. Combining multiple analyses, we demonstrated regional atrophy of anterior-medial and posterior-dorsal thalamus in patients with IGE. Given the anatomical connection of these thalamic regions with the frontal lobe, our finding of greater thalamic atrophy in relation to increasing disease duration further supports the pathophysiological concept of thalamo-frontal network abnormality underlying IGE, and may implicate frontal cognitive dysfunctions and disease progression.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghakhani Y, Bagshaw AP, Benar CG, Hawco C, Andermann F, Dubeau F, Gotman J (2004) fMRI activation during spike and wave discharges in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Brain 127:1127–1144
Anderson J, Hamandi K (2011) Understanding juvenile myoclonic epilepsy: contributions from neuroimaging. Epilepsy Res 94:127–137
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2005) Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 26:839–851
Banerjee PK, Snead OC 3rd (1994) Thalamic mediodorsal and intralaminar nuclear lesions disrupt the generation of experimentally induced generalized absence-like seizures in rats. Epilepsy Res 17:193–205
Behrens TE, Johansen-Berg H, Woolrich MW, Smith SM, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Boulby PA, Barker GJ, Sillery EL, Sheehan K, Ciccarelli O, Thompson AJ, Brady JM, Matthews PM (2003) Non-invasive mapping of connections between human thalamus and cortex using diffusion imaging. Nat Neurosci 6:750–757
Bernasconi A, Bernasconi N, Natsume J, Antel SB, Andermann F, Arnold DL (2003) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy and imaging of the thalamus in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Brain 126:2447–2454
Bernhardt BC, Rozen DA, Worsley KJ, Evans AC, Bernasconi N, Bernasconi A (2009) Thalamo-cortical network pathology in idiopathic generalized epilepsy: insights from MRI-based morphometric correlation analysis. Neuroimage 46:373–381
Betting LE, Mory SB, Li LM, Lopes-Cendes I, Guerreiro MM, Guerreiro CA, Cendes F (2006) Voxel-based morphometry in patients with idiopathic generalized epilepsies. Neuroimage 32:498–502
Betting LE, Mory SB, Lopes-Cendes I, Li LM, Guerreiro MM, Guerreiro CA, Cendes F (2006) MRI volumetry shows increased anterior thalamic volumes in patients with absence seizures. Epilepsy Behav 8:575–580
Blumenfeld H (2005) Cellular and network mechanisms of spike-wave seizures. Epilepsia 46(Suppl 9):21–33
Brevard ME, Kulkarni P, King JA, Ferris CF (2006) Imaging the neural substrates involved in the genesis of pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures. Epilepsia 47:745–754
Carney PW, Masterton RA, Harvey AS, Scheffer IE, Berkovic SF, Jackson GD (2010) The core network in absence epilepsy. Differences in cortical and thalamic BOLD response. Neurology 75:904–911
Chan CH, Briellmann RS, Pell GS, Scheffer IE, Abbott DF, Jackson GD (2006) Thalamic atrophy in childhood absence epilepsy. Epilepsia 47:399–405
Chatzikonstantinou A, Gass A, Forster A, Hennerici MG, Szabo K (2011) Features of acute DWI abnormalities related to status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res 97:45–51
Coscia DM, Narr KL, Robinson DG, Hamilton LS, Sevy S, Burdick KE, Gunduz-Bruce H, McCormack J, Bilder RM, Szeszko PR (2009) Volumetric and shape analysis of the thalamus in first-episode schizophrenia. Hum Brain Mapp 30:1236–1245
Crum RM, Anthony JC, Bassett SS, Folstein MF (1993) Population-based norms for the Mini-Mental State Examination by age and educational level. JAMA 269:2386–2391
Deppe M, Kellinghaus C, Duning T, Moddel G, Mohammadi S, Deppe K, Schiffbauer H, Kugel H, Keller SS, Ringelstein EB, Knecht S (2008) Nerve fiber impairment of anterior thalamocortical circuitry in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Neurology 71:1981–1985
Devinsky O, Gershengorn J, Brown E, Perrine K, Vazquez B, Luciano D (1997) Frontal functions in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Neuropsychiatry Neuropsychol Behav Neurol 10:243–246
Elger CE, Helmstaedter C, Kurthen M (2004) Chronic epilepsy and cognition. Lancet Neurol 3:663–672
Gelineau-Morel R, Tomassini V, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, Matthews PM, Palace J (2012) The effect of hypointense white matter lesions on automated gray matter segmentation in multiple sclerosis. Hum Brain Mapp 33:2802–2814
Grieve KL, Acuna C, Cudeiro J (2000) The primate pulvinar nuclei: vision and action. Trends Neurosci 23:35–39
Helms G, Ciumas C, Kyaga S, Savic I (2006) Increased thalamus levels of glutamate and glutamine (Glx) in patients with idiopathic generalised epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77:489–494
Johansen-Berg H, Behrens TE, Sillery E, Ciccarelli O, Thompson AJ, Smith SM, Matthews PM (2005) Functional-anatomical validation and individual variation of diffusion tractography-based segmentation of the human thalamus. Cereb Cortex 15:31–39
Kato K, Urino T, Hori T, Tsuda H, Yoshida K, Hashizume K, Tanaka T (2008) Experimental petit mal-like seizure induced by microinjection of kainic acid into the unilateral mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 48:285–290
Katramados AM, Burdette D, Patel SC, Schultz LR, Gaddam S, Mitsias PD (2009) Periictal diffusion abnormalities of the thalamus in partial status epilepticus. Epilepsia 50:265–275
Keller SS, Ahrens T, Mohammadi S, Moddel G, Kugel H, Ringelstein EB, Deppe M (2011) Microstructural and volumetric abnormalities of the putamen in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsia 52:1715–1724
Kim JH, Im KC, Kim JS, Lee SA, Kang JK (2005) Correlation of interictal spike-wave with thalamic glucose metabolism in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. NeuroReport 16:1151–1155
Kim JH, Lee JK, Koh SB, Lee SA, Lee JM, Kim SI, Kang JK (2007) Regional grey matter abnormalities in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy: a voxel-based morphometry study. Neuroimage 37:1132–1137
Kim JH, Suh SI, Park SY, Seo WK, Koh I, Koh SB, Seol HY (2012) Microstructural white matter abnormality and frontal cognitive dysfunctions in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsia 53:1371–1378
Lin K, Carrete H Jr, Lin J, Peruchi MM, de Araujo Filho GM, Guaranha MS, Guilhoto LM, Sakamoto AC, Yacubian EM (2009) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals an epileptic network in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsia 50:1191–1200
Lin K, Jackowski AP, Carrete H Jr, de Araujo Filho GM, Silva HH, Guaranha MS, Guilhoto LM, Bressan RA, Yacubian EM (2009) Voxel-based morphometry evaluation of patients with photosensitive juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 86:138–145
Luo C, Li Q, Lai Y, Xia Y, Qin Y, Liao W, Li S, Zhou D, Yao D, Gong Q (2011) Altered functional connectivity in default mode network in absence epilepsy: a resting-state fMRI study. Hum Brain Mapp 32:438–449
McGill ML, Devinsky O, Kelly C, Milham M, Castellanos FX, Quinn BT, DuBois J, Young JR, Carlson C, French J, Kuzniecky R, Halgren E, Thesen T (2012) Default mode network abnormalities in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 23:353–359
McKeown MJ, Uthama A, Abugharbieh R, Palmer S, Lewis M, Huang X (2008) Shape (but not volume) changes in the thalami in Parkinson disease. BMC Neurol 8:8
Mirski MA, Tsai YC, Rossell LA, Thakor NV, Sherman DL (2003) Anterior thalamic mediation of experimental seizures: selective EEG spectral coherence. Epilepsia 44:355–365
Moeller F, Siebner HR, Wolff S, Muhle H, Boor R, Granert O, Jansen O, Stephani U, Siniatchkin M (2008) Changes in activity of striato-thalamo-cortical network precede generalized spike wave discharges. Neuroimage 39:1839–1849
Mory SB, Betting LE, Fernandes PT, Lopes-Cendes I, Guerreiro MM, Guerreiro CA, Cendes F, Li LM (2011) Structural abnormalities of the thalamus in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 21:407–411
Natsume J, Bernasconi N, Andermann F, Bernasconi A (2003) MRI volumetry of the thalamus in temporal, extratemporal, and idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Neurology 60:1296–1300
Nordli DR Jr (2005) Idiopathic generalized epilepsies recognized by the International League Against Epilepsy. Epilepsia 46(Suppl 9):48–56
O’Muircheartaigh J, Vollmar C, Barker GJ, Kumari V, Symms MR, Thompson P, Duncan JS, Koepp MJ, Richardson MP (2011) Focal structural changes and cognitive dysfunction in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Neurology 76:34–40
Panayiotopoulos CP (2005) Idiopathic generalized epilepsies: a review and modern approach. Epilepsia 46(Suppl 9):1–6
Pardoe H, Pell GS, Abbott DF, Berg AT, Jackson GD (2008) Multi-site voxel-based morphometry: methods and a feasibility demonstration with childhood absence epilepsy. Neuroimage 42:611–616
Patenaude B, Smith SM, Kennedy DN, Jenkinson M (2011) A Bayesian model of shape and appearance for subcortical brain segmentation. Neuroimage 56:907–922
Piazzini A, Turner K, Vignoli A, Canger R, Canevini MP (2008) Frontal cognitive dysfunction in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsia 49:657–662
Pulsipher DT, Dabbs K, Tuchsherer V, Sheth RD, Koehn MA, Hermann BP, Seidenberg M (2011) Thalamofrontal neurodevelopment in new-onset pediatric idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Neurology 76:28–33
Pulsipher DT, Seidenberg M, Guidotti L, Tuchscherer VN, Morton J, Sheth RD, Hermann B (2009) Thalamofrontal circuitry and executive dysfunction in recent-onset juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsia 50:1210–1219
Roebling R, Scheerer N, Uttner I, Gruber O, Kraft E, Lerche H (2009) Evaluation of cognition, structural, and functional MRI in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsia 50:2456–2465
Rosenberg DS, Mauguiere F, Catenoix H, Faillenot I, Magnin M (2009) Reciprocal thalamocortical connectivity of the medial pulvinar: a depth stimulation and evoked potential study in human brain. Cereb Cortex 19:1462–1473
Rosenberg DS, Mauguiere F, Demarquay G, Ryvlin P, Isnard J, Fischer C, Guenot M, Magnin M (2006) Involvement of medial pulvinar thalamic nucleus in human temporal lobe seizures. Epilepsia 47:98–107
Savic I, Osterman Y, Helms G (2004) MRS shows syndrome differentiated metabolite changes in human-generalized epilepsies. Neuroimage 21:163–172
Seeck M, Dreifuss S, Lantz G, Jallon P, Foletti G, Despland PA, Delavelle J, Lazeyras F (2005) Subcortical nuclei volumetry in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsia 46:1642–1645
Simister RJ, McLean MA, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (2003) Proton MRS reveals frontal lobe metabolite abnormalities in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Neurology 61:897–902
Song M, Du H, Wu N, Hou B, Wu G, Wang J, Feng H, Jiang T (2011) Impaired resting-state functional integrations within default mode network of generalized tonic-clonic seizures epilepsy. PLoS One 6:e17294
Swartz BE, Simpkins F, Halgren E, Mandelkern M, Brown C, Krisdakumtorn T, Gee M (1996) Visual working memory in primary generalized epilepsy: an 18FDG-PET study. Neurology 47:1203–1212
Szabo K, Poepel A, Pohlmann-Eden B, Hirsch J, Back T, Sedlaczek O, Hennerici M, Gass A (2005) Diffusion-weighted and perfusion MRI demonstrates parenchymal changes in complex partial status epilepticus. Brain 128:1369–1376
Tae WS, Kim SH, Joo EY, Han SJ, Kim IY, Kim SI, Lee JM, Hong SB (2008) Cortical thickness abnormality in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. J Neurol 255:561–566
Tosun D, Dabbs K, Caplan R, Siddarth P, Toga A, Seidenberg M, Hermann B (2011) Deformation-based morphometry of prospective neurodevelopmental changes in new onset paediatric epilepsy. Brain 134:1003–1014
Tyvaert L, Chassagnon S, Sadikot A, LeVan P, Dubeau F, Gotman J (2009) Thalamic nuclei activity in idiopathic generalized epilepsy: an EEG-fMRI study. Neurology 73:2018–2022
Vulliemoz S, Vollmar C, Koepp MJ, Yogarajah M, O’Muircheartaigh J, Carmichael DW, Stretton J, Richardson MP, Symms MR, Duncan JS (2011) Connectivity of the supplementary motor area in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy and frontal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 52:507–514
Wang Z, Lu G, Zhang Z, Zhong Y, Jiao Q, Tan Q, Tian L, Chen G, Liao W, Li K, Liu Y (2011) Altered resting state networks in epileptic patients with generalized tonic–clonic seizures. Brain Res 1374:134–141
Wang Z, Zhang Z, Jiao Q, Liao W, Chen G, Sun K, Shen L, Wang M, Li K, Liu Y, Lu G (2012) Impairments of thalamic nuclei in idiopathic generalized epilepsy revealed by a study combining morphological and functional connectivity MRI. PLoS One 7:e39701
Woermann FG, Free SL, Koepp MJ, Sisodiya SM, Duncan JS (1999) Abnormal cerebral structure in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy demonstrated with voxel-based analysis of MRI. Brain 122:2101–2108
Zarei M, Patenaude B, Damoiseaux J, Morgese C, Smith S, Matthews PM, Barkhof F, Rombouts SA, Sanz-Arigita E, Jenkinson M (2010) Combining shape and connectivity analysis: an MRI study of thalamic degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 49:1–8
Zhang D, Snyder AZ, Fox MD, Sansbury MW, Shimony JS, Raichle ME (2008) Intrinsic functional relations between human cerebral cortex and thalamus. J Neurophysiol 100:1740–1748
Zhang D, Snyder AZ, Shimony JS, Fox MD, Raichle ME (2010) Noninvasive functional and structural connectivity mapping of the human thalamocortical system. Cereb Cortex 20:1187–1194
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea Grant funded by the Korean Government (Grant No. 20100004827, 20110005418) and a Korea University Grant. The authors are very grateful to the participants for taking part in the present study.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical standard
This study was approved by the local ethics committee, and made to conform to the latest guideline of the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants gave written informed consent prior to inclusion in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. H. Kim and J. B. Kim contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.H., Kim, J.B., Seo, WK. et al. Volumetric and shape analysis of thalamus in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. J Neurol 260, 1846–1854 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-6891-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-6891-5