Abstract
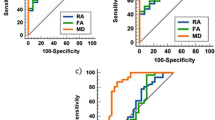
The white matter (WM) of the brain is damaged in multiple sclerosis (MS), even in areas that appear normal on standard MR imaging. The purpose of our study is to evaluate the damage of normal appearing white matter (NAWM) in patients with MS. In our study, 84 MS patients and 42 healthy adults underwent a routine brain MRI, including also diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). All studies were performed on a 3 T MRI scanner. Fractional anisotropy (FA) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values were obtained. The DTI parameters of NAWM were correlated with expanded disability status scales (EDSS) scores. Our results showed statistically significant differences in FA and ADC values between MS plaques and the symmetrical NAWM, as also between NAWM and the respective white matter in controls. The ADC values of the NAWM correlated with the EDSS scores. The present study demonstrated damage of the NAWM in MS patients, using DTI in 3.0 T. DTI may be used in the detection of subtle damage of the white matter.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pugliatti M, Sotgiu S, Rosati G (2002) The worldwide prevalence of multiple sclerosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 104:182–191
Sati P, Cross A, Luo J, Hildebolt CF, Yablonskiy DA (2010) In vivo quantitative evaluation of brain tissue damage in multiple sclerosis using gradient echo plural contrast imaging technique. Neuroimage 51:1089–1097
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Edan G et al (2005) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol 58:840–846
Ciccarelli O, Werring D, Barker G, Griffin CM, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Miller DH, Thompson AJ (2003) A study of the mechanisms of normal appearing white matter damage in multiple sclerosis using diffusion tensor imaging-evidence of Wallerian degeneration. J Neurol 250:287–292
Kuhlmann T, Lingfeld G, Bitsch A, Schuchardt J, Brück W (2002) Acute axonal damage in multiple sclerosis is most extensive in early disease stages and decreases over time. Brain 125:2202–2212
Kornek B, Storch MK, Weissert R, Wallstroem E, Stefferl A, Olsson T, Linington C, Schmidbauer M, Lassmann H (2000) Multiple sclerosis and chronic autoimmune encephalomyelitis: a comparative quantitative study of axonal injury in active, inactive and remyelinated lesions. Am J Pathol 157:267–276
Rovaris M, Gass A, Bammer R, Hickman SJ, Ciccarelli O, Miller DH, Filippi M (2005) Diffusion MRI in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 65:1526–1532
Sijens P, Irwan R, Potze J, Mostert JP, De Keyser J, Oudkerk M (2006) Relationships between brain water content and diffusion tensor imaging parameters (apparent diffusion coefficient and fractional anisotropy) in multiple sclerosis. Eur Radiol 16:898–904
Pierpaoli C, Jezzard P, Basser PJ, Barnett A, Di Chiro G (1996) Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the human brain. Radiology 201:637–648
Rovaris M, Agosta F, Pagani E, Filippi M (2009) Diffusion tensor MR imaging. Neuroimag Clin N Am 19:37–43
Tian W, Zhu T, Zhong J, Liu X, Rao P, Segal BM, Ekholm S (2012) Progressive decline in fractional anisotropy on serial DTI examinations of the corpus callosum: a putative marker of disease activity and progression in SPMS. Neuroradiology 54:287–297
Sigal T, Shmuel M, Mark D, Gil H, Anat A (2012) Diffusion tensor imaging of corpus callosum integrity in multiple sclerosis: correlation with disease variables. J Neuroimaging 22:33–37
Dziedzic T, Metz I, Dallenga T, König FB, Müller S, Stadelmann C, Brück W (2010) Wallerian degeneration: a major component of early axonal pathology in multiple sclerosis. Brain Pathol 5:976–985
Moll NM, Riietsch AM, Thomas S, Ransohoff AJ, Lee JC, Fox R, Chang A, Ransohoff RM, Fisher E (2011) Multiple sclerosis NAWM: pathology-imaging correlations. Ann Neurol 70:764–773
Fillippi M, Rocca M, Barkhof F et al (2012) Association between pathological and MRI findings in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 11:349–360
Kim DS, Garwood M (2003) High-field magnetic resonance techniques for brain research. Curr Opin Neurobiol 13:612–619
Rocca MA, Cercignani M, Iannucci G, Comi G, Filippi M (2000) Weekly diffusion-weighted imaging of normal-appearing white matter in MS. Neurology 55:882–884
Ceccarelli A, Rocca M, Falini A, Tortorella P, Pagani E, Rodegher M, Comi G, Scotti G, Filippi M (2007) Normal-appearing white and grey matter damage in MS. a volumetric and diffusion tensor MRI study at 3.0 Tesla. J Neurol 254:513–518
Rovaris M, Iannucci G, Falautano M, Possa F, Martinelli V, Comi G, Filippi M (2002) Cognitive dysfunction in patients with mildly disabling relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: an exploratory study with diffusion tensor MR imaging. J Neurol Sci 195:103–109
Naismith RT (2005) Cross AH multiple sclerosis and black holes: connecting the pixels. Arch Neurol 62:1666–1668
Fox RJ, Cronin T, Lin J, Wang X, Sakaie K, Ontaneda D, Mahmoud SY, Lowe MJ, Phillips MD (2011) Measuring myelin repair and axonal loss with diffusion tensor imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:85–91
Andrade RE, Gasparetto EL, Cruz LC Jr, Ferreira FB, Domingues RC, Marchiori E, Domingues RC (2007) Evaluation of white matter in patients with multiple sclerosis through diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 65:561–564
Rueda F, Hygino L, Domingues R, Vasconcelos CC, Papais-Alvarenga RM, Gasparetto EL (2008) Diffusion tensor MR imaging evaluation of the corpus callosum of patients with multiple sclerosis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 66(3A):449–453
Horsfield MA, Larsson HB, Jones DK, Gass A (1998) Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 64(Suppl 1):S80–84
Werring DJ, Brassat D, Droogan AG, Clark CA, Symms MR, Barker GJ, MacManus DG, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2000) The pathogenesis of lesions and normal-appearing white matter changes in multiple sclerosis. a serial diffusion MRI study. Brain 123:1667–1776
Yurtsever I, Hakyemez B, Taskapilioglu O, Erdogan C, Turan OF, Parlak M (2008) The contribution of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in multiple sclerosis during acute attack. Eur J Radiol 65:421–426
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gratsias, G., Kapsalaki, E., Kogia, S. et al. A quantitative evaluation of damage in normal appearing white matter in patients with multiple sclerosis using diffusion tensor MR imaging at 3 T. Acta Neurol Belg 115, 111–116 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-014-0338-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-014-0338-3