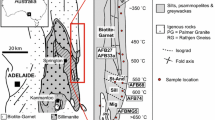
Abstract
The geochemical and isotopic characterization of an eclogite and the associated retrogressive amphibolite at Vårdalsneset, WGR, Norwegian Caledonide was undertaken to investigate the mobility of REE and Hf and the behavior of Lu–Hf and Sm–Nd geochronometers during metamorphic dehydration/rehydration. Eclogitic garnets display a distinct core–rim chemical zoning. Thermodynamic modeling indicates that both cores (13–22 kbar, 500–580°C) and rims (>16 kbar, 610–660°C) crystallized under eclogite-facies conditions. The core–rim zoning corresponds to the dehydration of the system. This petrographic disequilibrium is associated with Lu–Hf and Sm–Nd disequilibrium, which prevents dating of the eclogitic stages. At the rock scale, the incoming fluid responsible for eclogite–amphibolite retrogression brought in Sm and Nd, leached Lu, and had no influence on Hf. At the grain scale, mass balance shows that Sm and Nd were stored in clinozoisite since the first eclogitic stage, whereas Lu and Hf, which were more thoroughly redistributed among minerals during retrogression, enable the dating of the amphibolitic facies at 378 ± 17 Ma.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albarede F, Bottinga Y (1972) Kinetic disequilibrium in trace element partitioning between phenocrysts and host lava. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 36(2):141–156
Andersen TB, Austrheim H, Burke EAJ (1990) Fluid-induced retrogression of granulites in the Bergen Arcs, Caledonides of W. Norway: fluid inclusion evidence from amphibolite-facies shear zone. Lithos 27:29–42
Andersen TB, Osmundsen PT, Jolivet L (1994) Deep crustal fabrics and a model for the extensional collapse of the southwest Norwegian Caledonides. J Struct Geol 16:1191–1203
Austrheim H (1987) Eclogitization of lower crustal granulites by fluid migration through shear zones. Earth Planet Sci Lett 81:221–232
Austrheim H (1989) The granulite-eclogite facies transition: a comparison of experimental work and a natural occurence in the Bergen Arcs, western Norway. Lithos 25:163–169
Becker H, Jochum KP, Carlson RW (2000) Trace element fractionation during dehydration of eclogites from high-pressure terranes and the implications for element fluxes in subduction zones. Chem Geol 163:65–69
Bievre PD, Gallet M, Holden NE, Barnes IL (1984) Isotopic abundances and atomic weights of the elements. J Phys Chem Ref Data 13(3):809–891
Bizzarro M, Baker JA, Ulfbeck DG (2003) A new digestion and chemical separation technique for rapid and highly reproductible determination of Lu/Hf and Hf isotope ratios in geological material by MC-ICP-MS. Geostand Geoanal Res 27:133–145
Blichert-Toft J, Frei R (2001) Complex Sm-Nd and Lu-Hf isotope systematics in metamorphic garnets from the Isua supracrustal belt, West Greenland. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:3177–3187
Blichert-Toft J, Chauvel C, Albarède F (1997) Separation of Hf and Lu for high-precision isotope analysis of rock samples by magnetic sector-multiple collector ICP-MS. Contrib Mineral Petrol 127:248–260
Bryhni I, Sturt BA (1985) Caledonides of southwestern Norway. In: Gee DG, Sturt BA (eds) The Caledonide orogen-scandinavia and related areas, vol 1. Wiley, New York, pp 89–107
Carswell DA, Brueckner H, Cuthbert SJ, Metha K, O’Brien PJ (2003) The timing of stabilisation and the exhumation rate for ultra-high pressure rocks in the Western Gneiss Region of Norway. J Metamorph Geol 21:601–612
Chu NC, Taylor RN, Chavagnac V, Nesbitt RW, Boella RM, Milton JA, German CR, Bayon G, Burton K (2002) Hf isotope ratio analysis using multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: an evaluation of isobaric interference corrections. J Anal At Spectrom 17:1567–1574
Connolly JAD (1990) Multivariable phase diagrams; an algorithm based on generalized thermodynamics. Am J Sci 290(6):666–718
Connolly JAD (2005) Computation of phase equilibria by linear programming: a tool for geodynamic modeling and its application to subduction zone decarbonation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 236:524–541
Connolly JAD, Petrini K (2002) An automated strategy for calculation of phase diagram sections and retrieval of rock properties as a function of physical conditions. J Metamorph Geol 20:697–708
Dale J, Powell R, White RW, Elmer FL, Holland TJB (2005) A thermodynamic model for Ca–Na clinoamphiboles in Na2O–CaO–FeO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O–O for petrological calculations. J Metamorph Geol 23(8):771–791
Ellis DJ, Green DH (1979) An experimental study of the effect of Ca upon garnet-clinopyroxene Fe–Mg exchange equilibria. Contrib Mineral Petrol 71:13–22
Engvik AK, Andersen TB (2000) Evolution of Caledonian deformation fabrics under eclogite and amphibolite facies at Vårdalsneset, Western Gneiss Region, Norway. J Metamorph Geol 18:241–257
Engvik AK, Austrheim H, Erambert M (2001) Interaction between fluid flow, fracturing and mineral growth during eclogitization, an example from the Sunnfjord area, Western Gneiss Region, Norway. Lithos 57:111–141
Foreman R, Andersen TB, Wheeler J (2005) Eclogite-facies polyphase deformation of the Drøsdal eclogite, Western Gneiss Complex, Norway and implications for exhumation. Tectonophysics 389:1–32
Glodny J, Kühn A, Austrheim H (2008) Diffusion versus recrystallization processes in Rb–Sr geochronology: Isotopic relics in eclogite facies rocks, Western Gneiss Region, Norway. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:506–525
Gorbatschev R (1985) Precambrian basement of the Scandinavian Caledonides. In: Gee DG, Sturt BA (eds) The Caledonide orogen-scandinavia and related areas, vol 1. Wiley, pp 197–212
Graham CM, Powell R (1984) A garnet-hornblende geothermometer: calibration, testing, and application to the Pelona Schist, Southern California. J Metamorph Geol 2:13–31
Green E, Holland T, Powell R (2007) An order–disorder model for omphacitic pyroxenes in the system jadeite–diopside–hedenbergite–acmite, with applications to eclogitic rocks. Am Mineral 92(7):1181–1189
Griffin WL, Brueckner HK (1985) REE, Rb–Sr and Sm–Nd studies of Norwegian eclogites. Chem Geol Isot Geosci Sect 52(2):249–271
Hacker BR (2007) Ascent of the ultrahigh-pressure Western Gneiss Region, Norway. Geol Soc Am Spec Paper 149
Holland TJB (1980) The reaction albite = jadeite + quartz determined experimentally in the range 600–1200°C. Am Mineral 65:129–134
Holland T, Powell R (2003) Activity-composition relations for phases in petrological calculations: an asymmetric multicomponent formulation. Contrib Mineral Petrol 145:492–501
Hollister LS (1966) Garnet zoning: an interpretation based on the Rayleigh fractionation model. Science 164:1647–1651
Jamveit B, Bucher-Nurminen K, Austrheim H (1990) Fluid controlled eclogitization of granulites in deep crustal shear zones, Bergen arcs, Western Norway. Contrib Mineral Petrol 104:184–193
John T, Scherer EE, Haase K, Schenk V (2004) Trace element fractionation during fluid-induced eclogitization in a subducting slab: trace element and Lu-Hf-Sm-Nd isotope systematics. Earth Planet Sci Lett 227:441–456
John T, Klemd R, Gao J, Garbe-Schonberg CD (2008) Trace-element mobilization in slabs due to non steady-state fluid-rock interaction: Constraints from an eclogite-facies transport vein in blueschist (Tianshan, China). Lithos 103:1–24
Kleinhanns IC, Kreissig K, Kamber BS, Meisel T, Nagler TF, Kramers JD (2002) Combined chemical separation of Lu, Hf, Sm, Nd, and REEs from a single rock digest: precise and accurate isotope determinations of Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd using multicollector-ICPMS. Anal Chem 74:67–73
Konrad-Schmolke M, O’Brien PJ, de Capitani C, Carswell DA (2008a) Garnet growth at high- and ultra-high pressure conditions and the effect of element fractionation on mineral modes and composition. Lithos 103:309–332
Konrad-Schmolke M, Zack T, O’Brien PJ, Jacob DE (2008b) Combined thermodynamic and rare earth element modelling of garnet growth during subduction: examples from ultrahigh-pressure eclogite of the Western Gneiss Region, Norway. Earth Planet Sci Lett 272:488–498
Krogh TE (1982) Improved accuracy of U-Pb zircon ages by the creation of more concordant systems using an air abrasion technique. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 46:637–649
Krogh EJ (1988) The garnet-clinopyroxene Fe–Mg geothermometer: a reinterpretation of existing experimental data. Contrib Mineral Petrol 99:44–48
Krogh EJ, Brunfelt AO (1981) REE, Cs, Rb, Sr and Ba in glaucophane-bearing eclogites and associated rocks, Sunnfjord, Western Norway. Chem Geol 33:295–305
Kylander-Clark ARC, Hacker BR, Johnson CM, Beard BL, Mahlen NJ, Lapen TJ (2007) Coupled Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd geochronology constrains prograde and exhumation histories of high- and ultrahigh-pressure eclogites from western Norway. Chem Geol 242:137–154
Labrousse L, Jolivet L, Andersen TB, Agard P, Hébert R, Maluski H, and Schärer U (2004) Pressure–temperature–time deformation history of the exhumation of ultra-high pressure rocks in the Western Gneiss Region, Norway. Geol Soc Am Spec Paper 380
Lagos M, Scherer EE, Tomaschek F, Münker C, Keiter M, Berndt JB C (2007) High precision Lu-Hf geochronology of Eocene eclogite-facies rocks from Syros, Cyclades, Greece. Chem Geol 243:16–35
Lapen TJ, Mahlen NJ, Johnson CM, and Beard BL (2004) High precision Lu and Hf isotope analyses of both spiked and unspiked samples: a new approach. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 5:Q01010. doi:10.1029/2003GC000582
Le Fevre B, Pin C (2001) An extraction chromatography method for Hf separation prior to isotopic analysis using multiple collection ICP-mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 73:2453–2460
Leake BE (1978) Nomenclature of amphiboles. Am Miner 63(11–1):1023–1052
Luais B, Telouk P, Albarede F (1997) Precise and accurate neodymium isotopic measurements by plasma-source mass spectrometry. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61:4847–4854
Luais B, Duchene S, de Sigoyer J (2001) Sm-Nd disequilibrium in high-pressure, low-temperature Himalayan and Alpine rocks. Tectonophysics 342:1–22
Luais B, Carlier Le, de Veslud C, Géraud Y, Gauthier-Lafaye F (2009) Comparative behavior of Sr, Nd and Hf isotopic systems during fluid-related deformation at middle crust levels. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:2961–2977
Ludwig KR (1999) Isoplot/Ex Ver 2.06: a geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center Spec Publ 1(a)
Mahlen NJ, Johnson CM, Baumgartner LP, Skora S, Lapen TJ, and Beard BL (2007) Successes and failures of garnet Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd geochronology: examples in eclogites from the Western Alps. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71(15):A613–A613
Mahlen NJ, Beard BL, Johnson CM, and Lapen TJ (2008) An investigation of dissolution methods for Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotope studies in zircon- and garnet-bearing whole-rock samples. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 9:Q01002. doi:10.1029/2007GC001605
Martin C (2009) Mobilisation des REE et de l’Hf par les fluides lors du métamorphisme HP-BT. Influence sur les datations Sm-Nd et Lu-Hf. Ph-D, Nancy University
McCulloch MT, Gamble JA (1990) Geochemical and geodynamical constraints on subduction zone magmatism. Earth Planet Sci Lett 102:358–374
McCulloch MT, Rosman KJR, De Laeter JR (1977) The isotopic and elemental abundance of ytterbium in meteorites and terrestrial samples. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 41:1703–1707
Milnes AG, Wennberg OP, Skar O, Koestler AG (1997) Contraction, extension and timing in the South Norwegian Caledonides: the Sognefjord transect. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 121:123–148
Mork M, Mearns E (1986) Sm-Nd isotopic systematics of a gabbro-eclogite transition. Lithos 19:255–267
Munker C, Weyer S, Scherer E, and Mezger K (2001) Separation of high field strength elements (Nb, Ta, Zr, Hf) and Lu from rock samples for MC-ICPMS measurements. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 2. doi:10.1029/2001GC000183
Philippot P, Selverstone J (1991) Trace-element-rich brines in eclogitic veins: implications for fluid composition and transport during subduction. Contrib Miner Petrol 106:417–430
Powell R (1985) Regression diagnostics and robust regression in geothermometer/geobarometer calibration: the garnet-clinopyroxene geothermometer revisited. J Metamorph Geol 3:231–243
Powell R, Holland T (1999) Relating formulations of the thermodynamics of mineral solid solutions; activity modeling of pyroxenes, amphiboles, and micas. Am Mineral 84(1–2):1–14
Prince CI, Kosler J, Vance D, Günther D (2000) Comparison of laser ablation ICP-MS and isotope dilution REE analyses—implications for Sm–Nd garnet geochronology. Chem Geol 168:255–274
Raimbourg H, Goffé B, Jolivet L (2007) Garnet reequilibration and growth in the eclogite facies and geodynamical evolution near peak metamorphic conditions. Contrib Mineral Petrol 153:1–28
Ravna EJK (2000) The garnet-clinopyroxene Fe2+–Mg geothermometer: an updated calibration. J Metamorph Geol 18:211–219
Ringwood AE (1976) Phase transformations in descending plates and implications for mantle dynamics. Tectonophysics 32:129–143
Roberts D, Gee DG (1985) An introduction to the structure of the Scandinavian Caledonides. In: Gee DG, Sturt BA (eds) The Caledonide orogen-scandinavia and related areas, vol 1. Wiley, New York, pp 55–68
Root DB, Hacker BR, Mattinson JM, Wooden JL (2004) Zircon geochronology and ca. 400 Ma exhumation of Norwegian ultrahigh-pressure rocks: an ion microprobe and chemical abrasion study. Earth Planet Sci Lett 228:325–341
Rubatto D, Hermann J (2002) Zircon formation during fluid circulation in eclogites (Monviso, Western Alps) : Implications for Zr and Hf budget in subduction zones. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67:2173–2187
Rubie D (1990) Role of kinetics in the formation and preservation of eclogites. In: Carswell (ed) Eclogite facies rocks. Blackie, pp 111–140
Scharer U, Labrousse L (2003) Dating the exhumation of UHP rocks and associated crustal melting in the Norwegian Caledonides. Contrib Miner Petrol 144(6):758–770
Scherer E, Münker C, Mezger K (2001) Calibration of the lutetium–hafnium clock. Science 293:683–687
Schneider J, Bosch D, Monié P, Bruguier O (2007) Micro-scale element migration during eclogitisation in the Bergen arcs (Norway): a case study on the role of fluids and deformation. Lithos 96:325–352
Shatsky VS, Kozmenko OA, Sobolev NV (1990) Behaviour of rare-earth elements during high-pressure metamorphism. Lithos 25:219–226
Skora S, Baumgartner L, Mahlen N, Johnson C, Pilet S, Hellebrand E (2006) Diffusion-limited REE uptake by eclogite garnets and its consequences for Lu–Hf and Sm–Nd geochronology. Contrib Miner Petrol 152:703–720
Smith DC (1984) Coesite in clinopyroxene in the Caledonides and its implication for geodynamics. Nature 310:641–644
Tanaka T, Togashi S, Kamioka H, Amakawa H, Kagami H, Hamamoto T, Yuhara M, Orihashi Y, Yoneda S, Shimizu H, Kunimaru T, Takahashi K, Yanagi T, Nakano T, Fujimaki H, Shinjo R, Asahara Y, Tanimizu M, Dragusanu C (2000) JNdi-1: a neodymium isotopic reference in consistency with LaJolla neodymium. Chem Geol 168:279–281
Terry MP, Robinson P, Hamilton MA, Jercinovic MJ (2000) Monazite geochronology of UHP and HP metamorphism, deformation, and exhumation, Nordoyane, Western Gneiss Region, Norway. Am Miner 85(11–12):1651–1664
Thöni M (2003) Sm-Nd isotope systematics in garnet from different lithologies (Eastern Alps): age results, and an evaluation of potential problems for garnet Sm–Nd chronometry. Chem Geol 194:353–379
Tucker RD, Robinson P, Solli A, Gee DG, Thorsnes T, Krogh TE, Nordgulen O, Bickford ME (2004) Thrusting and extension in the Scandinavian hinterland, Norway: new U–Pb ages and tectonostratigraphic evidence. Am J Sci 304:477–532
Van der Straaten F, Schenk V, John T, Gao J (2008) Blueschist-facies rehydration of eclogites (Tian Shan, NW-China): Implications for fluid-rock interaction in the subduction channel. Chem Geol 255:195–219
Vervoort JD, Patchett PJ, Soderlund U, and Baker M (2004) Isotopic composition of Yb and the determination of Lu concentrations and Lu/Hf ratios by isotope dilution using MC-ICPMS. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 5:Q11002. doi:10.1029/2004GC000721
Waldbaum DR, Thompson JB (1969) Mixing properties of sanidine crystalline solutions: IV phase diagrams from equations of state. Am Mineral 54:1274–1298
Walsh EO, Hacker BR (2004) The fate of subducted continental margins: two-stage exhumation of the high-pressure to ultrahigh pressure Western Gneiss Region, Norway. J Metamorph Geol 22:671–687
Waters DJ, Martin HN (1993) Geothermobarometry in phengite-bearing eclogites. Terra Abstracts 5:410–411
Weis D, Kieffer B, Hanano D, Nobre Silva I, Barling J, Pretorius W, Maerschalk C, Mattielli N (2007) Hf isotope compositions of U.S. Geological Survey reference materials. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 8:Q06006. doi:10.1029/2006GC001473
White WM, Patchett J (1984) Hf-Nd-Sr isotopes and incompatible element abundances in island arcs: implications for magma origins and crust mantle evolution. Earth Planet Sci Lett 67:167–185
White RW, Powell R, Holland TJB, Worley BA (2000) The effect of TiO2 and Fe2O3 on metapelitic assemblages at greenschist and amphibolite facies conditions: mineral equilibria calculations in the system K2O–FeO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O–TiO2–Fe2O3. J Metamorph Geol 18(5):497–511
Zack T, John T (2007) An evaluation of reactive fluid flow and trace element mobility in subducting slabs. Chem Geol 239:199–216
Zhou B, Hensen BJ (1995) Inherited Sm/Nd isotope components preserved in monazite inclusions within garnets in leucogneiss from East Antarctica and implications for closure temperature studies. Chem Geol 121:317–326
Acknowledgments
Journal reviews by Peter Robinson and an anonymous reviewer helped to significantly improve this paper. The authors acknowledge Catherine Zimmermann for TIMS analyses, Delphine Yeghicheyan and Luc Marin for their help in chemical analysis. The authors are grateful to Carsten Münker and Eric Scherer for discussions about Hf chemistry, to Jonathan Patchett for making available an aliquot of the JMC 475Hf isotopic standard, to Janne Blichert-Toft for interesting discussion about Hf data and to Tim John for interesting discussion about petrology and mobility of trace elements. Béatrice Luais and Stéphanie Duchêne are grateful to Laurent Jolivet and Loic Labrousse for fieldwork in Norway in June 2000. Céline Martin acknowledges Bernhard Stöckert, Klaus Röller and Sandra Birtel (Ruhr Universität, Bochum) for the fieldtrip in Norway in August 2006. This work benefited from INSU-CNRS funding (IT, DYETI and 3F programs).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Keppler.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, C., Duchêne, S., Luais, B. et al. Behavior of trace elements in relation to Lu–Hf and Sm–Nd geochronometers during metamorphic dehydration–hydration in the HP domain of Vårdalsneset, Western Gneiss Region, Norway. Contrib Mineral Petrol 159, 437–458 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-009-0434-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-009-0434-1