Abstract
Investigations of brain structure in schizophrenia using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have identified variations in regional grey matter (GM) volume throughout the brain but the results are mixed. This study aims to investigate whether the inconsistent voxel-based morphometry (VBM) findings in schizophrenia are due to the use of different software packages. T1 MRI images were obtained from 86 first-episode schizophrenia (FESZ) patients and 86 age- and gender-matched Healthy controls (HCs). VBM analysis was carried out using FMRIB software library (FSL) 5.0 and statistical parametric mapping 8 (SPM8). All images were processed using the default parameter settings as provided by these software packages. FSL-VBM revealed widespread GM volume reductions in FESZ patients compared with HCs, however, for SPM-VBM, only increased and circumscribed GM volume changes were found, both software revealed increased GM volume within cerebellum. Significant correlations between Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) and GM volume were mainly found in frontal regions. Algorithms of GM tissue segmentation, image registration and statistical strategies might contribute to these disparate results.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adduru, V. R., Michael, A. M., Helguera, M., Baum, S. A., & Moore, G. J. (2017). Leveraging clinical imaging archives for Radiomics: reliability of automated methods for brain volume measurement. Radiology., 284, 862–869.
Andreasen, N. C., Paradiso, S., & O'Leary, D. S. (1998). “Cognitive Dysmetria” as an integrative theory of schizophrenia: a dysfunction in cortical-subcortical-cerebellar circuitry? Schizophrenia Bulletin, 24, 203–218.
Ashburner, J. (2007). A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. Neuroimage., 38, 95–113.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2000). Voxel-based morphometry--the methods. Neuroimage., 11, 805–821.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2005). Unified segmentation. Neuroimage., 26, 839–851.
Bergé, D., Carmona, S., Rovira, M., Bulbena, A., Salgado, P., & Vilarroya, O. (2011). Gray matter volume deficits and correlation with insight and negative symptoms in first-psychotic-episode subjects. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 123, 431–439.
Bi, Y., Yuan, K., Guan, Y., Cheng, J., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Yu, D., Qin, W., & Tian, J. (2017). Altered resting state functional connectivity of anterior insula in young smokers. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 11, 155–165.
Brakemeier, E. L., Wilbertz, G., Rodax, S., Danker-Hopfe, H., Zinka, B., Zwanzger, P., Grossheinrich, N., Várkuti, B., Rupprecht, R., & Bajbouj, M. (2008). Patterns of response to repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in major depression: replication study in drug-free patients. Journal of Affective Disorders, 108, 59–70.
Chan, R. C., Di, X., Mcalonan, G. M., & Gong, Q. Y. (2011). Brain anatomical abnormalities in high-risk individuals, First-episode, and chronic schizophrenia: an activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of illness progression. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 37, 177–188.
Crespo-Facorro, B., Roiz-Santiáñez, R., Pérez-Iglesias, R., Rodriguez-Sanchez, J. M., Mata, I., Tordesillas-Gutierrez, D., Sanchez, E., Tabarés-Seisdedos, R., Andreasen, N., & Magnotta, V. (2011). Global and regional cortical thinning in first-episode psychosis patients: Relationships with clinical and cognitive features. Psychological Medicine, 41, 1449–1460.
Czepielewski, L. S., Wang, L., Gama, C. S., & Barch, D. M. (2016). The relationship of intellectual functioning and cognitive performance to brain structure in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 43, sbw090.
Derakhshan, M., Caramanos, Z., Giacomini, P. S., Narayanan, S., Maranzano, J., Francis, S. J., Arnold, D. L., & Collins, D. L. (2010). Evaluation of automated techniques for the quantification of grey matter atrophy in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neuroimage., 52, 1261–1267.
Douaud, G., Smith, S., Jenkinson, M., Behrens, T., Johansenberg, H., Vickers, J., James, S., Voets, N., Watkins, K., & Matthews, P. M. (2007). Anatomically related grey and white matter abnormalities in adolescent-onset schizophrenia. Brain., 130, 2375–2386.
Ellisonwright, I., Glahn, D. C., Laird, A. R., Thelen, S. M., & Bullmore, E. (2008). The anatomy of First-episode and chronic schizophrenia: an anatomical likelihood estimation meta-analysis. American Journal of Psychiatry, 165, 1015–1023.
First, M. B., Spitzer, R. L., Gibbon, M. & Williams, J. B (1996). Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV Axis I disorders. New York: Biometrics Research Department, New York State Psychiatric Institute.
Garner, B., Berger, G. E., Nicolo, J. P., Mackinnon, A., Wood, S. J., Pariante, C. M., Dazzan, P., Proffitt, T. M., Markulev, C., & Kerr, M. (2009). Pituitary volume and early treatment response in drug-naïve first-episode psychosis patients. Schizophrenia Research, 113, 65–71.
Harms, M. P., Wang, L., Campanella, C., Aldridge, K., Moffitt, A. J., Kuelper, J., Ratnanather, J. T., Miller, M. I., Barch, D. M., & Csernansky, J. G. (2010). Structural abnormalities in gyri of the prefrontal cortex in individuals with schizophrenia and their unaffected siblings. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 196, 150–157.
Honea, R., Crow, T. J., Passingham, D., & Mackay, C. E. (2005). Regional deficits in brain volume in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 162, 2233–2245.
Ichimiya, T., Okubo, Y., Suhara, T., & Sudo, Y. (2001). Reduced volume of the cerebellar vermis in neuroleptic-naive schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry, 49, 20–27.
John, J. P., Lukose, A., Bagepally, B. S., Halahalli, H. N., Moily, N. S., Vijayakumari, A. A., & Jain, S. (2015). A systematic examination of brain volumetric abnormalities in recent-onset schizophrenia using voxel-based, surface-based and region-of-interest-based morphometric analyses. Journal of Negative Results in Biomedicine, 14, 11.
Kasai, K., Shenton, M. E., Salisbury, D. F., Hirayasu, Y., Lee, C. U., Ciszewski, A. A., Yurgeluntodd, D., Kikinis, R., Jolesz, F. A., & Mccarley, R. W. (2003). Progressive decrease of left superior temporal gyrus gray matter volume in patients with first-episode schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry, 160, 156–164.
Kay, S. R., Fiszbein, A., & Opler, L. A. (1986). The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 13, 261.
Kim, G. W., Kim, Y. H., & Jeong, G. W. (2017). Whole brain volume changes and its correlation with clinical symptom severity in patients with schizophrenia: a DARTEL-based VBM study. PLoS One, 12, e0177251.
Li, W., Liang, Y., Yu, D., Peng, L., Pernstich, K. P., Shen, T., Hight Walker, A. R., Cheng, G., Hacker, C. A., & Richter, C. A. (2012). Decrease in temporal gyrus gray matter volume in First-episode, early onset schizophrenia: an MRI study. PLoS One, 7, e40247.
Lui, S., Deng, W., Huang, X., Jiang, L., Ma, X., Chen, H., Zhang, T., Li, X., Li, D., & Zou, L. (2009). Association of cerebral deficits with clinical symptoms in antipsychotic-naive first-episode schizophrenia: an optimized voxel-based morphometry and resting state functional connectivity study. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 166, 196–205.
Malla, A. K., Bodnar, M., Joober, R., & Lepage, M. (2011). Duration of untreated psychosis is associated with orbital-frontal grey matter volume reductions in first episode psychosis. Schizophrenia Research, 125, 13–20.
Mothersill, O., Knee-Zaska, C., & Donohoe, G. (2016). Emotion and theory of mind in schizophrenia—Investigating the role of the cerebellum. Cerebellum., 15, 357–368.
Palaniyappan, L., Maayan, N., Bergman, H., Davenport, C., Adams, C.E., & Soares-Weiser, K. (2015). Voxel-based morphometry for separation of schizophrenia from other types of psychosis in first episode psychosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 7(8), CD011021. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011021.pub2.
Palaniyappan, L., Hodgson, O., Balain, V., Iwabuchi, S., Gowland, P., & Liddle, P. (2018). Structural covariance and cortical reorganisation in schizophrenia: a MRI-based morphometric study. Psychological Medicine, 44, 1–9.
Robyn, H., Crow, T. J., Dick, P., & Mackay, C. E. (2005). Regional deficits in brain volume in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 162, 2233–2245.
Rosa, P. G., Zanetti, M. V., Duran, F. L., Santos, L. C., Menezes, P. R., Scazufca, M., Murray, R. M., Busatto, G. F., & Schaufelberger, M. S. (2015). What determines continuing grey matter changes in first-episode schizophrenia and affective psychosis? Psychological Medicine, 45, 817–828.
Sapara, A., Cooke, M., Fannon, D., Francis, A., Buchanan, R. W., Anilkumar, A. P., Barkataki, I., Aasen, I., Kuipers, E., & Kumari, V. (2007). Prefrontal cortex and insight in schizophrenia: a volumetric MRI study. Schizophrenia Research, 89, 22–34.
Shah, C., Zhang, W., Xiao, Y., Yao, L., Zhao, Y., Gao, X., Liu, L., Liu, J., Li, S., & Tao, B. (2016). Common pattern of gray-matter abnormalities in drug-naive and medicated first-episode schizophrenia: a multimodal meta-analysis. Psychological Medicine, 47, 401–413.
Shepherd, A. M., Laurens, K. R., Matheson, S. L., Carr, V. J., & Green, M. J. (2012). Systematic meta-review and quality assessment of the structural brain alterations in schizophrenia. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 36, 1342–1356.
Smith, S. M. (2010). Fast robust automated brain extraction. Human Brain Mapping, 17, 143–155.
Smith, S. M., & Nichols, T. E. (2008). Smith SM, Nichols TE. Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. NeuroImage, 44, 83–98.
Storelli, L., Rocca, M. A., Pagani, E., Van, W. H., Horsfield, M. A., De, N. S., Rovira, A., Sastregarriga, J., Palace, J., & Sima, D. (2018). Measurement of whole-brain and gray matter atrophy in multiple sclerosis: assessment with MR imaging. Radiology, 288(2). https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2018172468.
Suga, M., Yamasue, H., Abe, O., Yamasaki, S., Yamada, H., Inoue, H., Takei, K., Aoki, S., & Kasai, K. (2010). Reduced gray matter volume of Brodmann’s Area 45 is associated with severe psychotic symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 260, 465–473.
Suzuki, M., Zhou, S. Y., Takahashi, T., Hagino, H., Kawasaki, Y., Niu, L., Matsui, M., Seto, H., & Kurachi, M. (2005). Differential contributions of prefrontal and temporolimbic pathology to mechanisms of psychosis. Brain., 128, 2109–2122.
Szeszko, P. R., Narr, K. L., Phillips, O. R., Joanne, M. C., Serge, S., Handan, G. B., Kane, J. M., Bilder, R. M., & Robinson, D. G. (2012). Magnetic resonance imaging predictors of treatment response in first-episode schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 38, 569–578.
Torres, U. S., Duran, F. L. S., Schaufelberger, M. S., Crippa, J. A. S., Louzã, M. R., Sallet, P. C., Kanegusuku, C. Y. O., Elkis, H., Gattaz, W. F., & Bassitt, D. P. (2016). Patterns of regional gray matter loss at different stages of schizophrenia: a multisite, cross-sectional VBM study in first-episode and chronic illness. Neuroimage Clinical, 12, 1–15.
Van Haren, N. E. M., Schnack, H. G., Cahn, W., van den Heuvel, M. P., Lepage, C., Collins, L., Evans, A. C., Pol, H. E. H., & Kahn, R. S. (2011). Changes in cortical thickness during the course of illness in schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry, 68, 871–880.
Yamasue, H., Iwanami, A., Hirayasu, Y., Yamada, H., Abe, O., Kuroki, N., Fukuda, R., Tsujii, K., Aoki, S., & Ohtomo, K. (2004). Localized volume reduction in prefrontal, temporolimbic, and paralimbic regions in schizophrenia: an MRI parcellation study. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, 131, 195–207.
Yuan, K., Qin, W., Liu, J., Guo, Q., Dong, M., Sun, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, P., Wang, W., & Wang, Y. (2010). Altered small-world brain functional networks and duration of heroin use in male abstinent heroin-dependent individuals. Neuroscience Letters, 477, 37–42.
Yuan, K., Qin, W., Yu, D., Bi, Y., Xing, L., Jin, C., & Tian, J. (2016a). Core brain networks interactions and cognitive control in internet gaming disorder individuals in late adolescence/early adulthood. Brain Structure & Function, 221, 1427–1442.
Yuan, K., Yu, D., Cai, C., Feng, D., Li, Y., Bi, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, Y., Jin, C., & Li, L. (2016b). Frontostriatal circuits, resting state functional connectivity and cognitive control in internet gaming disorder. Addiction Biology, 22, 813–822.
Yue, Y., Kong, L., Wang, J., Li, C., Tan, L., Su, H., & Xu, Y. (2016). Regional abnormality of Grey matter in schizophrenia: effect from the illness or treatment? PLoS One, 11, e0147204.
Zhang, Y., Brady, M., & Smith, S. (2001). Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 20, 45–57.
Zhang, C., Wang, Q., Ni, P., Deng, W., Li, Y., Zhao, L., Ma, X., Wang, Y., Yu, H., & Li, X. (2017). Differential cortical gray matter deficits in adolescent- and adult-onset First-episode treatment-Naïve patients with schizophrenia. Scientific Reports, 7, 10267.
Zhu, Y., Wang, L., Xi, Y., Dai, T., Fei, N., Liu, L., Xu, Z., Yang, X., Fu, C., & Sun, J. (2017a). White matter microstructural properties are related to inter-individual differences in cognitive instability after sleep deprivation. Neuroscience., 365, 206–216.
Zhu, Y., Xi, Y., Fei, N., Liu, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, L., Xu, Z., Sun, J., Yang, X., & Yin, H. (2017b). Dynamics of cerebral responses to sustained attention performance during one night of sleep deprivation. Journal of Sleep Research, 27, 184–196.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 81571651, 81601474 and 81801772 and the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province (2017ZDXM-SF-048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have indicated no financial conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Xijing Hospital of the Fourth Military Medical University Subcommittee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Figure S1
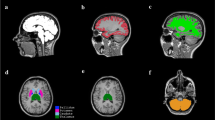
Correlations between PANSS Scale and GM volume of brain regions, correlations were only found in brain regions which showed GM reductions revealed by FSL-VBM. (PNG 2411 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Liu, W., Guo, F. et al. Voxel-based morphometry results in first-episode schizophrenia: a comparison of publicly available software packages. Brain Imaging and Behavior 14, 2224–2231 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00172-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00172-x