Abstract.
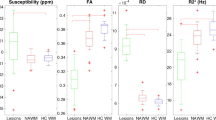
Previous diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging (DT-MRI) studies reported mean diffusivity (\({\overline D}\)) and fractional anisotropy (FA) changes in lesions and normal-appearing white matter (NAWM) of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), but neglected the additional information which can be obtained by the analysis of the inter-voxel coherence (C). The present study is based on a large sample of patients with MS and it is aimed at assessing the potential role of C in the quantification of MS-related tissue damage of T2-visible lesions and NAWM. We obtained dual-echo, T1-weighted and DT-MRI scans from 78 patients with relapsing-remitting (RR), secondary progressive (SP), or primary progressive (PP) MS and from 26 healthy volunteers. We calculated \({\overline D}\), FA and C of T2-hyperintense lesions, T1-isointense lesions, T1-hypointense lesions and several areas of the NAWM. \({\overline D}\) and FA of the majority of NAWM regions studied from MS patients were different from the corresponding quantities of the white matter from controls. NAWM C from patients was lower than white matter C from controls only for the parietal pericallosal areas. SPMS patients had higher corpus callosum \({\overline D}\) and lower corpus callosum FA and C than patients with either RRMS or PPMS. Average lesion \({\overline D}\) was higher, and average FA and C lower than the corresponding quantities measured in the NAWM. Average T1-hypointense lesion \({\overline D}\) was higher and average FA lower than the corresponding quantities of T1-isointense lesions, whereas average C of these two lesion populations were not different. SPMS had higher average lesion \({\overline D}\) than both PPMS and RRMS patients. NAWM \({\overline D}\) and C of the corpus callosum were moderately correlated with disability. This study confirms the role of DT-MRI metrics to identify MS lesions with different amounts of tissue damage and to detect diffuse changes in the NAWM. It also shows that measuring C enables us to obtain additional information about tissue damage, which is complementary to that given by the analysis of \({\overline D}\) and FA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 July 2001, Received in revised form: 15 January 2002, Accepted: 22 January 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cercignani, M., Bozzali, M., Iannucci, G. et al. Intra-voxel and inter-voxel coherence in patients with multiple sclerosis assessed using diffusion tensor MRI. J Neurol 249, 875–883 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-002-0752-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-002-0752-y