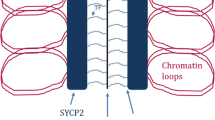
Abstract
Meiotic prophase serves as an arena for the interplay of two important cellular activities, meiotic recombination and synapsis of homologous chromosomes. Synapsis is mediated by the synaptonemal complex (SC), originally characterized as a structure linked to pairing of meiotic chromosomes (Moses (1958) J Biophys Biochem Cytol 4:633–638). In 1975, the first electron micrographs of human pachytene stage SCs were presented (Moses et al. (1975) Science 187:363–365) and over the next 15 years the importance of the SC to normal meiotic progression in human males and females was established (Jhanwar and Chaganti (1980) Hum Genet 54:405–408; Pathak and Elder (1980) Hum Genet 54:171–175; Solari (1980) Chromosoma 81:315–337; Speed (1984) Hum Genet 66:176–180; Wallace and Hulten (1985) Ann Hum Genet 49(Pt 3):215–226). Further, these studies made it clear that abnormalities in the assembly or maintenance of the SC were an important contributor to human infertility (Chaganti et al. (1980) Am J Hum Genet 32:833–848; Vidal et al. (1982) Hum Genet 60:301–304; Bojko (1983) Carlsberg Res Commun 48:285–305; Bojko (1985) Carlsberg Res Commun 50:43–72; Templado et al. (1984) Hum Genet 67:162–165; Navarro et al. (1986) Hum Reprod 1:523–527; Garcia et al. (1989) Hum Genet 2:147–53). However, the utility of these early studies was limited by lack of information on the structural composition of the SC and the identity of other SC-associated proteins. Fortunately, studies of the past 15 years have gone a long way toward remedying this problem. In this minireview, we highlight the most important of these advances as they pertain to human meiosis, focusing on temporal aspects of SC assembly, the relationship between the SC and meiotic recombination, and the contribution of SC abnormalities to human infertility.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson LK, Reeves A, Webb LM, Ashley T (1999) Distribution of crossing over on mouse synaptonemal complexes using immunofluorescent localization of MLH1 protein. Genetics 151:1569–1579
Ashley T (2004) The mouse “tool box” for meiotic studies. Cytogenet Genome Res 105:166–171
Baker SM, Bronner CE, Zhang L, Plug AW, Robatzek M, Warren G, Elliott EA, Yu J, Ashley T, Arnheim N, Flavell RA, Liskay RM (1995) Male mice defective in the DNA mismatch repair gene PMS2 exhibit abnormal chromosome synapsis in meiosis. Cell 82:309–319
Baker SM, Plug AW, Prolla TA, Bronner CE, Harris AC, Yao X, Christie DM, Monell C, Arnheim N, Bradley A, Ashley T, Liskay RM (1996) Involvement of mouse Mlh1 in DNA mismatch repair and meiotic crossing over. Nat Genet 13:336–342
Barlow AL, Hulten MA (1998) Crossing over analysis at pachytene in man. Eur J Hum Genet 6:350–358
Barlow AL, Benson FE, West SC, Hulten MA (1997) Distribution of the Rad51 recombinase in human and mouse spermatocytes. EMBO J 16:5207–5215
Bishop DK, Zickler D (2004) Early decision; meiotic crossover interference prior to stable strand exchange and synapsis. Cell 117:9–15
Bojko M (1983) Human meiosis VIII: chromosome pairing and formation of the synaptonemal complex in oocytes. Carlsberg Res Commun 48:285–305
Bojko M (1985) Human meiosis IX: crossing over and chiasma formation in oocytes. Carlsberg Res Commun 50:43–72
Broman KW, Murray JC, Sheffield VC, White RL, Weber JL (1998) Comprehensive human genetic maps: individual and sex-specific variation in recombination. Am J Hum Genet 63:861–869
Brown PW, Judis L, Chan ER, Schwartz S, Seftel A, Thomas A, Hassold TJ (2005) Meiotic synapsis proceeds from a limited number of subtelomeric sites in the human male. Am J Hum Genet 77:556–566
Chaganti RS, Jhanwar SC, Ehrenbard LT, Kourides IA, Williams JJ (1980) Genetically determined asynapsis, spermatogenic degeneration, and infertility in men. Am J Hum Genet 32:833–848
Christensen GL, Ivanov IP, Atkins JF, Mielnik A, Schlegel PN, Carrell DT (2005) Screening the SPO11 and EIF5A2 genes in a population of infertile men. Fertil Steril 84:758–760
Cohen PE, Pollard JW (2001) Regulation of meiotic recombination and prophase I progression in mammals. Bioessays 23:996–1009
Colaiacovo MP, MacQueen AJ, Martinez-Perez E, McDonald K, Adamo A, La Volpe A, Villeneuve AM (2003) Synaptonemal complex assembly in C. elegans is dispensable for loading strand-exchange proteins but critical for proper completion of recombination. Dev Cell 3:463–474
Cooke HJ, Saunders PT (2002) Mouse models of male infertility. Nat Rev Genet 3:790–801
Dernburg AF, McDonald K, Moulder G, Barstead R, Dresser M, Villeneuve AM (1998) Meiotic recombination in C. elegans initiates by a conserved mechanism and is dispensable for homologous chromosome synapsis. Cell 94:387–398
Dobson MJ, Pearlman RE, Karaiskakis A, Spyropoulos B, Moens PB (1994) Synaptonemal complex proteins: occurrence, epitope mapping and chromosome disjunction. J Cell Sci 107(Pt 10):2749–2760
Eichenlaub-Ritter U (2005) Mouse genetic models for aneuploidy induction in germ cells. Cytogenet Genome Res 111:392–400
Eijpe M, Heyting C, Gross B, Jessberger R (2000a) Association of mammalian SMC1 and SMC3 proteins with meiotic chromosomes and synaptonemal complexes. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 4):673–682
Eijpe M, Offenberg H, Goedecke W, Heyting C (2000b) Localisation of RAD50 and MRE11 in spermatocyte nuclei of mouse and rat. Chromosoma 109:123–132
Eijpe M, Offenberg H, Jessberger R, Revenkova E, Heyting C (2003) Meiotic cohesin REC8 marks the axial elements of rat synaptonemal complexes before cohesins SMC1beta and SMC3. J Cell Biol 160:657–670
Garcia M, Dietrich A, Pujol R, Egozcue J (1989) Nucleolar structures in chromosome and SC preparations from human oocytes at first meiotic prophase. Hum Genet 2:147–153
Gibson J, Tapper W, Zhang W, Morton N, Collins A (2005) Cosmopolitan linkage disequilibrium maps. Hum Genomics 2:20–27
Gonsalves J, Sun F, Schlegel PN, Turek PJ, Hopps CV, Greene C, Martin RH, Pera RA (2004) Defective recombination in infertile men. Hum Mol Genet 13:2875–2883
Hamer G, Roepers-Gajadien HL, van Duyn-Goedhart A, Gademan IS, Kal HB, van Buul PP, de Rooij DG (2003) DNA double-strand breaks and gamma-H2AX signaling in the testis. Biol Reprod 68:628–634
Hassold T, Merrill M, Adkins K, Freeman S, Sherman S (1995) Recombination and maternal age-dependent nondisjunction: molecular studies of trisomy 16. Am J Hum Genet 57:867–874
Hassold T, Judis L, Chan ER, Schwartz S, Seftel A, Lynn A (2004) Cytological studies of meiotic recombination in human males. Cytogenet Genome Res 107:249–255
Hulten M (1974) Chiasma distribution at diakinesis in the normal human male. Hereditas 76:55–78
Jang JK, Sherizen DE, Bhagat R, Manheim EA, McKim KS (2003) Relationship of DNA double-strand breaks to synapsis in Drosophila. J Cell Sci 116:3069–3077
Jhanwar SC, Chaganti RS (1980) Silver-stained synaptonemal complexes of human pachytene bivalents studied by light microscopy. Hum Genet 54:405–408
Jorgenson E, Tang H, Gadde M, Province M, Leppert M, Kardia S, Schork N, Cooper R, Rao DC, Boerwinkle E, Risch N (2005) Ethnicity and human genetic linkage maps. Am J Hum Genet 76:276–290
Judis L, Chan ER, Schwartz S, Seftel A, Hassold T (2004) Meiosis I arrest and azoospermia in an infertile male explained by failure of formation of a component of the synaptonemal complex. Fertil Steril 81:205–209
Kerrebrock AW, Miyazaki WY, Birnby D, Orr-Weaver TL (1992) The Drosophila mei-S332 gene promotes sister-chromatid cohesion in meiosis following kinetochore differentiation. Genetics 130:827–841
Kleckner N (1996) Meiosis: how could it work? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:8167–8174
Kleckner N, Storlazzi A, Zickler D (2003) Coordinate variation in meiotic pachytene SC length and total crossover/chiasma frequency under conditions of constant DNA length. Trends Genet 19:623–628
Kong A, Gudbjartsson DF, Sainz J, Jonsdottir GM, Gudjonsson SA, Richardsson B, Sigurdardottir S, Barnard J, Hallbeck B, Masson G, Shlien A, Palsson ST, Frigge ML, Thorgeirsson TE, Gulcher JR, Stefansson K (2002) A high-resolution recombination map of the human genome. Nat Genet 31:241–247
Kong X, Murphy K, Raj T, He C, White PS, Matise TC (2004) A combined linkage-physical map of the human genome. Am J Hum Genet 75:1143–1148
Krogh BO, Symington LS (2004) Recombination proteins in yeast. Annu Rev Genet 38:233–271
Laurie DA, Hulten MA (1985a) Further studies on bivalent chiasma frequency in human males with normal karyotypes. Ann Hum Genet 49(Pt 3):189–201
Laurie DA, Hulten MA (1985b) Further studies on chiasma distribution and interference in the human male. Ann Hum Genet 49(Pt 3):203–214
Laurie DA, Hulten M, Jones GH (1981) Chiasma frequency and distribution in a sample of human males: chromosomes 1, 2, and 9. Cytogenet Cell Genet 31:153–166
Lenzi ML, Smith J, Snowden T, Kim M, Fishel R, Poulos BK, Cohen PE (2005) Extreme heterogeneity in the molecular events leading to the establishment of chiasmata during meiosis I in human oocytes. Am J Hum Genet 76:112–127
Lynn A, Koehler KE, Judis L, Chan ER, Cherry JP, Schwartz S, Seftel A, Hunt PA, Hassold TJ (2002) Covariation of synaptonemal complex length and mammalian meiotic exchange rates. Science 296:2222–2225
MacQueen AJ, Colaiacovo MP, McDonald K, Villeneuve AM (2002) Synapsis-dependent and -independent mechanisms stabilize homolog pairing during meiotic prophase in C. elegans. Genes Dev 16:2428–2442
Matise TC, Perlin M, Chakravarti A (1994) Automated construction of genetic linkage maps using an expert system (MultiMap): a human genome linkage map. Nat Genet 6:384–390
Matise TC, Sachidanandam R, Clark AG, Kruglyak L, Wijsman E, Kakol J, Buyske S et al. (2003) A 3.9-centimorgan-resolution human single-nucleotide polymorphism linkage map and screening set. Am J Hum Genet 73:271–284
McDermott A (1973) The frequency and distribution of chiasmata in man. Ann Hum Genet 37:13–20
McKim KS, Jang JK, Theurkauf WE, Hawley RS (1993) Mechanical basis of meiotic metaphase arrest. Nature 362:364–366
McKim KS, Jang JK, Manheim EA (2002) Meiotic recombination and chromosome segregation in Drosophila females. Annu Rev Genet 36:205–232
Miyamoto T, Hasuike S, Yogev L, Maduro MR, Ishikawa M, Westphal H, Lamb DJ (2003) Azoospermia in patients heterozygous for a mutation in SYCP3. Lancet 362:1714–1719
Moens PB (1995) Histones H1 and H4 of surface-spread meiotic chromosomes. Chromosoma 104:169–174
Moens PB, Spyropoulos B (1995) Immunocytology of chiasmata and chromosomal disjunction at mouse meiosis. Chromosoma 104:175–182
Moens PB, Heyting C, Dietrich AJ, van Raamsdonk W, Chen Q (1987) Synaptonemal complex antigen location and conservation. J Cell Biol 105:93–103
Moens PB, Pearlman RE, Heng HH, Traut W (1998) Chromosome cores and chromatin at meiotic prophase. Curr Top Dev Biol 37:241–262
Mohrenweiser HW, Tsujimoto S, Gordon L, Olsen AS (1998) Regions of sex-specific hypo- and hyper-recombination identified through integration of 180 genetic markers into the metric physical map of human chromosome 19. Genomics 47:153–162
Moses MJ (1958) The relation between the axial complex of meiotic prophase chromosomes and chromosome pairing in a salamander (Plethodon cinereus). J Biophys Biochem Cytol 4:633–638
Moses MJ, Counce SJ, Paulson DF (1975) Synaptonemal complex complement of man in spreads of spermatocytes, with details of the sex chromosome pair. Science 187:363–365
Murakami H, Nurse P (2000) DNA replication and damage checkpoints and meiotic cell cycle controls in the fission and budding yeasts. Biochem J 349:1–12
Myers S, Bottolo L, Freeman C, McVean G, Donnelly P (2005) A fine-scale map of recombination rates and hotspots across the human genome. Science 310:321–324
Navarro J, Vidal F, Templado C, Benet J, Marina S, Pomerol JM, Egozcue J (1986) Meiotic chromosome studies and synaptonemal complex analyses by light and electron microscopy in 47 infertile or sterile males. Hum Reprod 1:523–527
Nievergelt CM, Smith DW, Kohlenberg JB, Schork NJ (2004) Large-scale integration of human genetic and physical maps. Genome Res 14:1199–1205
Offenberg HH, Schalk JA, Meuwissen RL, van Aalderen M, Kester HA, Dietrich AJ, Heyting C (1998) SCP2: a major protein component of the axial elements of synaptonemal complexes of the rat. Nucleic Acids Res 26:2572–2579
Oliver-Bonet M, Turek PJ, Sun F, Ko E, Martin RH (2005) Temporal progression of recombination in human males. Mol Hum Reprod 11:517–522
Padmore R, Cao L, Kleckner N (1991) Temporal comparison of recombination and synaptonemal complex formation during meiosis in S. cerevisiae. Cell 66:1239–1256
Pasierbek P, Jantsch M, Melcher M, Schleiffer A, Schweizer D, Loidl J (2001) A Caenorhabditis elegans cohesion protein with functions in meiotic chromosome pairing and disjunction. Genes Dev 15:1349–1360
Pathak S, Elder FF (1980) Silver-stained accessory structures on human sex chromosomes. Hum Genet 54:171–175
Pineda-Krch M, Redfield RJ (2005) Persistence and loss of meiotic recombination hotspots. Genetics 169:2319–2333
Plug AW, Peters AH, Keegan KS, Hoekstra MF, de Boer P, Ashley T (1998) Changes in protein composition of meiotic nodules during mammalian meiosis. J Cell Sci 111(Pt 4):413–423
Prieto I, Tease C, Pezzi N, Buesa JM, Ortega S, Kremer L, Martinez A, Martinez AC, Hulten MA, Barbero JL (2004) Cohesin component dynamics during meiotic prophase I in mammalian oocytes. Chromosome Res 12:197–213
Revenkova E, Eijpe M, Heyting C, Hodges CA, Hunt PA, Liebe B, Scherthan H, Jessberger R (2004) Cohesin SMC1 beta is required for meiotic chromosome dynamics, sister chromatid cohesion and DNA recombination. Nat Cell Biol 6:555–562
Roeder GS (1995) Sex and the single cell: meiosis in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:10450–10456
Roeder GS, Bailis JM (2000) The pachytene checkpoint. Trends Genet 16:395–403
Roig I, Liebe B, Egozcue J, Cabero L, Garcia M, Scherthan H (2004) Female-specific features of recombinational double-stranded DNA repair in relation to synapsis and telomere dynamics in human oocytes. Chromosoma 113:22–33
de Rooij DG, de Boer P (2003) Specific arrests of spermatogenesis in genetically modified and mutant mice. Cytogenet Genome Res 103:267–276
Schalk JA, Dietrich AJ, Vink AC, Offenberg HH, van Aalderen M, Heyting C (1998) Localization of SCP2 and SCP3 protein molecules within synaptonemal complexes of the rat. Chromosoma 107:540–548
Scherthan H (2003) Knockout mice provide novel insights into meiotic chromosome and telomere dynamics. Cytogenet Genome Res 103:235–244
Serre D, Nadon R, Hudson TJ (2005) Large-scale recombination rate patterns are conserved among human populations. Genome Res 15:1547–1552
Siomos MF, Badrinath A, Pasierbek P, Livingstone D, White J, Glotzer M, Nasmyth K (2001) Separase is required for chromosome segregation during meiosis I in Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr Biol 11:1825–1835
Solari AJ (1980) Synaptosomal complexes and associated structures in microspread human spermatocytes. Chromosoma 81:315–337
Solari AJ (2002) Primitive forms of meiosis: the possible evolution of meiosis. Biocell 26:1–13
Speed RM (1984) Meiotic configurations in female trisomy 21 foetuses. Hum Genet 66:176–180
Sun H, Treco D, Schultes NP, Szostak JW (1989) Double-strand breaks at an initiation site for meiotic gene conversion. Nature 338:87–90
Sun F, Kozak G, Scott S, Trpkov K, Ko E, Mikhaail-Philips M, Bestor TH, Moens P, Martin RH (2004) Meiotic defects in a man with non-obstructive azoospermia: case report. Hum Reprod 19:1770–1773
Sun F, Oliver-Bonet M, Liehr T, Starke H, Trpkov K, Ko E, Rademaker A, Martin RH (2005a) Discontinuities and unsynapsed regions in meiotic chromosomes have a cis effect on meiotic recombination patterns in normal human males. Hum Mol Genet 14(20):3013-3018
Sun F, Trpkov K, Rademaker A, Ko E, Martin RH (2005b) Variation in meiotic recombination frequencies among human males. Hum Genet 116:172–178
Tarsounas M, Morita T, Pearlman RE, Moens PB (1999) RAD51 and DMC1 form mixed complexes associated with mouse meiotic chromosome cores and synaptonemal complexes. J Cell Biol 147:207–220
Tease C, Hulten MA (2004) Inter-sex variation in synaptonemal complex lengths largely determine the different recombination rates in male and female germ cells. Cytogenet Genome Res 107:208–215
Tease C, Hartshorne GM, Hulten MA (2002) Patterns of meiotic recombination in human fetal oocytes. Am J Hum Genet 70:1469–1479
Templado C, Vidal F, Navarro J, Marina S, Egozcue J (1984) Meiotic studies and synaptonemal complex analysis in two infertile males with a 13/14 balanced translocation. Hum Genet 67:162–165
Theurkauf WE, Hawley RS (1992) Meiotic spindle assembly in Drosophila females: behavior of nonexchange chromosomes and the effects of mutations in the nod kinesin-like protein. J Cell Biol 116:1167–1180
Vidal F, Templado C, Navarro J, Brusadin S, Marina S, Egozcue J (1982) Meiotic and synaptonemal complex studies in 45 subfertile males. Hum Genet 60:301–304
Wallace BM, Hulten MA (1985) Meiotic chromosome pairing in the normal human female. Ann Hum Genet 49(Pt 3):215–226
Wei K, Kucherlapati R, Edelmann W (2002) Mouse models for human DNA mismatch-repair gene defects. Trends Mol Med 8:346–353
Weiner BM, Kleckner N (1994) Chromosome pairing via multiple interstitial interactions before and during meiosis in yeast. Cell 77:977–991
Yamamoto A, Hiraoka Y (2001) How do meiotic chromosomes meet their homologous partners? Lessons from fission yeast. Bioessays 23:526–533
Zickler D, Kleckner N (1999) Meiotic chromosomes: integrating structure and function. Annu Rev Genet 33:603–754
Acknowledgement
Work conducted in the Hassold and Cheng laboratories as discussed in this review was supported by NIH grant HD21341.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Benavente
The synaptonemal complex–50 years
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vallente, R.U., Cheng, E.Y. & Hassold, T.J. The synaptonemal complex and meiotic recombination in humans: new approaches to old questions. Chromosoma 115, 241–249 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-006-0058-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-006-0058-4