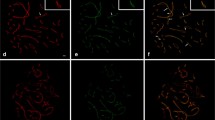
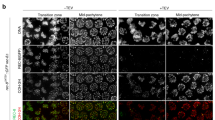
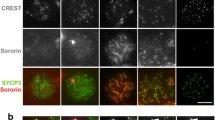
Abstract
Immunocytological and in situ hybridization evidence supports the hypothesis that at meiosis of chiasmate organisms, chromosomal disjunction and reductional segregation of sister centromeres are integrated with synaptonemal complex functions. The Mr 125,000 synaptic protein, Syn1, present between cores of paired homologous chromosomes during pachytene of meiotic prophase, is lost from synaptonemal complexes coordinately with homolog separation at diplotene. Separation is constrained by exchanges between non-sister chromatids, the chiasmata. We show that the Mr 30,000 chromosomal core protein, Cor1, associated with sister chromatid pairs, remains an axial component of post-pachytene chromosomes until metaphase I. We demonstrate that at this time the chromatin loops are still attached to their cores. A reciprocal exchange event between two homologous non-sister chromatids is therefore immobilized by anchorage of sister chromatids to their respective cores. Cores thus contribute to the sister chromatid cohesiveness required for maintenance of chiasmata and proper chromosomal disjunction. Cor1 protein accumulates in juxtaposition to pairs of sister centromeres during metaphase I. Presumably, independent movement of sister centromeres at anaphase I is restricted by Cor1 anchorage. That reductional separation of sister centromeres is mediated by Cor1, is supported by the dissociation of Cor1 from separating sister centromeres at anaphase II and by its absence from mitotic anaphases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carpenter ATC (1994) Chiasma function. Cell 77:959–962
Dobson MJ, Pearlman RE, Karaiskakis A, Spyropoulos B, Moens PB (1994) Synaptonemal complex proteins: occurrence, epitope mapping and chromosome disjunction. J Cell Sci 107:2749–2760
Earnshaw WC, Bernat RL (1991) Chromosomal passengers: Toward an integrated view of mitosis. Chromosoma 100:139–146
Heng HHQ, Tsui L-C, Moens PB (1994) Organization of heterologous DNA inserts on the mouse meiotic chromosome core. Chromosoma 103:401–407
Jones GH (1987) Chiasmata. In: Moens PB (ed) Meiosis. Academic Press, New York, pp 213–244
Lammers JH, Offenberg HH, Van Aaldern MA, Vink C, Dietrich AJ, Heyting C (1994) The gene encoding a major component of the lateral element of synaptonemal complexes of the rat is related to X-linked lymphocyte-regulated genes. Mol Cell Biol 14:1137–1146
Maguire MP (1974) The need for a chiasma binder. J Theor Biol 48:485–487
Maguire MP (1978a) Evidence for separate genetic control of crossing over and chiasma maintenance in maize. Chromosoma 65:173–183
Maguire MP (1978b) A role for the synaptonemal complex in chiasma maintenance. Exp Cell Res 112:297–308
Maguire MP (1993) Sister chromatid association at meiosis. Maydica 38:93–106
Maguire MP, Paredes AM, Riess RW (1991) The desynaptic mutant of maize as a combined defect of synaptonemal complex and chiasma maintenance. Genome 34:879–887
Maguire MP, Riess RW, Paredes AM (1993) Evidence from a maize desynaptic mutant points to a probable role of synaptonemal complex central region components in provision for subsequent chiasma maintenance. Genome 36:797–807
Meuwissen RLJ, Offenberg HH, Dietrich AJJ, Riesewijk A, Van Iersel M, Heyting C (1992) A coiled-coil related protein specific for synapsed regions of meiotic prophase chromosomes. EMBO J 11:5091–5100
Moens PB (1994) Molecular perspectives of chromosome pairing at meiosis. BioEssays 16:101–106
Moens PB, Church K (1979) The distribution of synaptonemal complex material in metaphase I bivalents of Locusta and Chloealtis (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Chromosoma 73:247–254
Moens PB, Spyropoulos B, Dobson M, Karaiskakis A, Pearlman RE (1992) Searching for synaptonemal complex proteins and their genes. Dev Genet 13:435–439
Orr-Weaver T, Moore D, Kerrebrock A, Bickel S, Wyman D (1995) Proteins controlling sister chromatid cohesion. Cell (in press)
Pankov R, Lemieux M, Hancock R (1990) An antigen located in the kinetochore region in metaphase and on polar microtubule ends in the midbody region in anaphase, characterized using a monoclonal antibody. Chromosoma 99:95–101
PearlmanRE, TsaoN, MoensPB (1992) Synaptonemal complexes from DNase-treated rat pachytene chromosomes contain (GT)n and LINE/SINE sequences. Genetics 130:865–872
RattnerJB, RaoA, FritzlerMJ, ValenciaDW, YenTJ (1993) CENP-F is a ca 400 kDa kinetochore protein that exhibits a cell-cycle dependent localization. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 26: 214–226
RockmillB, RoederGS (1994) The yeast med1 mutant undergoes both meiotic homolog nondisjunction and precocious separation of sister chromatids. Genetics 136:65–74
RufasJS, Gimenez-AbianJ, SujaJA, De LaVegaCG (1987) Chromosome organization in meiosis revealed by light micro-scope analysis of silver-stained cores. Genome 29:706–712
RufasJS, SantosJL, DiezM, SujaJA (1992) Meiotic chromosome structure: relationship between the synaptonemal complex and the chromatid cores. Genome 35:1054–1061
SolariAJ (1970) The behaviour of chromosome axes during diplotene in mouse spermatocytes. Chromosoma 31:217–230
SolariAJ, TandlerCJ (1991) Presence of a centromeric filament during meiosis. Genome 34: 888–894
SymM, RoederGS (1994) Crossover interference is abolished in the absence of a synaptonemal complex protein. Cell 79: 283–292
WeithA, TrautW (1980) Synaptonemal complexes with associated chromatin in a moth Ephestia kuehniella. Z. Chromosoma 78:275–291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moens, P.B., Spyropoulos, B. Immunocytology of chiasmata and chromosomal disjunction at mouse meiosis. Chromosoma 104, 175–182 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352182
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352182