Summary
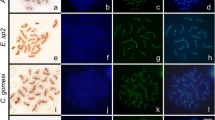
Using a combination of silver-staining and light microscopic techniques on human male meiotic preparations, it is feasible to study the morphology and behavior of both autosomal synaptonemal complexes and sex chromosome axes. During leptotene and early zygotene, the X and Y chromosomes are separate; their axes appearing as thin, filamentous structures. During late zygotene/early pachytene, the sex chromosomes come close to each other and a distinct sex vesicle is formed. We confirm the existence of a short synaptonemal complex between the terminal ends of the X and Y chromosomes. In our preparations, a number of accessory structures can be seen along the axes of the sex chromosomes. These structures appear to be similar in morphology to those previously observed in several other mammalian species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, A. T. L., Falek, A.: Cytological evidence for the association of the short arms of the X and Y chromosomes in the human male. Nature 232, 555–556 (1971)
Counce, S. J., Meyer, G. F.: Differentiation of the synaptonemal complex and the kinetochore in Locusta spermatocytes studied by whole mount electron microscopy. Chromosoma 44, 231–253 (1973)
Dresser, M. E., Moses, M. J.: Silver staining of synaptonemal complexes in surface spreads for light and electron microscopy. Exp. Cell Res. 121, 416–419 (1979)
Elder, F. F. B., Pathak, S.: Light microscopic observations on the behavior of silver-stained trivalents in pachytene cells of Sigmodon fulviventer (Rodentia, Muridae) heterozygous for centric fusion. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. (in press, 1980)
Fletcher, J. M.: Light microscope analysis of meiotic prophase chromosomes by silver-staining. Chromosoma 72, 241–248 (1979)
Hofgärtner, F. J., Schmid, M., Krone, W., Zenzes, M. T., Engel, W.: Pattern of activity of nucleolus organizers during spermatogenesis in mammals as analyzed by silver-staining. Chromosoma 71, 197–216 (1979)
Moses, M. J.: Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in spermatocytes of the Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus) II. Morphology of the XY pair in spread preparations. Chromosoma 60, 127–137 (1977)
Moses, M. J., Counce, S. J., Paulson, D. F.: Synaptonemal complex complement of man in spreads of spermatocytes, with details of the sex chromosome pair. Science 187, 363–365 (1965)
Moses, M. J., Russell, L. B., Cacheiro, N. L. A.: Mouse chromosome translocations: visualization and analysis by electron microscopy of the synaptonemal complex. Science 196, 892–894 (1977)
Noel, B., Quack, B., Benezech, M.: Le bivalent sexuel des mammiféres observé par marquage argentique au stade pachytene. Ann. Génét. 21, 83–87 (1978)
Page, B. M.: Identification of chromosome 9 in human male meiosis. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 12, 254–263 (1973)
Pathak, S., Hsu, T. C.: Chromosomes and DNA of Mus. The behavior of constitutive heterochromatin in spermatogenesis of M. dunni. Chromosoma 57, 227–234 (1976)
Pathak, S., Hsu, T. C.: Silver-stained structures in mammalian meiotic prophase. Chromosoma 70, 195–203 (1979)
Pathak, S., Lau, Y.-F., Drwinga, H. L.: Observation on the synaptonemal complex in Armenian hamster spermatocytes by light microscopy. Chromosoma 73, 53–60 (1979)
Pathak, S., Elder, F. F. B., Maxwell, B. L.: Asynaptic behavior of X and Y chromosomes in the Virginia opossum and the southern pygmy mouse. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 26, 142–149 (1980)
Pearson, P. L., Bobrow, M., Vosa, C.G.: Technique for identifying Y chromosomes in human interphase nuclei. Nature 226, 78–80 (1970)
Quack, B., Noel, B.: XY chromosome pair in mouse and human spermatocytes, visualized by silver-staining. Nature 267, 431–433 (1977)
Solari, A. J., Ashley, T.: Ultrastructure and behavior of the achiasmatic, telosynaptic XY pair of the sand rat (Psammomys obesus). Chromosoma 62, 319–336 (1977)
Tres, L. L.: Extensive pairing of the XY bivalent in mouse spermatocytes as visualized by whole-mount electron microscopy. J. Cell Sci. 25, 1–15 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pathak, S., Elder, F.F.B. Silver-Stained accessory structures on human sex chromosomes. Hum Genet 54, 171–175 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00278967
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00278967